Stellar Evolution of low and intermediate mass stars
... He core degenerates and grows in mass due to the H-shell Mcore ~ 0.45 Msun He flash ...
... He core degenerates and grows in mass due to the H-shell Mcore ~ 0.45 Msun He flash ...
Homework #7 (Ch. 19)
... How can we tell whether a star cluster is young or old? 12. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.20 In the formation of a star cluster with a wide range of stellar masses, is it possible for some stars to die out before others have finished forming? Do you think this will have any effect on the cluster ...
... How can we tell whether a star cluster is young or old? 12. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.20 In the formation of a star cluster with a wide range of stellar masses, is it possible for some stars to die out before others have finished forming? Do you think this will have any effect on the cluster ...
course - HSCPhysics
... http://es.rice.edu/ES/humsoc/Galileo//Things/copernican_system.html as above but with details on the Copernican system http://es.rice.edu/ES/humsoc/Galileo//Things/ptolemaic_system.html is part of the very impressive Galilieo Project site, a repository for all things concerning Galileo's astronomy, ...
... http://es.rice.edu/ES/humsoc/Galileo//Things/copernican_system.html as above but with details on the Copernican system http://es.rice.edu/ES/humsoc/Galileo//Things/ptolemaic_system.html is part of the very impressive Galilieo Project site, a repository for all things concerning Galileo's astronomy, ...
MS Word version
... eccentricity? (Look at the system along the long axis – change the longitude to 90°.) When the system is viewed from this orientation note how one eclipse is “fatter” than the other. Why is this? (The stars move very rapidly when near perihelion yielding a narrow/short eclipse and very slowly near a ...
... eccentricity? (Look at the system along the long axis – change the longitude to 90°.) When the system is viewed from this orientation note how one eclipse is “fatter” than the other. Why is this? (The stars move very rapidly when near perihelion yielding a narrow/short eclipse and very slowly near a ...
The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought
... The Moon takes a longer time than any of the other satellites to orbit the Earth. Give one other way in which the Moon is different from the other satellites in the table. ...
... The Moon takes a longer time than any of the other satellites to orbit the Earth. Give one other way in which the Moon is different from the other satellites in the table. ...
PSF - ESO
... of performing this, but the basic idea is to produce an initial list of approximate centroid positions for all stars that can be distinguished in the two dimensional data array. The star finder must have at least some ability to tell the difference between a single star, a blended clump of stars, a ...
... of performing this, but the basic idea is to produce an initial list of approximate centroid positions for all stars that can be distinguished in the two dimensional data array. The star finder must have at least some ability to tell the difference between a single star, a blended clump of stars, a ...
The Physical Properties of Normal A Stars
... I give the name, spectral type, Teff, log g, log Fe/H, log Si/log Sr, v sin i, and . My “model” was that stars rotating sufficiently fast have normal abundances all over their surfaces. When the rotation decreases below some critical value, the poles begin to show peculiar abundances. These regions ...
... I give the name, spectral type, Teff, log g, log Fe/H, log Si/log Sr, v sin i, and . My “model” was that stars rotating sufficiently fast have normal abundances all over their surfaces. When the rotation decreases below some critical value, the poles begin to show peculiar abundances. These regions ...
Black Holes in Binary Systems and Galaxy Nuclei
... distribution of NS and BH can be suggested (Bailyn et al., 1998; Cherepashchuk, 1998). In this range (2 – 4) MSun the number of NS and BH discovered in binary systems up to now is close to zero. It can be shown that this gap is not due to observational selection effects (Cherepashchuk, 2001, 2003; Ö ...
... distribution of NS and BH can be suggested (Bailyn et al., 1998; Cherepashchuk, 1998). In this range (2 – 4) MSun the number of NS and BH discovered in binary systems up to now is close to zero. It can be shown that this gap is not due to observational selection effects (Cherepashchuk, 2001, 2003; Ö ...
theh – rdiagramsofyoungclust ersandtheformati on ofp
... to the present radius of pluto's orbit, and its mass ten times the present mass of the planetary system, hence the density of the solar nebula at that stage was 2.5 X 10-14 gm/cm3. As the dust follows the motion of the gas, its concentration in the solar nebula was increased accordingly in relation ...
... to the present radius of pluto's orbit, and its mass ten times the present mass of the planetary system, hence the density of the solar nebula at that stage was 2.5 X 10-14 gm/cm3. As the dust follows the motion of the gas, its concentration in the solar nebula was increased accordingly in relation ...
Red Dwarf Stars: Ages, Rotation, Magnetic
... used this WD age to calibrate the measured Ca ii HK and coronal X-ray luminosity (LX ) of the K1 V and M4.5 V stars. We have been carrying out photometry to determine the photometric rotation periods for these benchmark stars. We have also been carrying out photometry and spectroscopy of wide binary ...
... used this WD age to calibrate the measured Ca ii HK and coronal X-ray luminosity (LX ) of the K1 V and M4.5 V stars. We have been carrying out photometry to determine the photometric rotation periods for these benchmark stars. We have also been carrying out photometry and spectroscopy of wide binary ...
Summary Of the Structure of the Milky Way
... Way. These clusters are more luminous than open clusters because they typically contain 500,000 stars many of which are red giants. Also, they are not (generally) buried in the dust of the Milky Way's disk, but are seen in the dust-free halo above and below the disk. The distribution of globular clu ...
... Way. These clusters are more luminous than open clusters because they typically contain 500,000 stars many of which are red giants. Also, they are not (generally) buried in the dust of the Milky Way's disk, but are seen in the dust-free halo above and below the disk. The distribution of globular clu ...
DTU_9e_ch12
... Stars forming around a massive star 2500 ly away in the constellation Monoceros’s Cone Nebula. The stars (small dots on the right side of the inset) arrayed around the bright, massive central star are believed to have formed as a result of the central star compressing surrounding gas with high-speed ...
... Stars forming around a massive star 2500 ly away in the constellation Monoceros’s Cone Nebula. The stars (small dots on the right side of the inset) arrayed around the bright, massive central star are believed to have formed as a result of the central star compressing surrounding gas with high-speed ...
Chapter 12 - Indiana State University
... – Superimposed on this orbital motion are small random motions of about 20 km/sec – In addition to their motion through space, stars spin on their axes and this spin can be measured using the Doppler shift technique – young stars are found to rotate faster than old stars ...
... – Superimposed on this orbital motion are small random motions of about 20 km/sec – In addition to their motion through space, stars spin on their axes and this spin can be measured using the Doppler shift technique – young stars are found to rotate faster than old stars ...
talk
... ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rotation curve data with theoretical models require baryons in dwarfs to occupy ...
... ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rotation curve data with theoretical models require baryons in dwarfs to occupy ...
Lecture 4
... Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spectra are dominated by lines of Hydrogen and Helium and small amounts of metals. Original scheme had classes OBAFGKM (now extended to L, T and Y dwarfs) Most import ...
... Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spectra are dominated by lines of Hydrogen and Helium and small amounts of metals. Original scheme had classes OBAFGKM (now extended to L, T and Y dwarfs) Most import ...
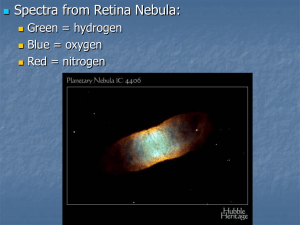
No Slide Title
... What type of star has the mass of our Sun and the radius of the Earth but it doesn’t emit enough light or other radiation to be easily detected? ...
... What type of star has the mass of our Sun and the radius of the Earth but it doesn’t emit enough light or other radiation to be easily detected? ...
Condensates in Neutron Star Interiors
... On July 4th 1054, a supernova went off in the constellation of Taurus as observed widely by astronomers on Earth (and termed as nova stella, a new star). Centuries later, in 1731, John Bevis discovered the supernova remnant, which was later christened the Crab nebula (or M1, the first entry in the M ...
... On July 4th 1054, a supernova went off in the constellation of Taurus as observed widely by astronomers on Earth (and termed as nova stella, a new star). Centuries later, in 1731, John Bevis discovered the supernova remnant, which was later christened the Crab nebula (or M1, the first entry in the M ...
No Slide Title
... • describe the formation of the extra-solar planets: • Planets form from dust which agglomerates into cores which then accrete gas from a disc. • A gravitational instability in a protostellar disc creates a number of giant planets. • Both models have trouble reproducing both the observed distributio ...
... • describe the formation of the extra-solar planets: • Planets form from dust which agglomerates into cores which then accrete gas from a disc. • A gravitational instability in a protostellar disc creates a number of giant planets. • Both models have trouble reproducing both the observed distributio ...
Chapter 10 Neutron Stars and General Relativity
... • A binary must form with two stars massive enough to become supernovae and produce neutron stars, and the neutron stars thus formed must remain bound to each other through the two supernova explosions. • The neutron star binary must result from gravitational capture of one neutron star by another. ...
... • A binary must form with two stars massive enough to become supernovae and produce neutron stars, and the neutron stars thus formed must remain bound to each other through the two supernova explosions. • The neutron star binary must result from gravitational capture of one neutron star by another. ...
Life Stages of High
... of objects with <0.08MSun before the core temperature becomes hot enough for fusion. • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs. ...
... of objects with <0.08MSun before the core temperature becomes hot enough for fusion. • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs. ...