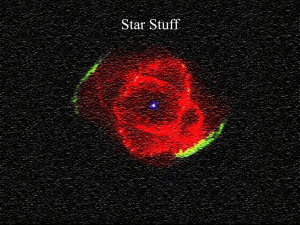
The Evolution of Stars - a More Detailed Picture (Chapter 8
... Potential Energy is transformed into kinetic energy, which gets thermalised, so the temperature goes up. This phase lasts a relatively short time. When the cloud is hot enough, the gas is ionised and OPACITY sets in. When that is the case, the gas finds it harder to lose energy, and becomes hotter e ...
... Potential Energy is transformed into kinetic energy, which gets thermalised, so the temperature goes up. This phase lasts a relatively short time. When the cloud is hot enough, the gas is ionised and OPACITY sets in. When that is the case, the gas finds it harder to lose energy, and becomes hotter e ...
Chapter 10
... The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested in the interstellar medium because a) dense interstellar clouds are the birth place of stars b) Dark clouds alter and absorb the l ...
... The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested in the interstellar medium because a) dense interstellar clouds are the birth place of stars b) Dark clouds alter and absorb the l ...
Astronomical units
... The absolute magnitude is defined as the apparent magnitude a source would have if it were at a distance of 10 pc (1 pc = 3.086 x 1018 cm). Measure of the luminosity in some waveband. Difference between the apparent magnitude m and the absolute magnitude M (any band) is a measure of the distance to ...
... The absolute magnitude is defined as the apparent magnitude a source would have if it were at a distance of 10 pc (1 pc = 3.086 x 1018 cm). Measure of the luminosity in some waveband. Difference between the apparent magnitude m and the absolute magnitude M (any band) is a measure of the distance to ...
CCD BVRI and 2MASS Photometry of the Poorly Studied Open
... – astrometry – Stars: luminosity function – Mass function. Open star clusters (OCs) are ideal objects for studying the main properties of the Milky Way Galaxy, i.e. star formation, stellar evolution, and distance scale of the Galaxy. The fundamental parameters of an open cluster; e.g. distance, age, ...
... – astrometry – Stars: luminosity function – Mass function. Open star clusters (OCs) are ideal objects for studying the main properties of the Milky Way Galaxy, i.e. star formation, stellar evolution, and distance scale of the Galaxy. The fundamental parameters of an open cluster; e.g. distance, age, ...
Full Poster - Cool Cosmos
... Optical astronomy has provided us with a wealth of information about our solar system. Space missions have shown us detailed, close up views of the planets and their moons. Through visiblelight observations we have studied comets and asteroids as well as the surface of the Sun. What more can we lear ...
... Optical astronomy has provided us with a wealth of information about our solar system. Space missions have shown us detailed, close up views of the planets and their moons. Through visiblelight observations we have studied comets and asteroids as well as the surface of the Sun. What more can we lear ...
Recipe for a Star
... core made of neutrons surrounded by collapsing outer layers. The star “bounces” against its own neutron core, and all of the layers explode into space, leaving the core behind. ...
... core made of neutrons surrounded by collapsing outer layers. The star “bounces” against its own neutron core, and all of the layers explode into space, leaving the core behind. ...
DIRECT OBSERVATION OF GRAVITATIONAL WAVES DIRECT
... exploding stars, and even the birth of the universe itself. Albert Einstein predicted the existence of gravitational waves in 1916, derived from his General Theory of Relativity. Einstein’s mathematics showed that massive accelerating objects would disrupt spacetime in such a way that waves of disto ...
... exploding stars, and even the birth of the universe itself. Albert Einstein predicted the existence of gravitational waves in 1916, derived from his General Theory of Relativity. Einstein’s mathematics showed that massive accelerating objects would disrupt spacetime in such a way that waves of disto ...
DIRECT OBSERVATION OF GRAVITATIONAL WAVES DIRECT
... exploding stars, and even the birth of the universe itself. Albert Einstein predicted the existence of gravitational waves in 1916, derived from his General Theory of Relativity. Einstein’s mathematics showed that massive accelerating objects would disrupt spacetime in such a way that waves of disto ...
... exploding stars, and even the birth of the universe itself. Albert Einstein predicted the existence of gravitational waves in 1916, derived from his General Theory of Relativity. Einstein’s mathematics showed that massive accelerating objects would disrupt spacetime in such a way that waves of disto ...
PDF
... order to prevent wholesale destruction of spirals by merging, dark-matter enthusiasts have suggested that large galaxies must have assembled quite recently so that many ellipticals are, in fact, the merger product of two spirals. The rate of merging expected in the darkmatter models is sensitive to ...
... order to prevent wholesale destruction of spirals by merging, dark-matter enthusiasts have suggested that large galaxies must have assembled quite recently so that many ellipticals are, in fact, the merger product of two spirals. The rate of merging expected in the darkmatter models is sensitive to ...
Properties of Stars - Indiana State University
... – Superimposed on this orbital motion are small random motions of about 20 km/sec – In addition to their motion through space, stars spin on their axes and this spin can be measured using the Doppler shift technique – young stars are found to rotate faster than old stars ...
... – Superimposed on this orbital motion are small random motions of about 20 km/sec – In addition to their motion through space, stars spin on their axes and this spin can be measured using the Doppler shift technique – young stars are found to rotate faster than old stars ...
Measuring Distances
... Measuring Distances Hold your finger out in front of your face at arm’s length. Look at your finger through each eye separately. What do you notice? This change in perspective is known as parallax. Ancient Greek astronomers expected to see a similar change in the positions of nearby stars if Earth ...
... Measuring Distances Hold your finger out in front of your face at arm’s length. Look at your finger through each eye separately. What do you notice? This change in perspective is known as parallax. Ancient Greek astronomers expected to see a similar change in the positions of nearby stars if Earth ...
Spectroscopy Applications - Astrophysics and
... Moving one step closer to finding the fingerprints of life in a habitable planet beyond the solar system, astronomers have for the first time detected carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a planet that orbits a star other than the sun Fall 2008 ...
... Moving one step closer to finding the fingerprints of life in a habitable planet beyond the solar system, astronomers have for the first time detected carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a planet that orbits a star other than the sun Fall 2008 ...
Here
... relatively easily by its spectral type or color. If the distance is known, then we can measure its luminosity, and then compute its radius. Note, however, that the radius measured this way is not very accurate, owing to the uncertainty in the distance. • Is it possible to measure the radius of a dis ...
... relatively easily by its spectral type or color. If the distance is known, then we can measure its luminosity, and then compute its radius. Note, however, that the radius measured this way is not very accurate, owing to the uncertainty in the distance. • Is it possible to measure the radius of a dis ...
Determination of kinetic energies of stars using Hipparcos data *
... that remains, can be explained by inaccuracy in mass N 1526 determination or other reasons and needs to studied in 7085 detail. In our opinion, there are two directions, in which the present paper can be extended: – The individual radial velocities can be used to obtain the spatial velocity for each ...
... that remains, can be explained by inaccuracy in mass N 1526 determination or other reasons and needs to studied in 7085 detail. In our opinion, there are two directions, in which the present paper can be extended: – The individual radial velocities can be used to obtain the spatial velocity for each ...
Low-Mass Star Formation Triggered by Supernova in Primordial
... They have a long life time and survive up to now They can be observed (Beers et al. 1992, Norris et al. 1999) ...
... They have a long life time and survive up to now They can be observed (Beers et al. 1992, Norris et al. 1999) ...
The Fate of the X-ray Emitting Gas in the Early
... The molecular gas arises from the thermally unstable hot gas. ...
... The molecular gas arises from the thermally unstable hot gas. ...
1 Origin of the Elements. Isotopes and Atomic Weights
... catastrophic changes may then occur which result in much of the stellar material being ejected into space, where it becomes incorporated together with further hydrogen and helium in the next generation of stars. It should be noted, however, that, as iron is at the maximum of the nuclear binding ener ...
... catastrophic changes may then occur which result in much of the stellar material being ejected into space, where it becomes incorporated together with further hydrogen and helium in the next generation of stars. It should be noted, however, that, as iron is at the maximum of the nuclear binding ener ...
ted_2012_power_of_design
... to the incomprehensibly large. We will do our best not to break your brain. We begin subatomically, with protons and neutrons. One or more positively charged protons (diameter 1.6−1.7 fm) reside in each atomic nucleus—this equaling the atomic number. Slightly heavier than protons, neutrons have no c ...
... to the incomprehensibly large. We will do our best not to break your brain. We begin subatomically, with protons and neutrons. One or more positively charged protons (diameter 1.6−1.7 fm) reside in each atomic nucleus—this equaling the atomic number. Slightly heavier than protons, neutrons have no c ...
Neutron Stars
... Neutron Stars Example: A star is rotating with = 1 rev/sec. If the core begins wit ha radius equal to the radius of the sun, and collapses to a final radius of 0.01 R, what will its final angular speed become after the collapse? Assume the mass stays a constant. ...
... Neutron Stars Example: A star is rotating with = 1 rev/sec. If the core begins wit ha radius equal to the radius of the sun, and collapses to a final radius of 0.01 R, what will its final angular speed become after the collapse? Assume the mass stays a constant. ...