Review: How does a star`s mass determine its life story?
... White dwarf supernova: Carbon fusion suddenly begins as a white dwarf in close binary system reaches white dwarf limit, causing total explosion. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... White dwarf supernova: Carbon fusion suddenly begins as a white dwarf in close binary system reaches white dwarf limit, causing total explosion. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter14 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard-pptx
... • What is a white dwarf? – A white dwarf is the inert core of a dead star. – Electron degeneracy pressure balances the inward pull of gravity. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? – Matter from its close binary companion can fall onto the white dwarf through an accretion disk ...
... • What is a white dwarf? – A white dwarf is the inert core of a dead star. – Electron degeneracy pressure balances the inward pull of gravity. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? – Matter from its close binary companion can fall onto the white dwarf through an accretion disk ...
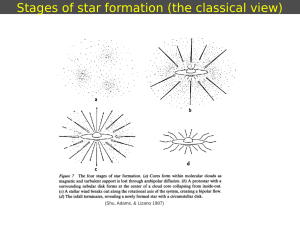
Stages of star formation (the classical view)
... intensity is amplified exponentially. The brightness temperature of a maser transition can be extremely high. For example, for Tex= -20 K, |τ0| = 20, we have T0 = 1010 K. Maser radiations is produced in very compact regions (maser spots), and the flux density is not extremely high. Maser emission is ...
... intensity is amplified exponentially. The brightness temperature of a maser transition can be extremely high. For example, for Tex= -20 K, |τ0| = 20, we have T0 = 1010 K. Maser radiations is produced in very compact regions (maser spots), and the flux density is not extremely high. Maser emission is ...
Astrophysics Lab “A”
... In the following we will present typical spectra of hot stars taken in the UV-range. The wavelength range covers 1150 . . . 1850 Å. A first series of spectra consists of observations performed with the IUE (International Ultraviolet Explorer) satellite, one of the most important (earlier) instrumen ...
... In the following we will present typical spectra of hot stars taken in the UV-range. The wavelength range covers 1150 . . . 1850 Å. A first series of spectra consists of observations performed with the IUE (International Ultraviolet Explorer) satellite, one of the most important (earlier) instrumen ...
11 The Interstellar Medium
... sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to fuse in its core. ...
... sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to fuse in its core. ...
Determining the mass loss limit for close
... for blow-off in the case of the classic Newtonian gravitational potential. For very massive or Jupiter-class exoplanets exposed to less intense stellar XUV fluxes at orbital distances > 0.15 AU the exobase temperatures can be lower than the critical temperature for the onset of the blow-off. This wi ...
... for blow-off in the case of the classic Newtonian gravitational potential. For very massive or Jupiter-class exoplanets exposed to less intense stellar XUV fluxes at orbital distances > 0.15 AU the exobase temperatures can be lower than the critical temperature for the onset of the blow-off. This wi ...
flyer
... detect weaker signals and therefore are said to have higher (or greater) sensitivity. Spin-down: Pulsars are rotating neutron stars whose rotational speed is seen to decrease with time (equivalent to an increase in rotational period). Spin-down limit: The limit placed on the amplitude of gravitation ...
... detect weaker signals and therefore are said to have higher (or greater) sensitivity. Spin-down: Pulsars are rotating neutron stars whose rotational speed is seen to decrease with time (equivalent to an increase in rotational period). Spin-down limit: The limit placed on the amplitude of gravitation ...
http://www.highpoint.edu/~afuller/PHY-1050
... layers into space. • If the initial mass of the star on the main sequence is not too large (< 25 Msun), the remnant inner core will stabilize and become a neutron star, supported by degenerate neutron pressure. • However, if the initial stellar mass is much larger, even the pressure of ...
... layers into space. • If the initial mass of the star on the main sequence is not too large (< 25 Msun), the remnant inner core will stabilize and become a neutron star, supported by degenerate neutron pressure. • However, if the initial stellar mass is much larger, even the pressure of ...
Evolution of Population II Stars in the Helium
... some definite value, without mixing between the hydrogen-rich envelope and the helium region. Evolution of Population I stars with 15.6 M 0 4>, 5> and 4 M 0 6> in the heliumburning phase has been investigated taking into account the effect of helium depletion on the mean molecular weight and on the ...
... some definite value, without mixing between the hydrogen-rich envelope and the helium region. Evolution of Population I stars with 15.6 M 0 4>, 5> and 4 M 0 6> in the heliumburning phase has been investigated taking into account the effect of helium depletion on the mean molecular weight and on the ...
ALFALFA H-alpha: The Star-Formation-Rate Density
... For astronomers studying past star-formation rates (SFRs), distances play the role of a time machine. Light travels at a finite speed; it travels slowly enough that astronomers can still view light from the Big Bang. Light emitted by the Sun takes more than eight minutes to reach Earth, roughly five ...
... For astronomers studying past star-formation rates (SFRs), distances play the role of a time machine. Light travels at a finite speed; it travels slowly enough that astronomers can still view light from the Big Bang. Light emitted by the Sun takes more than eight minutes to reach Earth, roughly five ...
Measurements of Neutron Star Masses
... eating the phase structure of dense cold quark eventually squeezed out at densities near n0 (32). If so, beginning at about 0.1 n0, there matter (35) has yielded novel states of matter, Motivation 1. Nuclear equation of state. could be a continuous change of the dimenincluding color-superconducting ...
... eating the phase structure of dense cold quark eventually squeezed out at densities near n0 (32). If so, beginning at about 0.1 n0, there matter (35) has yielded novel states of matter, Motivation 1. Nuclear equation of state. could be a continuous change of the dimenincluding color-superconducting ...
Nebula
... "HII" is used in professional astronomy to refer to ionized hydrogen. In contrast to emission nebulae, reflection nebulae do not produce significant amounts of visible light by themselves but instead reflect light from nearby stars. ...
... "HII" is used in professional astronomy to refer to ionized hydrogen. In contrast to emission nebulae, reflection nebulae do not produce significant amounts of visible light by themselves but instead reflect light from nearby stars. ...
HWWS 2010 - Monash University
... Neutron star mass/radius constraints 1. Search for maximally spinning neutron stars to constrain the equation-of-state 2. Search for redshifted spectral lines from the neutrons star surface to measure the gravitational redshift 3. Compare the behaviour of thermonuclear bursts with models to test ou ...
... Neutron star mass/radius constraints 1. Search for maximally spinning neutron stars to constrain the equation-of-state 2. Search for redshifted spectral lines from the neutrons star surface to measure the gravitational redshift 3. Compare the behaviour of thermonuclear bursts with models to test ou ...
New Mass Loss Measurements from Astrospheric Lyα Absorption
... In order to measure a mass-loss rate from the observed astrospheric absorption, it is necessary to know the ISM wind velocity seen by the star (VISM) and the orientation of the astrosphere relative to our line of sight (v), which are both listed in Table 1. The orientation angle, v, is the angle bet ...
... In order to measure a mass-loss rate from the observed astrospheric absorption, it is necessary to know the ISM wind velocity seen by the star (VISM) and the orientation of the astrosphere relative to our line of sight (v), which are both listed in Table 1. The orientation angle, v, is the angle bet ...
H-Band spectroscopic classification of OB stars
... 3.1.2. He I and He II A relatively strong line of He I (4–3) is visible at 1.7002 µm. To be useful for classification purposes, the wavelength range of interest must contain various lines sensitive to different excitation in the stellar atmosphere. In the present case, the Brackett series lines (as ...
... 3.1.2. He I and He II A relatively strong line of He I (4–3) is visible at 1.7002 µm. To be useful for classification purposes, the wavelength range of interest must contain various lines sensitive to different excitation in the stellar atmosphere. In the present case, the Brackett series lines (as ...
The extreme ultraviolet and X-ray Sun in Time: High
... on the MS, giving observational constraints on the percentiles at these ages (with 230, 134, and 36 stars, respectively at the considered ages). We use additional constraints for pre-mainsequence (PMS) rotation from the ≈2 Myr cluster NGC 6530 (28 stars; Henderson & Stassun 2012) and the ≈12 Myr clu ...
... on the MS, giving observational constraints on the percentiles at these ages (with 230, 134, and 36 stars, respectively at the considered ages). We use additional constraints for pre-mainsequence (PMS) rotation from the ≈2 Myr cluster NGC 6530 (28 stars; Henderson & Stassun 2012) and the ≈12 Myr clu ...
PDF format
... The White Dwarf Limit • Quantum mechanics says that electrons must move faster as they are squeezed into a very small space. • As a white dwarf's mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be m ...
... The White Dwarf Limit • Quantum mechanics says that electrons must move faster as they are squeezed into a very small space. • As a white dwarf's mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be m ...
Chapter 1
... range much broader than the discrete, narrow bands from transitions of specific atoms or molecules. In the end, these results led to the belief that solid particles must reside in space alongside the gaseous material obvious from absorption spectra. By now, we know that the space between stars is fi ...
... range much broader than the discrete, narrow bands from transitions of specific atoms or molecules. In the end, these results led to the belief that solid particles must reside in space alongside the gaseous material obvious from absorption spectra. By now, we know that the space between stars is fi ...
don_lamb - New Views of the Universe
... Dominant timescale is set by jet propagation through collapsing core (~10-20 s) ...
... Dominant timescale is set by jet propagation through collapsing core (~10-20 s) ...
Calculating Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries
... Rebecca Rattray, Leslie Hebb, Keivan G. Stassun College of Arts and Science, Vanderbilt University Due to the complex nature of the spectra of low-mass M type stars, it is difficult to determine their metallicities and temperatures directly. By studying eclipsing binary pairs comprising one F, G, or ...
... Rebecca Rattray, Leslie Hebb, Keivan G. Stassun College of Arts and Science, Vanderbilt University Due to the complex nature of the spectra of low-mass M type stars, it is difficult to determine their metallicities and temperatures directly. By studying eclipsing binary pairs comprising one F, G, or ...
Entropy Production of Main-Sequence Stars
... to discuss of black holes, questions connected with the accelerated expansion of the Universe, to build and generalize gravitation theories, etc. (see, e.g., [6–10]). The majority of the papers, being strictly theoretical, place principal emphasis on functional relations between variables establishe ...
... to discuss of black holes, questions connected with the accelerated expansion of the Universe, to build and generalize gravitation theories, etc. (see, e.g., [6–10]). The majority of the papers, being strictly theoretical, place principal emphasis on functional relations between variables establishe ...
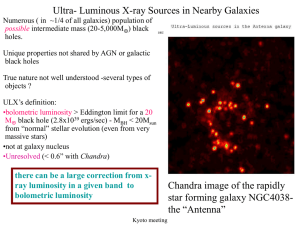
ULXs: General Properties and Variability - X
... elliptical galaxies are the most challenging to the association with star formation. • In NGC4649 a nearby giant elliptical with no star formation ULX 69 (Colbert and Ptak) has a ...
... elliptical galaxies are the most challenging to the association with star formation. • In NGC4649 a nearby giant elliptical with no star formation ULX 69 (Colbert and Ptak) has a ...
PoS(EVN 2014)058 - Proceeding of science
... Cygnus X region. Cyg OB2 is therefore ideally studied at radio wavelengths which are unaffected by the large and non-uniform visual extinction (ranging from 4 to 10 mag [1]). This association is known to contain a rich population of massive stars [2] including ∼ 120 ± 20 O-type stars and 2600 ± 400 ...
... Cygnus X region. Cyg OB2 is therefore ideally studied at radio wavelengths which are unaffected by the large and non-uniform visual extinction (ranging from 4 to 10 mag [1]). This association is known to contain a rich population of massive stars [2] including ∼ 120 ± 20 O-type stars and 2600 ± 400 ...