Abstracts - Physics of Evolved Stars 2015
... and planetary-nebula stages. AGB stars lose most of their stellar envelope in the form of a gaseous and dusty stellar wind. This wind eventually grows to such high mass-loss rates that the central star becomes entirely enshrouded by a dense, dusty superwind. Before reaching such high massloss rates, ...
... and planetary-nebula stages. AGB stars lose most of their stellar envelope in the form of a gaseous and dusty stellar wind. This wind eventually grows to such high mass-loss rates that the central star becomes entirely enshrouded by a dense, dusty superwind. Before reaching such high massloss rates, ...
Star 1 A star is a massive, luminous ball of plasma held together by
... lower than the inside of an earthly vacuum chamber. These regions are called molecular clouds and consist mostly of hydrogen, with about 23–28% helium and a few percent heavier elements. One example of such a star-forming region is the Orion Nebula.[54] As massive stars are formed from molecular clo ...
... lower than the inside of an earthly vacuum chamber. These regions are called molecular clouds and consist mostly of hydrogen, with about 23–28% helium and a few percent heavier elements. One example of such a star-forming region is the Orion Nebula.[54] As massive stars are formed from molecular clo ...
Hubble Diagram Instruction Sheet
... There are two classes of supernovae, Type I and Type II. For this activity we will be using Type Ia supernovae only. Type Ia supernovae are very important in astronomy as they offer the most reliable sources for measuring cosmic distances up to and beyond 1000 mega parsecs (Mpc). A parsec (pc) is a ...
... There are two classes of supernovae, Type I and Type II. For this activity we will be using Type Ia supernovae only. Type Ia supernovae are very important in astronomy as they offer the most reliable sources for measuring cosmic distances up to and beyond 1000 mega parsecs (Mpc). A parsec (pc) is a ...
arXiv:1705.00964v1 [astro-ph.GA] 2 May 2017
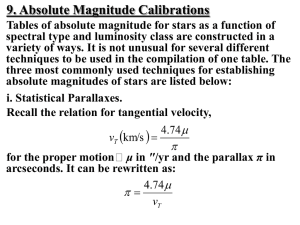
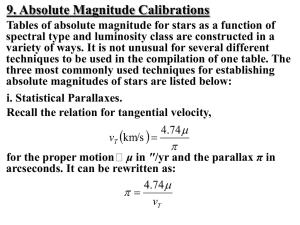
... we are drawing randomly from amongst all such local stars, and we can use the Hipparcos catalogue to estimate the chances of two random coincidences that are at least as close as the associations we have identified. We define “local”, here, to mean stars within 60 pc. We assume that the position and ...
... we are drawing randomly from amongst all such local stars, and we can use the Hipparcos catalogue to estimate the chances of two random coincidences that are at least as close as the associations we have identified. We define “local”, here, to mean stars within 60 pc. We assume that the position and ...
When we look at a neighboring galaxy (such as M31, the
... The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31, is a spiral galaxy physically larger, but less massive, than our Milky Way Galaxy. The Andromeda is the largest member of the Local Group, a cluster of about 30 galaxies that are gravitationally attracted to one another. At a distance of 2.5 million light-yea ...
... The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31, is a spiral galaxy physically larger, but less massive, than our Milky Way Galaxy. The Andromeda is the largest member of the Local Group, a cluster of about 30 galaxies that are gravitationally attracted to one another. At a distance of 2.5 million light-yea ...
Galaxies
... 1) Is there a connection between the types of galaxies? 2) Does one type of galaxy evolve from the other? All galaxies are of about the same age Spiral galaxies have stars just as old as the stars in elliptical galaxies Hubble tried to devise an evolutionary scheme for galaxies There is no evolution ...
... 1) Is there a connection between the types of galaxies? 2) Does one type of galaxy evolve from the other? All galaxies are of about the same age Spiral galaxies have stars just as old as the stars in elliptical galaxies Hubble tried to devise an evolutionary scheme for galaxies There is no evolution ...
- ANU Repository
... occurrence of Earth-size planets in the HZ. DC13 focused exclusively on the M dwarfs while G13 considered all host stars, although the less-luminous late K and M dwarfs dominate any estimation of η⊕ . Gaidos et al. (2014) used similar calculations for M dwarfs in the Kepler target catalogue and appl ...
... occurrence of Earth-size planets in the HZ. DC13 focused exclusively on the M dwarfs while G13 considered all host stars, although the less-luminous late K and M dwarfs dominate any estimation of η⊕ . Gaidos et al. (2014) used similar calculations for M dwarfs in the Kepler target catalogue and appl ...
The ATLAS3D project-XXII. Low-efficiency star formation in early
... using a universal local law to form stars in the simulations, we find that the earlytype galaxies are offset from the spirals on the large-scale Kennicutt relation, and form stars two to five times less efficiently. This offset is in agreement with previous results on morphological quenching: gas di ...
... using a universal local law to form stars in the simulations, we find that the earlytype galaxies are offset from the spirals on the large-scale Kennicutt relation, and form stars two to five times less efficiently. This offset is in agreement with previous results on morphological quenching: gas di ...
Comparing stars - The Open University
... bluish-white whereas Betelgeuse is a cooler supergiant, and it appears distinctly orange-white. Though we have not marked it on Figure 5, there is a class of stars that comprises the red giants plus the stars to their left that lie between the main sequence and the supergiants. This class is the gia ...
... bluish-white whereas Betelgeuse is a cooler supergiant, and it appears distinctly orange-white. Though we have not marked it on Figure 5, there is a class of stars that comprises the red giants plus the stars to their left that lie between the main sequence and the supergiants. This class is the gia ...
Astronomy - Glen Ridge Public Schools
... scientifically literate life-long learners. Our program fosters a spirit of intellectual curiosity and collaborative problem solving that is authentic, hands-on, inquiry based and developmentally appropriate. This is done through the study of Life, Physical, Earth and Environmental Science. Our stud ...
... scientifically literate life-long learners. Our program fosters a spirit of intellectual curiosity and collaborative problem solving that is authentic, hands-on, inquiry based and developmentally appropriate. This is done through the study of Life, Physical, Earth and Environmental Science. Our stud ...
Astonomy-Space The Final Frontier
... Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. Use mathematical or computational representations to predict the motion of orbiting objects in the solar system. Evaluate evidence of the past and current movements of continental and oceanic crust and the the ...
... Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. Use mathematical or computational representations to predict the motion of orbiting objects in the solar system. Evaluate evidence of the past and current movements of continental and oceanic crust and the the ...
Lu_Ye
... Main features of GRB060614 A long GRB with duration of 102 s A low red shift of z=0.125, and not associated with any supernova Interesting substructures: the light curve of BAT reveals a first short episode of emission (lasting 4s) followed by an extended and some softer episode (lasting 100s) ...
... Main features of GRB060614 A long GRB with duration of 102 s A low red shift of z=0.125, and not associated with any supernova Interesting substructures: the light curve of BAT reveals a first short episode of emission (lasting 4s) followed by an extended and some softer episode (lasting 100s) ...
Testing - uwyo.edu
... What would happen to a contracting cloud fragment if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change. B. Its mass would increase. C. Its internal pressure would increase. ...
... What would happen to a contracting cloud fragment if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change. B. Its mass would increase. C. Its internal pressure would increase. ...
THE N/O RATIO IN EARLY B-TYPE MAIN SEQUENCE STARS AS
... logC , logN , and logO for MS B-stars found in Ref. 14, together with recent estimates of the abundances of C, N, and O for the sun [15,16]. The latter were obtained using nonstationary hydrodynamic 3D models of the solar atmosphere. We note that the elemental abundances here and in the ...
... logC , logN , and logO for MS B-stars found in Ref. 14, together with recent estimates of the abundances of C, N, and O for the sun [15,16]. The latter were obtained using nonstationary hydrodynamic 3D models of the solar atmosphere. We note that the elemental abundances here and in the ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... statistical properties of stellar space velocities. Upsilon components apply when the Sun’s motion dominates group random velocities; tau components apply when group motions dominate. Both techniques have been applied to B stars and RR Lyrae variables, which are too distant for direct measurement of ...
... statistical properties of stellar space velocities. Upsilon components apply when the Sun’s motion dominates group random velocities; tau components apply when group motions dominate. Both techniques have been applied to B stars and RR Lyrae variables, which are too distant for direct measurement of ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... statistical properties of stellar space velocities. Upsilon components apply when the Sun’s motion dominates group random velocities; tau components apply when group motions dominate. Both techniques have been applied to B stars and RR Lyrae variables, which are too distant for direct measurement of ...
... statistical properties of stellar space velocities. Upsilon components apply when the Sun’s motion dominates group random velocities; tau components apply when group motions dominate. Both techniques have been applied to B stars and RR Lyrae variables, which are too distant for direct measurement of ...
103-122
... provide high quality spectra (see Spite, Francois & Spite 1985). We suggest that the totality of present evidence does not demand that the scatter in [α/Fe] at a given [Fe/H] be markedly greater in halo than in disc stars. If GS's ‘CASPEC abundances are disregarded, LB's study is the only one to pro ...
... provide high quality spectra (see Spite, Francois & Spite 1985). We suggest that the totality of present evidence does not demand that the scatter in [α/Fe] at a given [Fe/H] be markedly greater in halo than in disc stars. If GS's ‘CASPEC abundances are disregarded, LB's study is the only one to pro ...
Stellar Lifetimes
... clusters show that a star becomes larger, redder, and more luminous after its time on the main sequence is over. • At the end of their main sequence life time - when hydrogen in the core is exhausted - stars ascend the red giant ...
... clusters show that a star becomes larger, redder, and more luminous after its time on the main sequence is over. • At the end of their main sequence life time - when hydrogen in the core is exhausted - stars ascend the red giant ...
RES8_phys_content_ch..
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original ...
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original ...
Mass loss of massive stars near the Eddington luminosity by core
... observations may infer that some WR stars explode with much larger radii than those predicted by the current stellar evolution theory. One of the characteristics of massive stars shortly before the explosion is their huge neutrino luminosities. Neutrinos are constantly emitted from the stellar core ...
... observations may infer that some WR stars explode with much larger radii than those predicted by the current stellar evolution theory. One of the characteristics of massive stars shortly before the explosion is their huge neutrino luminosities. Neutrinos are constantly emitted from the stellar core ...
Measuring distances to the edge of the local group
... linear data trend. This does not rule out the possibility that something in the physics has changed, but rather shows that using certain measuring techniques, a more linear TF relation can be found for varying galaxy sizes. The central question that initiated this project was whether the TF relation ...
... linear data trend. This does not rule out the possibility that something in the physics has changed, but rather shows that using certain measuring techniques, a more linear TF relation can be found for varying galaxy sizes. The central question that initiated this project was whether the TF relation ...
McDonald I....Tisserand, P. et al ExELS an
... regime by detecting microlensing events in Galactic bulge. We show that ExELS can also detect large numbers of hot, transiting exoplanets in the same population. The combined microlensing+transit survey would allow the first self-consistent estimate of the relative frequencies of hot and cold sub-st ...
... regime by detecting microlensing events in Galactic bulge. We show that ExELS can also detect large numbers of hot, transiting exoplanets in the same population. The combined microlensing+transit survey would allow the first self-consistent estimate of the relative frequencies of hot and cold sub-st ...
Stars and Galaxies - Red Hook Central Schools
... http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/star/supernova/2004/09/results/50/ http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/nebula/supernova-remnant/2005/37/results/50/ http://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2009/casa/ ...
... http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/star/supernova/2004/09/results/50/ http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/nebula/supernova-remnant/2005/37/results/50/ http://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2009/casa/ ...


![arXiv:1705.00964v1 [astro-ph.GA] 2 May 2017](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013011793_1-8f89fb3e8b5cd5cf78613aebb3c8e2a5-300x300.png)