A search for debris disks in the Herschel
... than the value at which galaxies dominate over stars (Covey et al. 2007). Unsurprisingly due to their optical colours, none of the H-ATLAS main sequence locus objects have measured SDSS spectroscopic redshifts which would allow us to select out QSOs and unresolved galaxies. The inclusion of UKIDSS n ...
... than the value at which galaxies dominate over stars (Covey et al. 2007). Unsurprisingly due to their optical colours, none of the H-ATLAS main sequence locus objects have measured SDSS spectroscopic redshifts which would allow us to select out QSOs and unresolved galaxies. The inclusion of UKIDSS n ...
WELCOME TO THE MILKY WAY
... belonging to the Milky Way. Astronomers estimate the total number of stars in the Milky Way at over 300 billion. Sizes and numbers are overwhelming in space, but a galaxy like the Milky Way is still a very empty place. When two galaxies merge, there is so much clear space that their stars never coll ...
... belonging to the Milky Way. Astronomers estimate the total number of stars in the Milky Way at over 300 billion. Sizes and numbers are overwhelming in space, but a galaxy like the Milky Way is still a very empty place. When two galaxies merge, there is so much clear space that their stars never coll ...
Student copy of notes - User Web Areas at the University of York
... A type Ia supernova occurs when a white dwarf star acquires additional mass by siphoning matter away from a companion star, usually a red giant. This occurs in a binary system where one star has evolved to a white dwarf whilst the other has become a red giant. If close enough hydrogen rich material ...
... A type Ia supernova occurs when a white dwarf star acquires additional mass by siphoning matter away from a companion star, usually a red giant. This occurs in a binary system where one star has evolved to a white dwarf whilst the other has become a red giant. If close enough hydrogen rich material ...
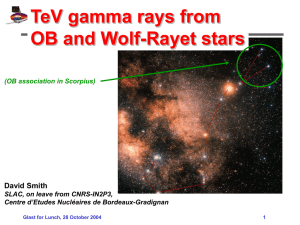
gamma rays interaction with matter
... Gamma Ray Bursts (GRBs) or Magnetars generate intense gamma radiation fields that could affect space travel and exploration. In addition, bursts of Terrestrial Gamma Ray Flashes (TGFs) occur relatively high in the atmosphere as a result of thunderstorms and are not from the same sources of gamma ray ...
... Gamma Ray Bursts (GRBs) or Magnetars generate intense gamma radiation fields that could affect space travel and exploration. In addition, bursts of Terrestrial Gamma Ray Flashes (TGFs) occur relatively high in the atmosphere as a result of thunderstorms and are not from the same sources of gamma ray ...
Satellite galaxies in hydrodynamical simulations of Milky Way sized
... observed properties of the Galaxy’s satellite population. For the first time, we include in such calculations feedback from cosmic rays injected into the star forming gas by supernovae as well as the energy input from supermassive black holes growing at the Milky Way’s centre and its progenitor syst ...
... observed properties of the Galaxy’s satellite population. For the first time, we include in such calculations feedback from cosmic rays injected into the star forming gas by supernovae as well as the energy input from supermassive black holes growing at the Milky Way’s centre and its progenitor syst ...
The star formation histories of two northern LMC fields
... the star formation rate in these fields, beginning approximately 2.5 Gyr ago, with the current metallicity in the region being Fe=H 20:38 ^ 0:10: The two fields have had very similar star formation rates until 200 Myr ago, at which point one shows a large increase. Key words: Magellanic Clouds ± ...
... the star formation rate in these fields, beginning approximately 2.5 Gyr ago, with the current metallicity in the region being Fe=H 20:38 ^ 0:10: The two fields have had very similar star formation rates until 200 Myr ago, at which point one shows a large increase. Key words: Magellanic Clouds ± ...
Lives of the Stars Lecture 5: Star birth
... Nearly all the nuclei with a few protons and neutrons are unstable or easily destroyed. Helium-4 is the only really stable one, so lots of Helium-4 was formed in the next few seconds. But apart from tiny amounts of Lithium-7, no other element can be easily formed. So when the era of fusion ended, a ...
... Nearly all the nuclei with a few protons and neutrons are unstable or easily destroyed. Helium-4 is the only really stable one, so lots of Helium-4 was formed in the next few seconds. But apart from tiny amounts of Lithium-7, no other element can be easily formed. So when the era of fusion ended, a ...
1 Astrobiologically Interesting Stars within 10
... perturbations sweep across the Galactic disk. In such a situation the passages across the spiral arms, and consequently the potential encounters with star-forming regions and giant molecular clouds, are presumably minimized. The first are thought to present the danger of biologically lethal X- and g ...
... perturbations sweep across the Galactic disk. In such a situation the passages across the spiral arms, and consequently the potential encounters with star-forming regions and giant molecular clouds, are presumably minimized. The first are thought to present the danger of biologically lethal X- and g ...
Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and lithium abundances of six
... 3.5 in steps of 0.5 dex, metallicities –0.6 < [Fe/H] < +0.6 in steps of 0.3 dex, and microturbulent velocity vt = 2 km s−1 . A code for interpolation in this grid was used to obtain the models corresponding to the stellar parameters of the sample stars. In Table 1 are reported the instrument used, v ...
... 3.5 in steps of 0.5 dex, metallicities –0.6 < [Fe/H] < +0.6 in steps of 0.3 dex, and microturbulent velocity vt = 2 km s−1 . A code for interpolation in this grid was used to obtain the models corresponding to the stellar parameters of the sample stars. In Table 1 are reported the instrument used, v ...
Lithium abundances along the red giant branch: FLAMES
... (e.g. only stars around the RGB bump). This circumstance hampers drawing definite conclusions on the evolutionary phase and length of the Li enrichment. Homogeneous samples, such as RGB stars in a cluster, are small (e.g. Pasquini et al. 2001, 2004). We therefore designed a programme to spectroscopi ...
... (e.g. only stars around the RGB bump). This circumstance hampers drawing definite conclusions on the evolutionary phase and length of the Li enrichment. Homogeneous samples, such as RGB stars in a cluster, are small (e.g. Pasquini et al. 2001, 2004). We therefore designed a programme to spectroscopi ...
FIRST STELLAR ABUNDANCES IN THE DWARF IRREGULAR
... The analysis of bright nebular emission lines of H II regions has been the most frequent approach to modeling chemical evolution of more distant galaxies to date (Matteucci & Tosi 1985). So far, only a very limited number of elements can be examined and quantified when using this approach. The chemi ...
... The analysis of bright nebular emission lines of H II regions has been the most frequent approach to modeling chemical evolution of more distant galaxies to date (Matteucci & Tosi 1985). So far, only a very limited number of elements can be examined and quantified when using this approach. The chemi ...
Test Ch. 27 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
Lecture 8: Spiral Structure
... • The spiral arms are a wave travelling backwards through the disk material ...
... • The spiral arms are a wave travelling backwards through the disk material ...
The ages of pre-main-sequence stars
... models in this range. We describe our models in detail in the following sections, but note that, because we use very similar physics, they do not differ greatly from those of D'Antona & Mazzitelli. However, stars do continue to accrete long after their photospheres are exposed, and they can be place ...
... models in this range. We describe our models in detail in the following sections, but note that, because we use very similar physics, they do not differ greatly from those of D'Antona & Mazzitelli. However, stars do continue to accrete long after their photospheres are exposed, and they can be place ...
T
... properties. They demonstrate the full capability of HARPS for asteroseismology, not only on very bright stars. These results show however also that the main limitation for HARPS will come from the stellar “noise” itself. The individual mode amplitudes of these stars are in the range 10−50 cm/s but t ...
... properties. They demonstrate the full capability of HARPS for asteroseismology, not only on very bright stars. These results show however also that the main limitation for HARPS will come from the stellar “noise” itself. The individual mode amplitudes of these stars are in the range 10−50 cm/s but t ...
WHITE DWARFS FROM LAMOST AND A CANDIDATE DEBRIS
... We have discovered a highly likely debris disk around the recently identified DA WD. In the study of the IR excesses in four WD gaseous disks, Brinkworth et al. (2012) noted that Tin higher than the 1400K (sublimation temperature) is favored when the commonly used debris-disk model, proposed by Juna ...
... We have discovered a highly likely debris disk around the recently identified DA WD. In the study of the IR excesses in four WD gaseous disks, Brinkworth et al. (2012) noted that Tin higher than the 1400K (sublimation temperature) is favored when the commonly used debris-disk model, proposed by Juna ...
Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars
... • rapidly rotating so that we see a bright spot with each rotation • periodically passing in front of and behind an ordinary star, so that we see changes in brightness with these transits and ...
... • rapidly rotating so that we see a bright spot with each rotation • periodically passing in front of and behind an ordinary star, so that we see changes in brightness with these transits and ...
The Clouds
... beacons in a steady-state Universe. They could have come into existence in the early Universe, or simply built up through collisions and coagulation of clouds of atoms. Although normal stars like our Sun consist of atoms and the gas from which they originate was also atomic, stars are born in molecu ...
... beacons in a steady-state Universe. They could have come into existence in the early Universe, or simply built up through collisions and coagulation of clouds of atoms. Although normal stars like our Sun consist of atoms and the gas from which they originate was also atomic, stars are born in molecu ...
Nucleosynthesis and Chemical Evolution of Oxygen
... the main stellar burning stages. We then analyze the oxygen yields predicted for highmass and low-mass stars, as well as for novae and Type Ia supernovae. Production of Oxygen in Mainline Stellar Burning Stages Hydrogen Burning. Stars shine. As a consequence, they radiate away energy. To compensate ...
... the main stellar burning stages. We then analyze the oxygen yields predicted for highmass and low-mass stars, as well as for novae and Type Ia supernovae. Production of Oxygen in Mainline Stellar Burning Stages Hydrogen Burning. Stars shine. As a consequence, they radiate away energy. To compensate ...
ROTATION CURVES OF HIGH-LUMINOSITY SPIRAL GALAXIES
... Current values of 0ort s constants are A = 15.6±2.8, B = -11.4±2.8 km/s per kpc (Fricke and Tsioumis 1975), although 0-B2 stars produce values as discrepant as A = +26, B = -37 (Asteriadis, 1977). At the la level, A = -B is not excluded, i.e., the rotation curve could be flat in the solar vicinity. ...
... Current values of 0ort s constants are A = 15.6±2.8, B = -11.4±2.8 km/s per kpc (Fricke and Tsioumis 1975), although 0-B2 stars produce values as discrepant as A = +26, B = -37 (Asteriadis, 1977). At the la level, A = -B is not excluded, i.e., the rotation curve could be flat in the solar vicinity. ...
Super-solar Metal Abundances in Two Galaxies at ζ ∼ 3.57
... We report on the surprisingly high metallicity measured in two absorption systems at high redshift, detected in the Very Large Telescope spectrum of the afterglow of the gamma-ray burst GRB 090323. The two systems, at redshift z = 3.5673 and z = 3.5774 (separation ∆v ≈ 660 km s−1 ), are dominated by ...
... We report on the surprisingly high metallicity measured in two absorption systems at high redshift, detected in the Very Large Telescope spectrum of the afterglow of the gamma-ray burst GRB 090323. The two systems, at redshift z = 3.5673 and z = 3.5774 (separation ∆v ≈ 660 km s−1 ), are dominated by ...
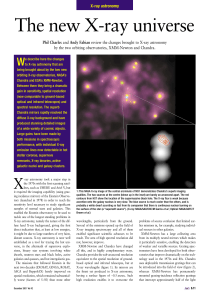
The new X-ray universe
... of sources) and at the known distance of M82 this implied that it was “ultraluminous” (Lx >1039 erg s–1; the source in M82 varies up 1041 erg s–1). While the existence of such objects was hinted at by earlier missions, a substantial number have now been found in Chandra and XMM observations of nearb ...
... of sources) and at the known distance of M82 this implied that it was “ultraluminous” (Lx >1039 erg s–1; the source in M82 varies up 1041 erg s–1). While the existence of such objects was hinted at by earlier missions, a substantial number have now been found in Chandra and XMM observations of nearb ...