Science 8 Name: Unit 2 Astronomy Date: Period: LAB
... The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is actually an elaborate graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. Absolute magnitude is how bright stars would appear to be if they were all the same distance away from Earth. Ra ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is actually an elaborate graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. Absolute magnitude is how bright stars would appear to be if they were all the same distance away from Earth. Ra ...
SUMMARY The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and
... The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is one of about a hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way, two other similarsize galaxies, and dozens of smaller galaxies compose the Local Group, which in turn is part of?the Local Supercluster of galaxi ...
... The Earth is one of eight planets orbiting the Sun, and the Sun is one of about a hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way, two other similarsize galaxies, and dozens of smaller galaxies compose the Local Group, which in turn is part of?the Local Supercluster of galaxi ...
April 2013
... composition from the larger gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. For this reason, astronomers sometimes place them in a separate category called 'ice giants'. Uranus's atmosphere, while similar to Jupiter's and Saturn's in its primary composition of hydrogen and helium, contains more 'ices' such as water, ...
... composition from the larger gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. For this reason, astronomers sometimes place them in a separate category called 'ice giants'. Uranus's atmosphere, while similar to Jupiter's and Saturn's in its primary composition of hydrogen and helium, contains more 'ices' such as water, ...
Branches of Earth Science Tools Used to Study Stars Constellations
... Contain few hundred to 1000 stars Young stars o Globular Cluster more common round , densely packed stars 100,000 to 1,000,000 stars older stars ...
... Contain few hundred to 1000 stars Young stars o Globular Cluster more common round , densely packed stars 100,000 to 1,000,000 stars older stars ...
The life of a Star (pages 468-471)
... 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layers will grow to be about 100 times its present size swallowing up Mercury, Venus, Earth and maybe even Mars 5. What is a neutron star? 6. What is a p ...
... 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layers will grow to be about 100 times its present size swallowing up Mercury, Venus, Earth and maybe even Mars 5. What is a neutron star? 6. What is a p ...
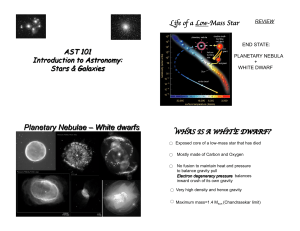
Planetary Nebulae – White dwarfs
... • May burn up to carbon but do not have enough mass to get temperatures high enough to go any higher up the periodic table • Degeneracy pressure stops the core from collapsing and heating enough: particles are squashed together as much as possible • End their lives with planetary nebulae, white d ...
... • May burn up to carbon but do not have enough mass to get temperatures high enough to go any higher up the periodic table • Degeneracy pressure stops the core from collapsing and heating enough: particles are squashed together as much as possible • End their lives with planetary nebulae, white d ...
The Milky Way * A Classic Galaxy
... • Pop I,II show MW formed spheroid first, then disk more gradually. • Hubble discovered Cepheids in Andromeda Nebula, so it’s a Galaxy, and we must be one too • Star formation happening in disk right through today • 10 million solar mass Giant black hole in nucleus of our Galaxy, evidence by rapid o ...
... • Pop I,II show MW formed spheroid first, then disk more gradually. • Hubble discovered Cepheids in Andromeda Nebula, so it’s a Galaxy, and we must be one too • Star formation happening in disk right through today • 10 million solar mass Giant black hole in nucleus of our Galaxy, evidence by rapid o ...
Star Energy Packet:
... are fused (joined) to form a larger atom. (Fusion is the opposite process from fission, which is used to power nuclear reactors on earth. Fission breaks a larger atom apart and makes smaller ones). When the hydrogen fuses into helium, a small amount of mass is lost – about 0.07%. This confused scien ...
... are fused (joined) to form a larger atom. (Fusion is the opposite process from fission, which is used to power nuclear reactors on earth. Fission breaks a larger atom apart and makes smaller ones). When the hydrogen fuses into helium, a small amount of mass is lost – about 0.07%. This confused scien ...
Astronomy
... 31. A star with a temperature of 15,000 K and a luminosity approximately 1/100 of the sun is a: a. White Dwarf ...
... 31. A star with a temperature of 15,000 K and a luminosity approximately 1/100 of the sun is a: a. White Dwarf ...
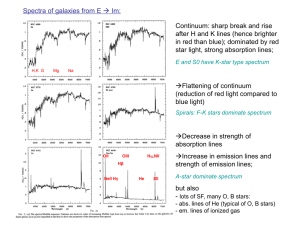
5X_Measuring_galaxy_redshifts
... One technique is to locate the image in the focal plane in register with that of a metal plate, prepared with drilled holes. Fibres are plugged into the holes. The 2dF/6dF systems (British-Australian) have the fibres connected to magnetic buttons (with miniature prisms). A robot sets up the field be ...
... One technique is to locate the image in the focal plane in register with that of a metal plate, prepared with drilled holes. Fibres are plugged into the holes. The 2dF/6dF systems (British-Australian) have the fibres connected to magnetic buttons (with miniature prisms). A robot sets up the field be ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... 1. Why is it difficult to find out how common the most luminous stars are ? The least luminous stars ? (Chapt. 9, Review Question 13) See p 186 of your text. It is difficult to count the most luminous stars in a known volume of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least lu ...
... 1. Why is it difficult to find out how common the most luminous stars are ? The least luminous stars ? (Chapt. 9, Review Question 13) See p 186 of your text. It is difficult to count the most luminous stars in a known volume of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least lu ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... (temperature)4 For a given size, hotter implies brighter. A bright, cool star must be unusually large (“red giant”). A faint, hot star must be unusually small (“white dwarf”). ...
... (temperature)4 For a given size, hotter implies brighter. A bright, cool star must be unusually large (“red giant”). A faint, hot star must be unusually small (“white dwarf”). ...
Problem Set No. 5
... A one solar mass star will spend 10 billion years on the main sequence. The universe is only 13-14 billion years old. From the formula T = 1/M 2.5 and the sun’s lifetime, we see that a star of 0.9 solar masses should spend 13 billion years on the main sequence. So no stars of lower mass would have h ...
... A one solar mass star will spend 10 billion years on the main sequence. The universe is only 13-14 billion years old. From the formula T = 1/M 2.5 and the sun’s lifetime, we see that a star of 0.9 solar masses should spend 13 billion years on the main sequence. So no stars of lower mass would have h ...
Blurbs 4th six weeks Earth and Space Students identify the role of
... When the sun and moon are in alignment, as during a new or full moon, the tide range is greatest. This is called spring tide and is characterized by higher and lower tides. When the sun and moon are at right angles, as during a first quarter or last/3rd quarter, the tidal range is lower. This is cal ...
... When the sun and moon are in alignment, as during a new or full moon, the tide range is greatest. This is called spring tide and is characterized by higher and lower tides. When the sun and moon are at right angles, as during a first quarter or last/3rd quarter, the tidal range is lower. This is cal ...
Chapter 1-Thinking about the universe
... Chapter 1-Thinking about the universe At the beginning of the chapter, the book tells a brief story about a scientist who lectured a group of people about what the universe truly is a vast collection of starts that orbit around the sun. At the end of his lecture, an old woman stood up and said that ...
... Chapter 1-Thinking about the universe At the beginning of the chapter, the book tells a brief story about a scientist who lectured a group of people about what the universe truly is a vast collection of starts that orbit around the sun. At the end of his lecture, an old woman stood up and said that ...
8.3 Stars
... Main Sequence Star 90% of all stars in the universe; when stars radiate (shine) energy into space ...
... Main Sequence Star 90% of all stars in the universe; when stars radiate (shine) energy into space ...