The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... http://www.seasky.org/cosmic/sky7a01.html and answer the following questions: 1. Stars begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called. 2. What is a protostar? ...
... http://www.seasky.org/cosmic/sky7a01.html and answer the following questions: 1. Stars begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called. 2. What is a protostar? ...
PowerPoint - Star Life Cycle
... Iron is the lightest element that doesn’t release energy when you attempt to fuse it together. You actually end up with less energy than you started with! So instead of generating pressure to hold up the outer layers, the iron fusion actually takes pressure out of the core. Thus, there is nothing ...
... Iron is the lightest element that doesn’t release energy when you attempt to fuse it together. You actually end up with less energy than you started with! So instead of generating pressure to hold up the outer layers, the iron fusion actually takes pressure out of the core. Thus, there is nothing ...
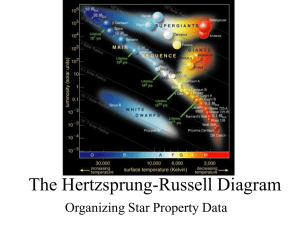
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... The orbital period comes from watching the stars, or the periodic variation of their velocity or brightness. To get orbital semimajor axis, you need either the parallax to a visual system or the velocity from a spectroscopic system. In a spectroscopic system, you only have a lower limit unless you k ...
... The orbital period comes from watching the stars, or the periodic variation of their velocity or brightness. To get orbital semimajor axis, you need either the parallax to a visual system or the velocity from a spectroscopic system. In a spectroscopic system, you only have a lower limit unless you k ...
Star- large ball of gas held together by large ball of gas held
... dust,, called a nebula, dust begins spinning & heating up. Eventually, it gets hot enough for fusion to take place, and a protostar is born. ...
... dust,, called a nebula, dust begins spinning & heating up. Eventually, it gets hot enough for fusion to take place, and a protostar is born. ...
Lesson 10 Red Shift
... "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, violet and red each have a characteristic range of wavelengths. In the visible spectrum, violet has the shortest wavelengths and red as the longest. Normally when we look at white light, such as from the Sun ...
... "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, violet and red each have a characteristic range of wavelengths. In the visible spectrum, violet has the shortest wavelengths and red as the longest. Normally when we look at white light, such as from the Sun ...
Lecture 15: The Main Sequence
... As H is fused into He, there are fewer nuclei: Remaining nuclei must move faster to maintain the same pressure The gas gets hotter, so fusion runs faster M-S stars get slowly brighter with age Small effect: ~1% brighter every 100 Myr years Compared to 4.5 billion years agao, the radius of the Sun ah ...
... As H is fused into He, there are fewer nuclei: Remaining nuclei must move faster to maintain the same pressure The gas gets hotter, so fusion runs faster M-S stars get slowly brighter with age Small effect: ~1% brighter every 100 Myr years Compared to 4.5 billion years agao, the radius of the Sun ah ...
Scientists classify stars by
... 2. If the remaining mass of the star is about 1.4 times that of our Sun, it will collapse further to become a neutron star. 3. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse and what is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hol ...
... 2. If the remaining mass of the star is about 1.4 times that of our Sun, it will collapse further to become a neutron star. 3. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse and what is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hol ...
fall_2000_final
... 54. a) With the aid of a labeled sketch, explain how the observations of pulsars are produced. (4 pts.) ...
... 54. a) With the aid of a labeled sketch, explain how the observations of pulsars are produced. (4 pts.) ...
Chapter11
... Open Clusters of Stars Large masses of Giant Molecular Clouds => Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Clusters of Stars. ...
... Open Clusters of Stars Large masses of Giant Molecular Clouds => Stars do not form isolated, but in large groups, called Open Clusters of Stars. ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... • EM radiation from protons/electrons + spin large magnetic fields • observe as repeating flashes of light PULSARS and seen in debris of known supernova explosions • discovered in 1967 by grad student Jocelyn Bell. Her advisor Anthony Hewitt won Nobel prize. Found in Crab Nebula where Chinese had ...
... • EM radiation from protons/electrons + spin large magnetic fields • observe as repeating flashes of light PULSARS and seen in debris of known supernova explosions • discovered in 1967 by grad student Jocelyn Bell. Her advisor Anthony Hewitt won Nobel prize. Found in Crab Nebula where Chinese had ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Giants and Supergiants are cool, but bright so they must be very large. The Main-Sequence is steeper than an “equal radius line” This is because large mass main sequence stars fuse fuel faster, making them hotter, thus brighter ...
... Giants and Supergiants are cool, but bright so they must be very large. The Main-Sequence is steeper than an “equal radius line” This is because large mass main sequence stars fuse fuel faster, making them hotter, thus brighter ...
The Stellar Graveyard
... not indicate what its initial mass was. A 0.5 solar mass white dwarf could have easily started out life as a 10 solar mass main sequence star. A white dwarf star is therefore the remnant carbon/oxygen core of a former main sequence star. All of the hydrogen and helium that used to be in the star has ...
... not indicate what its initial mass was. A 0.5 solar mass white dwarf could have easily started out life as a 10 solar mass main sequence star. A white dwarf star is therefore the remnant carbon/oxygen core of a former main sequence star. All of the hydrogen and helium that used to be in the star has ...
z - STScI
... Origins and Evolution of Galaxies Seeing the “Dark Ages” • When and how do the first stars and galaxies form? – HST and Keck have detected very luminous star ...
... Origins and Evolution of Galaxies Seeing the “Dark Ages” • When and how do the first stars and galaxies form? – HST and Keck have detected very luminous star ...
Star Classification
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
Chapter 21
... Betelgeuse a red supergiant, with about 20 times the mass and 800 times the radius of the Sun, so huge that it could easily contain the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars & Jupiter. It will probably explode as a supernova at some point within the next 100,000 years. Even at its relatively remote ...
... Betelgeuse a red supergiant, with about 20 times the mass and 800 times the radius of the Sun, so huge that it could easily contain the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars & Jupiter. It will probably explode as a supernova at some point within the next 100,000 years. Even at its relatively remote ...
xam2ans
... (c) Consider this weak reaction: p+ + e → n + e . Why does it almost never occur in the core of a main sequence star like the Sun? Answer: The rest mass energy of a neutron is larger than a proton plus electron. Consequently this reaction is endothermic, which means energetically unfavorable. (d) ...
... (c) Consider this weak reaction: p+ + e → n + e . Why does it almost never occur in the core of a main sequence star like the Sun? Answer: The rest mass energy of a neutron is larger than a proton plus electron. Consequently this reaction is endothermic, which means energetically unfavorable. (d) ...
unit a assessment 2 - d
... Colorado Academic Standards in High School Science - This unit has been designed to meet the following: ES 1: The history of the universe, solar system and Earth can be inferred from evidence left from past events. ES 2: As part of the solar system, Earth interacts with various extraterrestrial forc ...
... Colorado Academic Standards in High School Science - This unit has been designed to meet the following: ES 1: The history of the universe, solar system and Earth can be inferred from evidence left from past events. ES 2: As part of the solar system, Earth interacts with various extraterrestrial forc ...
PSC100 Transparant Replacement for Chapter 8 Measurement of
... astronomers spend their entire lives working on this. Even though it is critical to understanding many of the other properties of stars, we can only determine the distance to far away objects in space to about 50% accuracy. ...
... astronomers spend their entire lives working on this. Even though it is critical to understanding many of the other properties of stars, we can only determine the distance to far away objects in space to about 50% accuracy. ...
Our Community`s Place Among the Stars
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EO9CPO3CBF0 http://www.atomicarchive.com/Fusion/FusionMov.shtml ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EO9CPO3CBF0 http://www.atomicarchive.com/Fusion/FusionMov.shtml ...
Where do Stars Form ?
... Disks of matter accreted onto the protostar (“accretion disks”) often lead to the formation of jets ...
... Disks of matter accreted onto the protostar (“accretion disks”) often lead to the formation of jets ...