“brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains
... If an organism lives with another and harms that organism while it benefits then it could be called ...
... If an organism lives with another and harms that organism while it benefits then it could be called ...
Limiting Factors- Anything that prevents a population sized form
... reproduce. Territorial animals require larger area and may be more limited by space then others. Overcrowding may cause organisms to emigrate. Ex. Mountain lions ...
... reproduce. Territorial animals require larger area and may be more limited by space then others. Overcrowding may cause organisms to emigrate. Ex. Mountain lions ...
Marine Ecosystems
... This energy transfers up through the food web but only 10% of it is available to pass on to the next trophic level This limits the number of organisms at each trophic level Numbers of organisms drastically decline as you go from primary producers to high level predators There are far more pr ...
... This energy transfers up through the food web but only 10% of it is available to pass on to the next trophic level This limits the number of organisms at each trophic level Numbers of organisms drastically decline as you go from primary producers to high level predators There are far more pr ...
Vocabulary #4
... 3. Ecosystm - interactions among populations in a community, the community's physical surroundings or abiotic factors. 4. Niche - role of position a species has in its environment; included all biotic and abiotic interactions as an animal meets its needs for survival and reproduction. 5. Habitat - p ...
... 3. Ecosystm - interactions among populations in a community, the community's physical surroundings or abiotic factors. 4. Niche - role of position a species has in its environment; included all biotic and abiotic interactions as an animal meets its needs for survival and reproduction. 5. Habitat - p ...
Ecology
... other producers Carnivores- animals that eat other animals Omnivores- animals that eat both plants and animals Detritivores- organisms that eat organic wastes from dead organisms ...
... other producers Carnivores- animals that eat other animals Omnivores- animals that eat both plants and animals Detritivores- organisms that eat organic wastes from dead organisms ...
Energy Flow In Ecosystems ch. 5 sec. 1
... Ultimate source of Energy Sun Plants use sun and animals rely on plants Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce carbohydrates and oxygen. ...
... Ultimate source of Energy Sun Plants use sun and animals rely on plants Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce carbohydrates and oxygen. ...
Invasive Species
... does or is likely to cause economic or environmental harm or harm to human health • Aquatic invasive species (AIS) is simply an invasive species which has been introduced into an aquatic ecosystem, either freshwater or marine. ...
... does or is likely to cause economic or environmental harm or harm to human health • Aquatic invasive species (AIS) is simply an invasive species which has been introduced into an aquatic ecosystem, either freshwater or marine. ...
1. Organismal Ecology Ways the individual meets
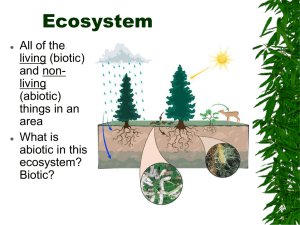
... Abiotic Factors of the Biosphere: temperature water sunlight wind rocks and soil periodic disturbances (e.g. tornadoes, hurricanes…) ...
... Abiotic Factors of the Biosphere: temperature water sunlight wind rocks and soil periodic disturbances (e.g. tornadoes, hurricanes…) ...
Clean out binders! - Mrs. Cindy Williams Biology website
... • Using what you know about the meaning of the prefix “Eco” (from ecosystem, ecofriendly, etc), hypothesize a definition for the word Ecology. ...
... • Using what you know about the meaning of the prefix “Eco” (from ecosystem, ecofriendly, etc), hypothesize a definition for the word Ecology. ...
Ecology Unit Crossword
... 8. living organisms and their abiotic surroundings they interact with 10. - C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O 12. - a group of population of different species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other 13. - the relationship between two species that attempt to use the same limited resource, s ...
... 8. living organisms and their abiotic surroundings they interact with 10. - C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O 12. - a group of population of different species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other 13. - the relationship between two species that attempt to use the same limited resource, s ...
Chapter 50 “An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere”
... Marine ecological importance: provides most of the planet’s rainfall, 75% earth’s surface, contribute to climate and wind patterns, large amount of world’s O2 supply from algae and photosynthetic bacteria, atmospheric carbon dioxide consumption by respiration Stratified: photic zone – light for phot ...
... Marine ecological importance: provides most of the planet’s rainfall, 75% earth’s surface, contribute to climate and wind patterns, large amount of world’s O2 supply from algae and photosynthetic bacteria, atmospheric carbon dioxide consumption by respiration Stratified: photic zone – light for phot ...
Carrying capacity
... …BUT environments and resources are finite. The number of organisms any habitat can support (carrying capacity) is limited • by the available energy, water, oxygen, and minerals, and • by the ability of ecosystems to recycle the residue of dead organisms through the activities of bacteria and fungi. ...
... …BUT environments and resources are finite. The number of organisms any habitat can support (carrying capacity) is limited • by the available energy, water, oxygen, and minerals, and • by the ability of ecosystems to recycle the residue of dead organisms through the activities of bacteria and fungi. ...
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in
... An area of characteristic climate, vegetation and animal life. Land biomes are called "terrestrial" and water biomes are called "aquatic." A water biome where fresh water empties into a salt water body creating a biome where organisms must be able to tolerate both. Portion of the shorline that lies ...
... An area of characteristic climate, vegetation and animal life. Land biomes are called "terrestrial" and water biomes are called "aquatic." A water biome where fresh water empties into a salt water body creating a biome where organisms must be able to tolerate both. Portion of the shorline that lies ...