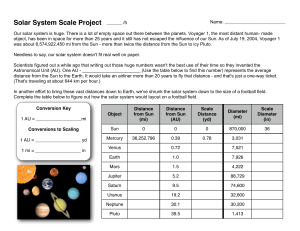
Solar System Scale Handout
... object, has been in space for more than 25 years and it still has not escaped the influence of our Sun. As of July 19, 2004, Voyager 1 was about 8,574,922,450 mi from the Sun - more than twice the distance from the Sun to icy Pluto. Needless to say, our solar system doesn't fit real well on paper. S ...
... object, has been in space for more than 25 years and it still has not escaped the influence of our Sun. As of July 19, 2004, Voyager 1 was about 8,574,922,450 mi from the Sun - more than twice the distance from the Sun to icy Pluto. Needless to say, our solar system doesn't fit real well on paper. S ...
8th_Qtr2_Science_Key
... 15. The tendency of an object to continue doing what it is doing is known as: Velocity Gravity Inertia Friction 16. The motion of Earth spinning on its access is known as: Motion Rotation Revolution Radiation 17. Axis is defined as: The imaginary line that passes through the center ...
... 15. The tendency of an object to continue doing what it is doing is known as: Velocity Gravity Inertia Friction 16. The motion of Earth spinning on its access is known as: Motion Rotation Revolution Radiation 17. Axis is defined as: The imaginary line that passes through the center ...
The Sun (power point) by Ms. Kimball the_sun_pp
... • Although the nuclear output of the sun is not entirely consistent, each second the Sun converts about 600,000,000 tons of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. • These fusion reactions convert part of these atoms' mass (roughly 4 million tons) into energy, and release an enormous amount of this hea ...
... • Although the nuclear output of the sun is not entirely consistent, each second the Sun converts about 600,000,000 tons of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. • These fusion reactions convert part of these atoms' mass (roughly 4 million tons) into energy, and release an enormous amount of this hea ...
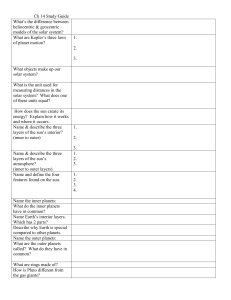
Ch 14 Study Guide What`s the difference between heliocentric
... Ch 14 Study Guide What’s the difference between heliocentric & geocentric models of the solar system? What are Kepler’s three laws of planet motion? ...
... Ch 14 Study Guide What’s the difference between heliocentric & geocentric models of the solar system? What are Kepler’s three laws of planet motion? ...
The Sun . . .
... Supergiant: 20 to 200 times larger than the Sun, but also much brighter, cooler and less ...
... Supergiant: 20 to 200 times larger than the Sun, but also much brighter, cooler and less ...
Here
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
VOC 3J-2
... Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
... Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
Origin of Elements - Madison Public Schools
... Temperature continued to drop; any free neutrons now bound to protons; already formed nuclei fused together ...
... Temperature continued to drop; any free neutrons now bound to protons; already formed nuclei fused together ...
Review3-2016
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? One of the Ca spectral lines ...
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? One of the Ca spectral lines ...
Announcements
... • Lighter nuclei are fused into heavier nuclei • all nuclei are positively charged ...
... • Lighter nuclei are fused into heavier nuclei • all nuclei are positively charged ...
Science Study Guide Chapter 7
... 2. Infer: What are the chances of finding liquid water on the surface of Venus? Thinking Critically: 1. Apply: What will happen when the Sun’s supply of hydrogen is used up? 2. Analyze: Suppose you are playing a guessing game with a friend. She says that she is thinking of a planet that takes 84 Ear ...
... 2. Infer: What are the chances of finding liquid water on the surface of Venus? Thinking Critically: 1. Apply: What will happen when the Sun’s supply of hydrogen is used up? 2. Analyze: Suppose you are playing a guessing game with a friend. She says that she is thinking of a planet that takes 84 Ear ...
The Sun
... Celsius at the core at 6,000 degrees at surface • It is hot because of it contains a lot of mass • So much matter is pushing to the center of the Sun and this is what causes so much heat • It is a billion billion billion toms of mostly hydrogen gas. If you had that much weight in bananas the same am ...
... Celsius at the core at 6,000 degrees at surface • It is hot because of it contains a lot of mass • So much matter is pushing to the center of the Sun and this is what causes so much heat • It is a billion billion billion toms of mostly hydrogen gas. If you had that much weight in bananas the same am ...
Astronomical Ideas – Math Review practice problems 1. The radius
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
Homework problems for Quiz 2: AY5 Spring 2013
... 3. In the fusion of four protons into helium, 4.7 × 10−26 grams of matter is turned into energy. How much energy does this amount of matter produce? E=∆mc2 = (4.7 × 10−26 ) × (3 × 1010 )2 grams-cm2 /sec2 (erg)= 42.3 × 10−6 ergs 4. How long will a 4M star with L = 5000L spend on the main-sequence? ...
... 3. In the fusion of four protons into helium, 4.7 × 10−26 grams of matter is turned into energy. How much energy does this amount of matter produce? E=∆mc2 = (4.7 × 10−26 ) × (3 × 1010 )2 grams-cm2 /sec2 (erg)= 42.3 × 10−6 ergs 4. How long will a 4M star with L = 5000L spend on the main-sequence? ...
Slides
... should be a friable core that provides a significant reduction of the Coulomb barrier between the interacting nuclei. In the present work, the problem of the development of the "classical" astrophysical nuclear catalysis and of the theory of cold (laboratory) transmutation of atomic nuclei (cold nuc ...
... should be a friable core that provides a significant reduction of the Coulomb barrier between the interacting nuclei. In the present work, the problem of the development of the "classical" astrophysical nuclear catalysis and of the theory of cold (laboratory) transmutation of atomic nuclei (cold nuc ...
Guided Notes on Our Solar System
... each planet orbits the Sun in an ellipse, rather than a circle. An ellipse is an oval shape that is centered on 2 points, instead of a single point, as in a circle. ...
... each planet orbits the Sun in an ellipse, rather than a circle. An ellipse is an oval shape that is centered on 2 points, instead of a single point, as in a circle. ...
Life and fate of a star
... ● The international ITER project currently being built in the South of France became so high that the nuclear aims at achieving controlled nuclear fusion for the first time. Its completion fusion reactions started. But is expected around 2027 these reactions slowly drain the available hydrogen reser ...
... ● The international ITER project currently being built in the South of France became so high that the nuclear aims at achieving controlled nuclear fusion for the first time. Its completion fusion reactions started. But is expected around 2027 these reactions slowly drain the available hydrogen reser ...
24 The Sun - Solar Physics Group
... Solar Interior The core is the energy source, where hydrogen fuses into helium. Heat from the core spreads out through the radiative and convective zones. ...
... Solar Interior The core is the energy source, where hydrogen fuses into helium. Heat from the core spreads out through the radiative and convective zones. ...
Our place in the Universe
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
Stellar Evolution
... • If a protostar forms with a mass less than 0.08 solar masses, its internal temperature never reaches a value high enough for thermonuclear fusion to begin. • This failed star is called a brown dwarf, halfway between a planet (like Jupiter) and a star. ...
... • If a protostar forms with a mass less than 0.08 solar masses, its internal temperature never reaches a value high enough for thermonuclear fusion to begin. • This failed star is called a brown dwarf, halfway between a planet (like Jupiter) and a star. ...