The Sun - TeacherWeb
... – This energy and light released from the sun takes 8 minutes to reach us! – So image how far away other stars are! ...
... – This energy and light released from the sun takes 8 minutes to reach us! – So image how far away other stars are! ...
Answer ALL questions from SECTION A and TWO questions from
... Show that for the case of a stellar interior, where photons are the transporting particles with a radiation energy density U = aT 4 and mean free path `ph = 1/(κρ), the equation of radiative transport is given by ...
... Show that for the case of a stellar interior, where photons are the transporting particles with a radiation energy density U = aT 4 and mean free path `ph = 1/(κρ), the equation of radiative transport is given by ...
Sun Lecture
... Source of the Sun’s Luminosity is _______________________________ Implications of the Sun’s Luminosity: The Sun produces energy by converting mass into energy. The luminosity of the Sun thus represents a continual mass loss. The Sun is currently converting 4.3 million metric tones of mass into ...
... Source of the Sun’s Luminosity is _______________________________ Implications of the Sun’s Luminosity: The Sun produces energy by converting mass into energy. The luminosity of the Sun thus represents a continual mass loss. The Sun is currently converting 4.3 million metric tones of mass into ...
Spring 2013 Final Exam Study Guide
... 44. In which layer of the sun does it produce its energy? 45. What is the process called that produces the Sun’s energy? 46. What gas is used to make the energy in the Sun? 47. What gas is produced when energy is made in the Sun? 48. What is a sunspot? 49. What is a solar flare? 50. Name the 8 plane ...
... 44. In which layer of the sun does it produce its energy? 45. What is the process called that produces the Sun’s energy? 46. What gas is used to make the energy in the Sun? 47. What gas is produced when energy is made in the Sun? 48. What is a sunspot? 49. What is a solar flare? 50. Name the 8 plane ...
07 September: The Solar System in a Stellar Context
... Distance to Sun in terms of light travel time d=vt (like driving to Des Moines) t=d/v The fastest anything can travel is speed of light = c = 2.9979E+08 meters/sec Distance to Sun = 1 au = 1.496E+11 meters (see Appendix 1), so light travel time from Sun is t=d/c =1.496E+11/2.9979E+08 = t=499.02 sec ...
... Distance to Sun in terms of light travel time d=vt (like driving to Des Moines) t=d/v The fastest anything can travel is speed of light = c = 2.9979E+08 meters/sec Distance to Sun = 1 au = 1.496E+11 meters (see Appendix 1), so light travel time from Sun is t=d/c =1.496E+11/2.9979E+08 = t=499.02 sec ...
Solar Evolution and The Ultimate Destruction of Life on Earth
... sweltering inferno (like Venus). Approximately a 50-100% increase in Solar luminosity should be sufficient for this to happen. How long do we have until life on Earth is destroyed? The Sun off the Main Sequence 5. About how long from now does the Sun leave the main sequence to turn into a red giant? ...
... sweltering inferno (like Venus). Approximately a 50-100% increase in Solar luminosity should be sufficient for this to happen. How long do we have until life on Earth is destroyed? The Sun off the Main Sequence 5. About how long from now does the Sun leave the main sequence to turn into a red giant? ...
The Sun`s Size, Heat, and Structure
... largest star known, Epsilon Aurigae, would be the size of a football field. ...
... largest star known, Epsilon Aurigae, would be the size of a football field. ...
Solar day and sidereal day …
... to the Sun) and a sidereal day (one day on Earth in relation to a distant star), reproduce the following scene. One volunteer symbolises a star, another the Sun and a third the Earth. To begin with, the Earth faces the Sun and the distant star, then the pupil representing the Earth begins to rotate ...
... to the Sun) and a sidereal day (one day on Earth in relation to a distant star), reproduce the following scene. One volunteer symbolises a star, another the Sun and a third the Earth. To begin with, the Earth faces the Sun and the distant star, then the pupil representing the Earth begins to rotate ...
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 10
... Review Questions, Week 10 This is not required homework. It will not be graded. Answers will be supplied next week. ...
... Review Questions, Week 10 This is not required homework. It will not be graded. Answers will be supplied next week. ...
that has been observed from here on Earth for over three hundred
... The Planet is named after the Roman god of war. It's distinctive rust color is red .Its surface features many mountains, canyons and even polar ice caps that look a lot like those here on Earth. We are doing some research to find out whether there is life forms on it. ...
... The Planet is named after the Roman god of war. It's distinctive rust color is red .Its surface features many mountains, canyons and even polar ice caps that look a lot like those here on Earth. We are doing some research to find out whether there is life forms on it. ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... Nebular Condensation (protoplanet) Model Most remnant heat from collapse retained near center After sun ignites, remaining dust reaches an equilibrium temperature Different densities of the planets are explained by condensation temperatures Nebular dust temperature increases to center of nebula ...
... Nebular Condensation (protoplanet) Model Most remnant heat from collapse retained near center After sun ignites, remaining dust reaches an equilibrium temperature Different densities of the planets are explained by condensation temperatures Nebular dust temperature increases to center of nebula ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... What determines what object will be left behind after a star dies out? What are the properties of each of those objects? How does Einstein’s model of gravity differ from Newton’s description? Why Einstein’s description taken to be “more complete” than Newton’s? What are the effects an outside obser ...
... What determines what object will be left behind after a star dies out? What are the properties of each of those objects? How does Einstein’s model of gravity differ from Newton’s description? Why Einstein’s description taken to be “more complete” than Newton’s? What are the effects an outside obser ...
Earth 351, Forming a Habitable Planet
... The Drake equation brings out the importance of understanding how long an intelligent civilization exists. One question is related to the life of a star. The sun's lifetime has been estimated from the fact that it gives off 3.9 x 1026 Watts (Joules/second), and comparing this luminosity to the energ ...
... The Drake equation brings out the importance of understanding how long an intelligent civilization exists. One question is related to the life of a star. The sun's lifetime has been estimated from the fact that it gives off 3.9 x 1026 Watts (Joules/second), and comparing this luminosity to the energ ...
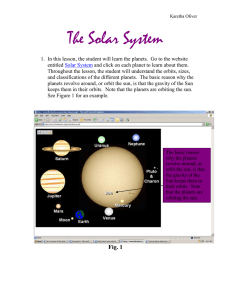
Solar System Study Guide 1
... Our sun is a star, a burning sphere of gases. This enormous fiery ball is more than 1 million kilometers (about 621,000 miles) in diameter. The sun is the largest object in the solar system. It is larger than all the others put together. The sun puts out a lot of energy in all directions. It is ...
... Our sun is a star, a burning sphere of gases. This enormous fiery ball is more than 1 million kilometers (about 621,000 miles) in diameter. The sun is the largest object in the solar system. It is larger than all the others put together. The sun puts out a lot of energy in all directions. It is ...