The Solar System - MHS-Integrated
... What are Nebulae? Nebula are cosmic clouds of gas and dust floating in space. Nebulae are the basic building blocks of the universe. They contain the elements from which stars and solar systems are built. ...
... What are Nebulae? Nebula are cosmic clouds of gas and dust floating in space. Nebulae are the basic building blocks of the universe. They contain the elements from which stars and solar systems are built. ...
Nucleosynthesis and the death of stars
... • A supernova is a massive explosion of a star that occurs under two possible scenarios. The first is that a white dwarf star undergoes a nuclear based explosion after it reaches its Chandrasekhar limit from absorbing mass from a neighboring star (usually a red giant). • The second, and more common, ...
... • A supernova is a massive explosion of a star that occurs under two possible scenarios. The first is that a white dwarf star undergoes a nuclear based explosion after it reaches its Chandrasekhar limit from absorbing mass from a neighboring star (usually a red giant). • The second, and more common, ...
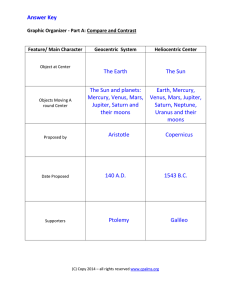
Geocentric and Heliocentric Graphic Organizer-Answer Key
... (C) Copy 2014 – all rights reserved www.cpalms.org ...
... (C) Copy 2014 – all rights reserved www.cpalms.org ...
MSc Project: A combined fit of neutrino models using astrophysics
... MSc Project: A combined fit of neutrino models using astrophysics and oscillation experiments Prof. Stefan Söldner-Rembold ...
... MSc Project: A combined fit of neutrino models using astrophysics and oscillation experiments Prof. Stefan Söldner-Rembold ...
The Sun and the Stars
... • How did astronomers estimate the masses of stars? Most stars in the solar system exist as binary stars, these starts are composed of 2 distinct stars which orbit each other, the sun is unusual in that it is not a binary star • By knowing the size of the orbit of the binary star and the revolution ...
... • How did astronomers estimate the masses of stars? Most stars in the solar system exist as binary stars, these starts are composed of 2 distinct stars which orbit each other, the sun is unusual in that it is not a binary star • By knowing the size of the orbit of the binary star and the revolution ...
ASTRONOMY 1001 FALL SEMESTER 2004
... granulation, solar wind, aurorae Energy transport, convection, radiation, conduction Gravitational contraction, gravitational potential energy, hydrostatic equilibrium Energy sources, fission, fusion, nuclear reactions, conversion of H to He, Solar neutrino problem, explanation 4) Stars: ...
... granulation, solar wind, aurorae Energy transport, convection, radiation, conduction Gravitational contraction, gravitational potential energy, hydrostatic equilibrium Energy sources, fission, fusion, nuclear reactions, conversion of H to He, Solar neutrino problem, explanation 4) Stars: ...
80.BrainPopLifeCycleStars
... under the pressure of gravity. _____________, it will begin to expand and contract, shedding its outer layers in the process. The remains of those out layers form a big cloud of gas and dust, called a ____________________. 13.At the center of a planetary nebula is a core of ___________, which after ...
... under the pressure of gravity. _____________, it will begin to expand and contract, shedding its outer layers in the process. The remains of those out layers form a big cloud of gas and dust, called a ____________________. 13.At the center of a planetary nebula is a core of ___________, which after ...
Lecture 23 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... Source of Energy (Nuclear Fusion): P-P Process: Protons must have enough energy to overcome electric repulsion and fuse together. This means 10 million degrees K (Kelvin = Centigrade + 273). Dominates in stars less than 1.5 solar masses. p + p --> D + positron + neutrino p + D --> 3He + gamma ray 2 ...
... Source of Energy (Nuclear Fusion): P-P Process: Protons must have enough energy to overcome electric repulsion and fuse together. This means 10 million degrees K (Kelvin = Centigrade + 273). Dominates in stars less than 1.5 solar masses. p + p --> D + positron + neutrino p + D --> 3He + gamma ray 2 ...
More stellar evolution…bloated stars and compact cores
... More stellar evolution…bloated stars and compact cores What’s the point of this? ...
... More stellar evolution…bloated stars and compact cores What’s the point of this? ...
Worksheet 1 – The Universe宇宙
... In the past, we also called _____________ (冥王星) as the 9th planet. Now, it belongs to dwarf planet (矮行星). (It is easy to complete the above order by saying “My Very Excellent Mother Just Sent Us Nine Pizzas.”) ...
... In the past, we also called _____________ (冥王星) as the 9th planet. Now, it belongs to dwarf planet (矮行星). (It is easy to complete the above order by saying “My Very Excellent Mother Just Sent Us Nine Pizzas.”) ...
Overview: The Sun The outer layers Photosphere: Visible Surface
... What is the Sun’s structure? ...
... What is the Sun’s structure? ...
Solar System Bead Distance Activity
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... In a high-mass main sequence star, hydrogen fusion occurs primarily through the ________. The Schwarzschild radius of a black hole depends on its __________. Following the completion of core hydrogen burning, a star like the Sun will next become a _______. The upper limit for the mass of a white dwa ...
... In a high-mass main sequence star, hydrogen fusion occurs primarily through the ________. The Schwarzschild radius of a black hole depends on its __________. Following the completion of core hydrogen burning, a star like the Sun will next become a _______. The upper limit for the mass of a white dwa ...
Neutrino Physics M. SPURIO University of Bologna and INFN
... Electron capture on protons becomes heavily favored and electron neutrinos are produced as the core gets neutronized (a process known as neutronization). When the core reaches densities above 1012 g/cm3, neutrinos become trapped (in the so-called neutrinosphere). The collapse continues until 3 ...
... Electron capture on protons becomes heavily favored and electron neutrinos are produced as the core gets neutronized (a process known as neutronization). When the core reaches densities above 1012 g/cm3, neutrinos become trapped (in the so-called neutrinosphere). The collapse continues until 3 ...
Formation of the Solar System Target 1 Notes
... __________________. Surrounding the sun was a rotating disc of space dust and gas. Over millions of years these particles of dust and gas began to collide with each other and increase in size and mass, forming the planets and many other bodies such as comets and asteroids which continue to orbit the ...
... __________________. Surrounding the sun was a rotating disc of space dust and gas. Over millions of years these particles of dust and gas began to collide with each other and increase in size and mass, forming the planets and many other bodies such as comets and asteroids which continue to orbit the ...
The Small Objects. The Sun.
... crucial to test our knowledge about solar physics. Neutrino observatories use huge amounts of different substances to detect nuclear reactions with neutrino. So far theory predicts more neutrino than is seen. ...
... crucial to test our knowledge about solar physics. Neutrino observatories use huge amounts of different substances to detect nuclear reactions with neutrino. So far theory predicts more neutrino than is seen. ...
The Assembly of M31`s Halo from Dwarf Galaxy Building Blocks
... Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. The luminosity of the Sun is 81 times that of the star X B. The typical photon emitted by star X has a lower energy than the typical photon emitted by the Sun C. Star X is reddish in color whereas the Sun is yellowish white D. If both stars were at the s ...
... Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. The luminosity of the Sun is 81 times that of the star X B. The typical photon emitted by star X has a lower energy than the typical photon emitted by the Sun C. Star X is reddish in color whereas the Sun is yellowish white D. If both stars were at the s ...