This is the Title - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... permit the carbon and oxygen from the core to move to the surface. Upon reaching the star’s surface, the metals are blown into the interstellar medium, along with the surface hydrogen and helium, by the star’s massive wind. IRC+10216, also known as CW Leo, is the most well-known example of a carbon- ...
... permit the carbon and oxygen from the core to move to the surface. Upon reaching the star’s surface, the metals are blown into the interstellar medium, along with the surface hydrogen and helium, by the star’s massive wind. IRC+10216, also known as CW Leo, is the most well-known example of a carbon- ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Way is part of a cluster called the Local Group. The Local Group is made up of about 45 galaxies in different sizes and shapes. There are three major types of galaxies. ...
... Way is part of a cluster called the Local Group. The Local Group is made up of about 45 galaxies in different sizes and shapes. There are three major types of galaxies. ...
Dynamics of Stars and Black Holes in Dense Stellar Systems:
... ⇒ stars exchange less energy and become dynamically cooler ⇒ gravothermal CATASTROPHE is reversed !!! Even if sources of heating (partially) switch off, the ejection of stars and the lowering of potential well ensures reversal of catastrophe (but see gravothermal oscillations at end of lecture) ...
... ⇒ stars exchange less energy and become dynamically cooler ⇒ gravothermal CATASTROPHE is reversed !!! Even if sources of heating (partially) switch off, the ejection of stars and the lowering of potential well ensures reversal of catastrophe (but see gravothermal oscillations at end of lecture) ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... ultimate nuclear nightmare, the explosion and fire over 20 years ago at Chernobyl Reactor number four. In the aftermath of Chernobyl experts predicted tens of thousands of deaths from cancer. Those predictions were based on a theory called the Linear No Threshold (LNT) model. ...
... ultimate nuclear nightmare, the explosion and fire over 20 years ago at Chernobyl Reactor number four. In the aftermath of Chernobyl experts predicted tens of thousands of deaths from cancer. Those predictions were based on a theory called the Linear No Threshold (LNT) model. ...
supernova remnants
... SNRs are probes both of their progenitor star (and of their pre-supernova life) and of the medium into which they explode (the ISM) They are also cosmic accelerators (cosmic rays). Birth places of neutron stars and stellar mass black holes. laboratories for study of magnetic fields, shock physics, ...
... SNRs are probes both of their progenitor star (and of their pre-supernova life) and of the medium into which they explode (the ISM) They are also cosmic accelerators (cosmic rays). Birth places of neutron stars and stellar mass black holes. laboratories for study of magnetic fields, shock physics, ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... a. Hollowed-out green spheres are sucking up matter in star forming regions and emitting gamma rays. b. Some X-ray binaries have an unseen object with masses greater than 3 solar masses. c. Some X-ray binaries emit pulses of radiation at radio wavelengths. d. We see areas that block the light from m ...
... a. Hollowed-out green spheres are sucking up matter in star forming regions and emitting gamma rays. b. Some X-ray binaries have an unseen object with masses greater than 3 solar masses. c. Some X-ray binaries emit pulses of radiation at radio wavelengths. d. We see areas that block the light from m ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... 28. At the time of Galileo and Kepler, which of the following observations was the strongest evidence for a heliocentric model of the solar system? (a) The moons of Jupiter. (b) Stellar parallax. (c) The sunspots. (d) The gibbous and the quarter phases of Venus. 29. The ancient Greek astronomer who ...
... 28. At the time of Galileo and Kepler, which of the following observations was the strongest evidence for a heliocentric model of the solar system? (a) The moons of Jupiter. (b) Stellar parallax. (c) The sunspots. (d) The gibbous and the quarter phases of Venus. 29. The ancient Greek astronomer who ...
The Formation and Evolution of the Milky Way
... it happens to be an ancient star is not a coincidence. When it was born the stellar chemical factories were only just beginning to start operation, so there was simply not a great abundance of metals that could be incorporated into the star. As a general rule [Fe/H] increases with time so old object ...
... it happens to be an ancient star is not a coincidence. When it was born the stellar chemical factories were only just beginning to start operation, so there was simply not a great abundance of metals that could be incorporated into the star. As a general rule [Fe/H] increases with time so old object ...
electron degeneracy pressure and white dwarfs
... stars will become Sirius white dwarfs after A they burn out and, lacking the gas pressure generated by their nuclear heat source, collapse under their weight. ?? What about Sirius A, which weighs a good 10 deal more than the limit? ...
... stars will become Sirius white dwarfs after A they burn out and, lacking the gas pressure generated by their nuclear heat source, collapse under their weight. ?? What about Sirius A, which weighs a good 10 deal more than the limit? ...
The Dual Nature of Light
... Plate scale s: how the linear measure on your detector corresponds to angular measure on the sky ...
... Plate scale s: how the linear measure on your detector corresponds to angular measure on the sky ...
SUPERNOVAE A. Supernovae.-Several years ago, Baade andI
... acquire considerable kinetic energies. The problems involved here are of great interest, but cannot as yet be treated in detail in the case of supernovae because of lack of knowledge regarding the determining physical conditions in the neighborhood of a supernova. (3) In both of the stages (1) and ( ...
... acquire considerable kinetic energies. The problems involved here are of great interest, but cannot as yet be treated in detail in the case of supernovae because of lack of knowledge regarding the determining physical conditions in the neighborhood of a supernova. (3) In both of the stages (1) and ( ...
The Northern Winter Constellations
... The Constellations of the Winter Sky If you live in the northern latitudes and you scan the sky from the southern horizon to the region overhead, you should be able to see the following constellations on a clear winter night: Orion the Hunter, Canis Major the Great Dog, Canis Minor the Little Dog, T ...
... The Constellations of the Winter Sky If you live in the northern latitudes and you scan the sky from the southern horizon to the region overhead, you should be able to see the following constellations on a clear winter night: Orion the Hunter, Canis Major the Great Dog, Canis Minor the Little Dog, T ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Deep Sky Objects
... All the stars, clusters and nebulae seen in the night sky with the unaided eye are part of the Milky Way Galaxy. (Slides #58 and 59 show photographs of the Milky Way.) The Milky Way is one of many millions (perhaps billions) of galaxies that are part of our universe. Though there are several types o ...
... All the stars, clusters and nebulae seen in the night sky with the unaided eye are part of the Milky Way Galaxy. (Slides #58 and 59 show photographs of the Milky Way.) The Milky Way is one of many millions (perhaps billions) of galaxies that are part of our universe. Though there are several types o ...
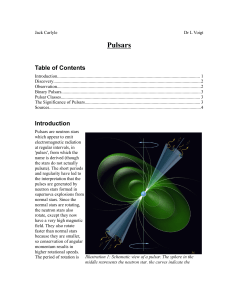
a report on pulsars, written for PHAS1901
... dispersion. All electromagnetic radiation moves at a constant speed through a vacuum, but is slowed proportionally to it's wavelength when it travels through a medium. the interstellar medium is often regarded as a vacuum, but in actual fact is occupied by atoms and free electrons, albeit at extreme ...
... dispersion. All electromagnetic radiation moves at a constant speed through a vacuum, but is slowed proportionally to it's wavelength when it travels through a medium. the interstellar medium is often regarded as a vacuum, but in actual fact is occupied by atoms and free electrons, albeit at extreme ...
THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM (ISM) Summary Notes: Part 2
... with more energetic (hotter!) free photoelectrons are needed to push the bound electrons of the O++ ion in the upper state from where 4363 Å line is emitted than to populate the lower energy levels from where 4959 or 5007 Å are emitted. So the line strength ratio λ4363/λ5007 immediately tells us h ...
... with more energetic (hotter!) free photoelectrons are needed to push the bound electrons of the O++ ion in the upper state from where 4363 Å line is emitted than to populate the lower energy levels from where 4959 or 5007 Å are emitted. So the line strength ratio λ4363/λ5007 immediately tells us h ...
Summary Of the Structure of the Milky Way
... • The Distribution of stars can reveal part of the disk-like nature of the Milky Way galaxy, but are not “deep” enough probes to fully reveal the structure of the Milky Way. • Open clusters can define the thickness of the Milky Way’s thin disk where star formation is active. • Globular clusters allo ...
... • The Distribution of stars can reveal part of the disk-like nature of the Milky Way galaxy, but are not “deep” enough probes to fully reveal the structure of the Milky Way. • Open clusters can define the thickness of the Milky Way’s thin disk where star formation is active. • Globular clusters allo ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 6 Notes: Internal Energy
... and it is a function solely of the type of gas: all monatomic ideal gasses have γa = (3/2 + 1)/(3/2) = 5/3, whether they are degenerate or not. All relativistic gasses have γa = 4/3, whether they are degenerate or not. The adiabatic index is a very useful quantity for know for a gas, because it desc ...
... and it is a function solely of the type of gas: all monatomic ideal gasses have γa = (3/2 + 1)/(3/2) = 5/3, whether they are degenerate or not. All relativistic gasses have γa = 4/3, whether they are degenerate or not. The adiabatic index is a very useful quantity for know for a gas, because it desc ...
A Modern Search for Wolf-Rayet Stars in the Magellanic Clouds. III
... One of the more interesting spectra we’ve encountered is that of LMCe058-1, shown in Fig. 7. The star is a known to be a super-soft x-ray source, RX J0513.9-6951, and its optical spectrum has been previously described by Cowley et al. (1993). The star is variable both in the x-ray region (Cowley et ...
... One of the more interesting spectra we’ve encountered is that of LMCe058-1, shown in Fig. 7. The star is a known to be a super-soft x-ray source, RX J0513.9-6951, and its optical spectrum has been previously described by Cowley et al. (1993). The star is variable both in the x-ray region (Cowley et ...
1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... The surface temperature of Barnard’s star is about 3 500 K. Using this information and information about its luminosity, explain why Barnard’s star cannot be (i) ...
... The surface temperature of Barnard’s star is about 3 500 K. Using this information and information about its luminosity, explain why Barnard’s star cannot be (i) ...
HEA_Pulsars
... cylinder close to neutron star surface… - no ‘wandering’ and directionality • Problem: ALL radiation mechanisms at different frequencies (coherent or not) must have same orientation along magnetic field. ...
... cylinder close to neutron star surface… - no ‘wandering’ and directionality • Problem: ALL radiation mechanisms at different frequencies (coherent or not) must have same orientation along magnetic field. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.