Part 2 - Aryabhat
... All stars shine but none do it like Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Aptly named, Sirius comes from the Greek word Seirius, meaning, "searing" or "scorching." Blazing at a visual magnitude of –1.42, it is twice as bright as any other star in our sky. Sirius resides in the constellation C ...
... All stars shine but none do it like Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Aptly named, Sirius comes from the Greek word Seirius, meaning, "searing" or "scorching." Blazing at a visual magnitude of –1.42, it is twice as bright as any other star in our sky. Sirius resides in the constellation C ...
The mid- and far-infrared range - International Space Science Institute
... Over the last three decades our understanding of interstellar dust and gas has increased dramatically. To a large extent this has been driven by rapid developments in IR detector technology. Sensitive IR spectrometers operating in all the IR windows are now standard at all major ground-based infrare ...
... Over the last three decades our understanding of interstellar dust and gas has increased dramatically. To a large extent this has been driven by rapid developments in IR detector technology. Sensitive IR spectrometers operating in all the IR windows are now standard at all major ground-based infrare ...
CEA - Nuclear astrophysics
... and planets were formed; – visible light tells us about the different nuclear reactions produced within the stars throughout their life; – radio waves, X-rays and gamma rays show us the sometimes very violent phenomena that occur at the end of a star’s life: supernovae, pulsars, neutron stars and bl ...
... and planets were formed; – visible light tells us about the different nuclear reactions produced within the stars throughout their life; – radio waves, X-rays and gamma rays show us the sometimes very violent phenomena that occur at the end of a star’s life: supernovae, pulsars, neutron stars and bl ...
Astronomy - Dr. Noha MH Elnagdi
... 2- Comparison must include the structure, advantages, and disadvantages of each type ...
... 2- Comparison must include the structure, advantages, and disadvantages of each type ...
Presentation - Relativity Group
... • What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. • What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see disti ...
... • What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. • What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see disti ...
Chapter 1-3
... binaries). In particular for so called double-lined eclipsing binaries, in which the spectral lines of both stars vary, it is possible to accurately measure both the masses and radii (with 1–2 % accuracy in some cases) by fitting the radial-velocity curves and the eclipse lightcurve. Together with ...
... binaries). In particular for so called double-lined eclipsing binaries, in which the spectral lines of both stars vary, it is possible to accurately measure both the masses and radii (with 1–2 % accuracy in some cases) by fitting the radial-velocity curves and the eclipse lightcurve. Together with ...
star - Cloudfront.net
... of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. 2b. Students know galaxies are made of billions of stars and comprise most of the visible mass of the universe. 2c. Students know the evidence indicating that all elements with an atomic number greater than that of lithium have be ...
... of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. 2b. Students know galaxies are made of billions of stars and comprise most of the visible mass of the universe. 2c. Students know the evidence indicating that all elements with an atomic number greater than that of lithium have be ...
What powers luminous infrared galaxies?
... Arp 220 and NGC 6240 concluded that the observed far-infrared luminosity is not dominated by recently formed, massive stars, implying that the last period of very active star formation must have occurred 108 years ago or that stars more massive than 20 to 30 M have recently not been forming. The r ...
... Arp 220 and NGC 6240 concluded that the observed far-infrared luminosity is not dominated by recently formed, massive stars, implying that the last period of very active star formation must have occurred 108 years ago or that stars more massive than 20 to 30 M have recently not been forming. The r ...
v A v A
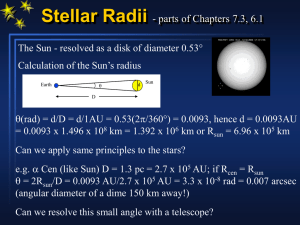
... = 0.0093 x 1.496 x 108 km = 1.392 x 106 km or Rsun = 6.96 x 105 km Can we apply same principles to the stars? e.g. Cen (like Sun) D = 1.3 pc = 2.7 x 105 AU; if Rcen = Rsun = 2Rsun/D = 0.0093 AU/2.7 x 105 AU = 3.3 x 10-8 rad = 0.007 arcsec (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve ...
... = 0.0093 x 1.496 x 108 km = 1.392 x 106 km or Rsun = 6.96 x 105 km Can we apply same principles to the stars? e.g. Cen (like Sun) D = 1.3 pc = 2.7 x 105 AU; if Rcen = Rsun = 2Rsun/D = 0.0093 AU/2.7 x 105 AU = 3.3 x 10-8 rad = 0.007 arcsec (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve ...
Protoplanetary disks, jets, and the birth of the stars
... scenario might be valid to describe the formation of stars of all masses. Also, radio jets have been found in all phases of the stellar formation process, from very young protostars to more evolved stars, associated with transitional disks, where accretion (and radio emission) is very low ([48]; see ...
... scenario might be valid to describe the formation of stars of all masses. Also, radio jets have been found in all phases of the stellar formation process, from very young protostars to more evolved stars, associated with transitional disks, where accretion (and radio emission) is very low ([48]; see ...
Star Formation Legacy of the Hubble Space Telescope Outline of Talk
... Summary of HST Disk Observations • HST validated the flared disk model of T Tauri star disks with the single image of HH 30 • The diversity of disks is impressive; all these are shown at the same scale • Morphology and internal structure of disks and rings gives clues about unseen companions • Spitz ...
... Summary of HST Disk Observations • HST validated the flared disk model of T Tauri star disks with the single image of HH 30 • The diversity of disks is impressive; all these are shown at the same scale • Morphology and internal structure of disks and rings gives clues about unseen companions • Spitz ...
Document
... only when they reached a place directly under the location of Mt.Olympus. The earth here was thin and crumbling, but it was thick enough for the plan they sought to carry out. “Here” the god of the underworld said, motioning to Hephaestus. Hephaestus transformed into his Roman form, Vulcan, who was ...
... only when they reached a place directly under the location of Mt.Olympus. The earth here was thin and crumbling, but it was thick enough for the plan they sought to carry out. “Here” the god of the underworld said, motioning to Hephaestus. Hephaestus transformed into his Roman form, Vulcan, who was ...
Object A
... Feb. 29 – Last day to drop with an automatic “W” Apr. 1 – Last day to drop a class with W, F, FA ...
... Feb. 29 – Last day to drop with an automatic “W” Apr. 1 – Last day to drop a class with W, F, FA ...
homework assignment 2
... yourselves and figure out some way of communicating with each other outside of class so that all of the group knows who is doing what over the next week. Elect a secretary/recorder, who will list all the group members’ names on a sheet of paper. Look over the list of statements below and choose thre ...
... yourselves and figure out some way of communicating with each other outside of class so that all of the group knows who is doing what over the next week. Elect a secretary/recorder, who will list all the group members’ names on a sheet of paper. Look over the list of statements below and choose thre ...
(Relative) Distances from the HST Snapshot Database
... must be sharply peaked around 0.505 solar masses, with all the stars within 0.006 solar masses. ...
... must be sharply peaked around 0.505 solar masses, with all the stars within 0.006 solar masses. ...
Gamma Ray Bursts: The biggest bang since the big one!
... • Outer layers blasted across interstellar space • Contains all heavy elements needed for life (C, N, O, Fe etc) • Where slams into molecular gas then triggers next generation of stars/planets(/life?) ...
... • Outer layers blasted across interstellar space • Contains all heavy elements needed for life (C, N, O, Fe etc) • Where slams into molecular gas then triggers next generation of stars/planets(/life?) ...
Slide 1
... details of core collision outcomes. Accretion (low-mass end) introduces variability. If a large number of variables determines the stellar mass and enter multiplicatively, by fragmentation (Larson 1973, Elmegreen & Mathieu 1983, Zinnecker 1984) or accretion rate (Adams & Fatuzzo 1996), 5-30 collisio ...
... details of core collision outcomes. Accretion (low-mass end) introduces variability. If a large number of variables determines the stellar mass and enter multiplicatively, by fragmentation (Larson 1973, Elmegreen & Mathieu 1983, Zinnecker 1984) or accretion rate (Adams & Fatuzzo 1996), 5-30 collisio ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.