STELLAR CLASSIFICATIONS: TYPE “O” STARS
... Barnard’s star is shown in the picture to the side and the only reason it appears bright is because its very close. Percent of All Stars: “M” class stars make up most of all the stars in the sky at 76.45%. This is good news as it means stars will be around for a long time! ...
... Barnard’s star is shown in the picture to the side and the only reason it appears bright is because its very close. Percent of All Stars: “M” class stars make up most of all the stars in the sky at 76.45%. This is good news as it means stars will be around for a long time! ...
Additional Cosmology Images
... stars, like the open clusters shown in this image. The stars in these open clusters are all relatively young and were born from the same cloud of interstellar gas. The stars in an open cluster will only remain together for a limited time and gradually disperse into space, pulled away by the gravitat ...
... stars, like the open clusters shown in this image. The stars in these open clusters are all relatively young and were born from the same cloud of interstellar gas. The stars in an open cluster will only remain together for a limited time and gradually disperse into space, pulled away by the gravitat ...
Linking Gas Fractions to Bimodalities in Galaxy Properties
... have demonstrated two distinct bimodalities in galaxy properties: a bimodality between recent-burst dominated and more continuous star formation histories (SFHs) as a function of stellar mass M∗ , divided at M∗ ∼ 3 × 1010 M⊙ (Kauffmann et al. 2003b), and a bimodality between blue late-type and red e ...
... have demonstrated two distinct bimodalities in galaxy properties: a bimodality between recent-burst dominated and more continuous star formation histories (SFHs) as a function of stellar mass M∗ , divided at M∗ ∼ 3 × 1010 M⊙ (Kauffmann et al. 2003b), and a bimodality between blue late-type and red e ...
Earth and Beyond - Swinton Community School
... Nuclear fusion In nuclear fusion reactions, lighter nuclei are joined together (fused)…… ….to form heavier atomic nuclei. This releases massive amounts or energy. In our Sun, a typical star, hydrogen is being fused into helium, this provides the energy for life on Earth. ...
... Nuclear fusion In nuclear fusion reactions, lighter nuclei are joined together (fused)…… ….to form heavier atomic nuclei. This releases massive amounts or energy. In our Sun, a typical star, hydrogen is being fused into helium, this provides the energy for life on Earth. ...
Pulsar properties - Pulsar Search Collaboratory
... Size of emission region is bounded by the so-called `light cylinder’ - this is an imaginary surface that co-rotates with the neutron star. Einstein asserts the co-rotation speed cannot be greater than the speed of light, c. This sets a fundamental size for the emission region. ...
... Size of emission region is bounded by the so-called `light cylinder’ - this is an imaginary surface that co-rotates with the neutron star. Einstein asserts the co-rotation speed cannot be greater than the speed of light, c. This sets a fundamental size for the emission region. ...
Our_Unique_Planet
... “Magnetic Field” surrounding the earth. This provides protection from hard stellar radiation (ex. Solar Wind ) for us as well as keeping the atmosphere from being ...
... “Magnetic Field” surrounding the earth. This provides protection from hard stellar radiation (ex. Solar Wind ) for us as well as keeping the atmosphere from being ...
Black Hole - The Crowned Anarchist Literature
... radiates X rays copiously before entering the event horizon of the black hole and disappearing forever. Many investigators believe that one of the component stars of the binary X-ray system Cygnus X-1 is a black hole. Discovered in 1971 in the constellation Cygnus, this binary consists of a blue sup ...
... radiates X rays copiously before entering the event horizon of the black hole and disappearing forever. Many investigators believe that one of the component stars of the binary X-ray system Cygnus X-1 is a black hole. Discovered in 1971 in the constellation Cygnus, this binary consists of a blue sup ...
Galaxies - science9atsouthcarletonhs
... Types of Galaxies III. Irregulars Irregular galaxies lack any specific form and contain stars, gas and dust generally associated with a youth. The irregular galaxy at right is the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite of the Milky Way located about 180,000 light years from the sun. The LMC is about 6 ...
... Types of Galaxies III. Irregulars Irregular galaxies lack any specific form and contain stars, gas and dust generally associated with a youth. The irregular galaxy at right is the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite of the Milky Way located about 180,000 light years from the sun. The LMC is about 6 ...
RAPID MASS ACCRETION IN THE SYMBIOTIC STAR AG DRA T
... The temperature of the hot component of AG Dra in the quiescent stage is about 150000 K which is derived from the intensities of He H 4686 and He 14471 relative to Hg obtained on August 5, 1980 (Blair et al., 1983) using the formula of Iijima (1982). The luminosity of the hot component in the ultrav ...
... The temperature of the hot component of AG Dra in the quiescent stage is about 150000 K which is derived from the intensities of He H 4686 and He 14471 relative to Hg obtained on August 5, 1980 (Blair et al., 1983) using the formula of Iijima (1982). The luminosity of the hot component in the ultrav ...
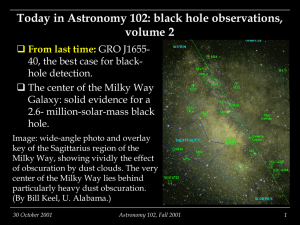
Today in Astronomy 102: black hole observations, v.2
... neighborhood of Sgr A*’s black hole to provide a quasarlike luminosity. This would also explain the lack of jets. It’s also not quite massive enough for quasar-size luminosity, as we shall see. 30 October 2001 ...
... neighborhood of Sgr A*’s black hole to provide a quasarlike luminosity. This would also explain the lack of jets. It’s also not quite massive enough for quasar-size luminosity, as we shall see. 30 October 2001 ...
Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... These individual views may be referred to as the “North,” “South,” “East,” West,” and “Zenith” skies. We know of no pattern of stars in art, either ancient or modern, that attempts to link stars spread over large areas of the entire sky. The magnitude 1 simulations were not very interesting; there a ...
... These individual views may be referred to as the “North,” “South,” “East,” West,” and “Zenith” skies. We know of no pattern of stars in art, either ancient or modern, that attempts to link stars spread over large areas of the entire sky. The magnitude 1 simulations were not very interesting; there a ...
Falling Stars
... Describe the characteristics of comets, asteroids, and meteors. hours or days to see its movement. The center of a comet is a ball of frozen gas, dust, and water. Like planets or moons, comets orbit around the Sun. The comet that causes the Leonids is called Tempel-Tuttle. It is named after two scie ...
... Describe the characteristics of comets, asteroids, and meteors. hours or days to see its movement. The center of a comet is a ball of frozen gas, dust, and water. Like planets or moons, comets orbit around the Sun. The comet that causes the Leonids is called Tempel-Tuttle. It is named after two scie ...
Down Under from North Florida
... However, astute Gainesville area residents can easily spot this bright star low over the southern winter horizon with careful planning. See Figure 1. Note: Atmospheric extinction may dim Canopus (mag. -0.62) by one or two magnitudes, which therefore unfortunately belies its actual brilliance. Still, ...
... However, astute Gainesville area residents can easily spot this bright star low over the southern winter horizon with careful planning. See Figure 1. Note: Atmospheric extinction may dim Canopus (mag. -0.62) by one or two magnitudes, which therefore unfortunately belies its actual brilliance. Still, ...
Background Presentation
... The NASA E/PO Program at Sonoma State University A group of people working collaboratively to educate the public about current and future NASA high energy astrophysics/astronomy missions. Swift Led by Prof. Lynn Cominsky ...
... The NASA E/PO Program at Sonoma State University A group of people working collaboratively to educate the public about current and future NASA high energy astrophysics/astronomy missions. Swift Led by Prof. Lynn Cominsky ...
The spectral energy distribution of protoplanetary
... performed by Spitzer have mapped ∼90 per cent of all the starforming regions within 500 pc of the Sun and have obtained spectra for over 2000 young stellar objects (YSOs) contained therein. Observations of those star-forming regions nearest to us have, to date, dominated the literature as they conta ...
... performed by Spitzer have mapped ∼90 per cent of all the starforming regions within 500 pc of the Sun and have obtained spectra for over 2000 young stellar objects (YSOs) contained therein. Observations of those star-forming regions nearest to us have, to date, dominated the literature as they conta ...
1 AST 104 LAB 1 Temperature and Luminosity of Stars: Wein`s Law
... To understand how thermal spectra can be used to evaluate the temperature of a star To understand how temperature and radius of a star determine a star’s luminosity Introduction: In this activity we will learn how light from a star can tell us its temperature and how much energy per second the s ...
... To understand how thermal spectra can be used to evaluate the temperature of a star To understand how temperature and radius of a star determine a star’s luminosity Introduction: In this activity we will learn how light from a star can tell us its temperature and how much energy per second the s ...
Pretty Pictures of the Cosmos
... with the Hubble Space Telescope, distant galaxies form a dramatic backdrop for disrupted spiral galaxy Arp 188, the Tadpole Galaxy. The cosmic Tadpole is a mere 420 million light-years distant toward the northern constellation Draco. Its eye-catching tail is about 280 thousand light-years long and f ...
... with the Hubble Space Telescope, distant galaxies form a dramatic backdrop for disrupted spiral galaxy Arp 188, the Tadpole Galaxy. The cosmic Tadpole is a mere 420 million light-years distant toward the northern constellation Draco. Its eye-catching tail is about 280 thousand light-years long and f ...
Powerpoint
... Over the next few days the temperature falls to ~5500 K, at which point, for the densities near the photosphere, hydrogen recombines. The recombination does not occur all at once for the entire envelope, but rather as a wave that propagates inwards in mass – though initially outwards in radius. Duri ...
... Over the next few days the temperature falls to ~5500 K, at which point, for the densities near the photosphere, hydrogen recombines. The recombination does not occur all at once for the entire envelope, but rather as a wave that propagates inwards in mass – though initially outwards in radius. Duri ...
geol0810 homework 1: early solar system history
... information about the sequence of events in early Solar System history. A variety of isotopic systems can be used, but we will focus on only two of them: the hafnium-tungsten and aluminum-26. As we discussed in class, the hafnium (182Hf)-tungsten (182W) system tracks the timing of core formation. Be ...
... information about the sequence of events in early Solar System history. A variety of isotopic systems can be used, but we will focus on only two of them: the hafnium-tungsten and aluminum-26. As we discussed in class, the hafnium (182Hf)-tungsten (182W) system tracks the timing of core formation. Be ...
Astro Physics Notes and Study Guide 2015-17
... Describe the discovery of cosmic background (CMB) radiation by Penzias and Wilson. ...
... Describe the discovery of cosmic background (CMB) radiation by Penzias and Wilson. ...
Lecture 1 - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... Cool, dense clouds suspended above surface by magnetic field. ...
... Cool, dense clouds suspended above surface by magnetic field. ...
lecture_1_mbu - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... Cool, dense clouds suspended above surface by magnetic field. ...
... Cool, dense clouds suspended above surface by magnetic field. ...
The Northern Winter Constellations - Science
... The Constellations of the Winter Sky If you live in the northern latitudes and you scan the sky from the southern horizon to the region overhead, you should be able to see the following constellations on a clear winter night: Orion the Hunter, Canis Major the Great Dog, Canis Minor the Little Dog, T ...
... The Constellations of the Winter Sky If you live in the northern latitudes and you scan the sky from the southern horizon to the region overhead, you should be able to see the following constellations on a clear winter night: Orion the Hunter, Canis Major the Great Dog, Canis Minor the Little Dog, T ...
Mise en page 1
... light years away or a few thousand, but to us they appear dotted on a giant dome rotating above the Earth. Although we now know that it is the Earth that rotates, the illusion serves as a convenient model. Since the axis of the Earth’s rotation goes through the poles, a patient observer at the North ...
... light years away or a few thousand, but to us they appear dotted on a giant dome rotating above the Earth. Although we now know that it is the Earth that rotates, the illusion serves as a convenient model. Since the axis of the Earth’s rotation goes through the poles, a patient observer at the North ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.