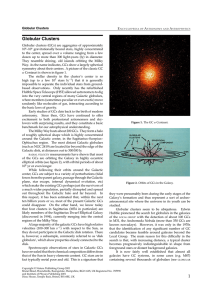
Globular Clusters
... eventually stops the contraction. The star reaches a nice equilibrium, balancing energy production and transfer and global brightness, and enters into the main sequence (MS). This equilibrium holds on the MS for more than 70% of the total stellar lifetime (∼1010 yr), until the nuclear fuel (hydrogen ...
... eventually stops the contraction. The star reaches a nice equilibrium, balancing energy production and transfer and global brightness, and enters into the main sequence (MS). This equilibrium holds on the MS for more than 70% of the total stellar lifetime (∼1010 yr), until the nuclear fuel (hydrogen ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
The Astronomical Search for Origins
... The Electromagnetic Spectrum Our eyes see only part of the ...
... The Electromagnetic Spectrum Our eyes see only part of the ...
Why does Sirius twinkle?
... is a white main sequence star) and "Sirius B," a Sirius appears to twinkle or shimmer more than white dwarf star. As seen with the naked eye, Sirius can be seen to twinkle many different colors other stars for some very simple reasons. It is very bright, which can amplify atmospheric effects and it ...
... is a white main sequence star) and "Sirius B," a Sirius appears to twinkle or shimmer more than white dwarf star. As seen with the naked eye, Sirius can be seen to twinkle many different colors other stars for some very simple reasons. It is very bright, which can amplify atmospheric effects and it ...
chapter 8
... is, the energy source for emitted radiation is the heat or thermal energy in the body. The emission process occurs at the atomic level and involves electrons in the atoms undergoing transitions from high energy states to lower energy states. If an object is sufficiently hot that it gives off visible ...
... is, the energy source for emitted radiation is the heat or thermal energy in the body. The emission process occurs at the atomic level and involves electrons in the atoms undergoing transitions from high energy states to lower energy states. If an object is sufficiently hot that it gives off visible ...
So What All Is Out There, Anyway?
... together in a large, flat disk with long arms reaching out into space in a spiral. This beautiful collection of stars, star clusters, and nebulas, is slowly rotating. At its center is a black hole, a mass of matter that is so dense not even light can escape the clutches of its gravity if it gets too ...
... together in a large, flat disk with long arms reaching out into space in a spiral. This beautiful collection of stars, star clusters, and nebulas, is slowly rotating. At its center is a black hole, a mass of matter that is so dense not even light can escape the clutches of its gravity if it gets too ...
幻灯片 1
... •Stellar members have almost the same age, composition and dynamic environment within a cluster. know one, know all •Stellar members are well studied within a cluster higher certainty of mass, radius, temperature and distance. ...
... •Stellar members have almost the same age, composition and dynamic environment within a cluster. know one, know all •Stellar members are well studied within a cluster higher certainty of mass, radius, temperature and distance. ...
astro2_lec1 - Astronomy & Astrophysics Group
... Evolution and the Tuning Fork diagram For many years the prevailing belief was that ellipticals evolve into spirals, from left to right in the tuning fork (although Hubble did not argue for the tuning fork diagram as an evolutionary sequence). ...
... Evolution and the Tuning Fork diagram For many years the prevailing belief was that ellipticals evolve into spirals, from left to right in the tuning fork (although Hubble did not argue for the tuning fork diagram as an evolutionary sequence). ...
Kepler-452b is not a new Earth A twin of the Sun
... First detection of lithium from an exploding star The light chemical element lithium is one of the few elements that is predicted to have been created by the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago. But understanding the amounts of lithium observed in stars around us today in the Universe has given astrono ...
... First detection of lithium from an exploding star The light chemical element lithium is one of the few elements that is predicted to have been created by the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago. But understanding the amounts of lithium observed in stars around us today in the Universe has given astrono ...
Superhero science 2
... devices will be reduced in size, but for now they are neither small nor sustainably producing electricity. Ironman’s arc reactor uses Palladium in its core which has been proposed (although largely discredited) as a possible material for fusion at lower temperatures (cold fusion). It is more likely ...
... devices will be reduced in size, but for now they are neither small nor sustainably producing electricity. Ironman’s arc reactor uses Palladium in its core which has been proposed (although largely discredited) as a possible material for fusion at lower temperatures (cold fusion). It is more likely ...
PROBLEM SET #9 SOLUTIONS AST142 1. Quasar luminosity
... is accreting at the Eddington rate, and show that these two findings are consistent with one another. ...
... is accreting at the Eddington rate, and show that these two findings are consistent with one another. ...
Homework # 1
... m. Since our eyes are limited to a rather narrow range of light, how is it possible for us to see stars outside of the range of spectral types that you discovered in the previous question? ...
... m. Since our eyes are limited to a rather narrow range of light, how is it possible for us to see stars outside of the range of spectral types that you discovered in the previous question? ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... built of the same (`solar abundance') atomic matter that forms the Earth, subject to constant motion through vacuum, collision, and coalescence (accretion). Who invented the solar nebula: Kant & Laplace or Leucippus? ...
... built of the same (`solar abundance') atomic matter that forms the Earth, subject to constant motion through vacuum, collision, and coalescence (accretion). Who invented the solar nebula: Kant & Laplace or Leucippus? ...
ph507lecnote06
... • using a large number of lines in the spectrum to allow shifts of much less than one pixel to be determined. Absolute wavelength calibration and stability over long timescales is achieved by: • passing stellar light through a cell containing iodine, imprinting large number of additional lines of kn ...
... • using a large number of lines in the spectrum to allow shifts of much less than one pixel to be determined. Absolute wavelength calibration and stability over long timescales is achieved by: • passing stellar light through a cell containing iodine, imprinting large number of additional lines of kn ...
Ridgway - Betelgeuse Workshop 2016
... How the mass-loss rates of red-supergiants determine the fate of massive stars? The evolution of Red Supergiants at very low metallicity Atmospheric Structure and dynamics Atmospheric structure and dynamics: the spatial and temporal domains The Temperatures of Red Supergiants: how cool are the coole ...
... How the mass-loss rates of red-supergiants determine the fate of massive stars? The evolution of Red Supergiants at very low metallicity Atmospheric Structure and dynamics Atmospheric structure and dynamics: the spatial and temporal domains The Temperatures of Red Supergiants: how cool are the coole ...
Distance to the SMC
... Walter Baade, using the newly built Palomar 200 inch telescope, discovered that stars can be classified into two general age categories. Population I stars are relatively young and formed after the interstellar medium was enriched with metals from the explosions of supernova and the deaths of other ...
... Walter Baade, using the newly built Palomar 200 inch telescope, discovered that stars can be classified into two general age categories. Population I stars are relatively young and formed after the interstellar medium was enriched with metals from the explosions of supernova and the deaths of other ...
ExamView - es S1 dept final.tst
... d. periods. 19. Young Earth formed a core, mantle, and crust in a process called a. layering. c. dispersion. b. settling. d. differentiation. 20. Early fresh water oceans became salty when a. rainwater carried dissolved solid rock to the oceans. b. coral reefs created a salty ocean bottom. c. salt p ...
... d. periods. 19. Young Earth formed a core, mantle, and crust in a process called a. layering. c. dispersion. b. settling. d. differentiation. 20. Early fresh water oceans became salty when a. rainwater carried dissolved solid rock to the oceans. b. coral reefs created a salty ocean bottom. c. salt p ...
star
... The Milky Way’s flattened disk shape is caused by its rotation. The sun takes about 220 million years to complete one orbit around the galaxy’s center. Recent evidence suggests that there is a massive black hole at our galaxy’s center. Stars are forming in the galaxy's spiral arms. ...
... The Milky Way’s flattened disk shape is caused by its rotation. The sun takes about 220 million years to complete one orbit around the galaxy’s center. Recent evidence suggests that there is a massive black hole at our galaxy’s center. Stars are forming in the galaxy's spiral arms. ...
The Most Luminous Protostars in Molecular Clouds: A Hint to
... from a typical density for the clouds (n[H2 ] = 3 × 104 cm−3 ), as suggested by the authors (Sugitani et al. 1991). In one of our earlier studies toward the Cygnus region (Dobashi et al. 1996), we found that the virial masses are generally in good agreement with the LTE masses for GMCs, especially i ...
... from a typical density for the clouds (n[H2 ] = 3 × 104 cm−3 ), as suggested by the authors (Sugitani et al. 1991). In one of our earlier studies toward the Cygnus region (Dobashi et al. 1996), we found that the virial masses are generally in good agreement with the LTE masses for GMCs, especially i ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Way is part of a cluster called the Local Group. The Local Group is made up of about 45 galaxies in different sizes and shapes. There are three major types of galaxies. ...
... Way is part of a cluster called the Local Group. The Local Group is made up of about 45 galaxies in different sizes and shapes. There are three major types of galaxies. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.