Question 1
... the source of energy is very small. energy is coming from matter and antimatter. the energy source is rotating rapidly. a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. there are many separate sources of energy in the core. ...
... the source of energy is very small. energy is coming from matter and antimatter. the energy source is rotating rapidly. a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. there are many separate sources of energy in the core. ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... is high enough for hydrogen burning. The whole process repeats, the produced helium falls on to lower layers which finally start burning helium in another helium shell flash. The star is very unstable and the repeated helium flashes result in huge mass losses from the star. The outer layers of the s ...
... is high enough for hydrogen burning. The whole process repeats, the produced helium falls on to lower layers which finally start burning helium in another helium shell flash. The star is very unstable and the repeated helium flashes result in huge mass losses from the star. The outer layers of the s ...
THE SUN IS NOT AN AVERAGE STAR Sometimes biblical creation
... a hundred billion others; and even the Milky Way is just one among a hundred billion galaxies in the universe."5 2. "Our star, the sun, is rather ordinary ... In many respects the sun is entirely a run-of-the-mill entity."6 3. "Our sun, so important to us, is merely an ordinary, `gardenvariety' star ...
... a hundred billion others; and even the Milky Way is just one among a hundred billion galaxies in the universe."5 2. "Our star, the sun, is rather ordinary ... In many respects the sun is entirely a run-of-the-mill entity."6 3. "Our sun, so important to us, is merely an ordinary, `gardenvariety' star ...
Star Constellations
... When you look at the sky on a clear night, you can see hundreds of stars. A star is a giant ball of glowing gas that is very, very hot. A star generates energy by nuclear fusion reactions. Most of these stars are like our Sun. However, some stars are smaller than our Sun, and some are larger. Except ...
... When you look at the sky on a clear night, you can see hundreds of stars. A star is a giant ball of glowing gas that is very, very hot. A star generates energy by nuclear fusion reactions. Most of these stars are like our Sun. However, some stars are smaller than our Sun, and some are larger. Except ...
Lecture - Ann Arbor Earth Science
... spectrum of a star that is moving away from the Earth. Notice how the entire pattern of black lines has been shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. If the bottom band had been a star that is moving toward the Earth, then the pattern of black lines would have been shifted toward the blue end of ...
... spectrum of a star that is moving away from the Earth. Notice how the entire pattern of black lines has been shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. If the bottom band had been a star that is moving toward the Earth, then the pattern of black lines would have been shifted toward the blue end of ...
A billion pixels, a billion stars
... all sources that are bright enough. However, some sources can suddenly change dramatically in brightness, putting them over the threshold at which they become “visible” to Gaia. These transient and variable sources are the subject of a special data analysis procedure, known as the Gaia photometric s ...
... all sources that are bright enough. However, some sources can suddenly change dramatically in brightness, putting them over the threshold at which they become “visible” to Gaia. These transient and variable sources are the subject of a special data analysis procedure, known as the Gaia photometric s ...
No. 53 - Institute for Astronomy
... in the plane of Earth’s orbit (the ecliptic). During the K2 mission, many of the extrasolar planets discovered by the Kepler telescope will have this lucky double cosmic alignment that would allow for mutual discovery—if there is anyone on those planets to discover Earth. The three new planets orbit ...
... in the plane of Earth’s orbit (the ecliptic). During the K2 mission, many of the extrasolar planets discovered by the Kepler telescope will have this lucky double cosmic alignment that would allow for mutual discovery—if there is anyone on those planets to discover Earth. The three new planets orbit ...
Nucleosynthesis and the death of stars
... • A Type I supernova is a massive explosion of a star that occurs under two possible scenarios. The first is that a white dwarf star undergoes a nuclear based explosion after it reaches its Chandrasekhar limit (1.44 solar masses) from absorbing mass from a neighboring star (usually a red giant). • A ...
... • A Type I supernova is a massive explosion of a star that occurs under two possible scenarios. The first is that a white dwarf star undergoes a nuclear based explosion after it reaches its Chandrasekhar limit (1.44 solar masses) from absorbing mass from a neighboring star (usually a red giant). • A ...
SRP_Space_Lesson 5 - Scientist in Residence Program
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
An interesting nebular object in LDN 288
... cavity. The velocity of the dark cloud is ~2.5 km/s and its distance is estimated as (380-990) pc. The object SNO 85 itself is associated with an IRAS point source IRAS 17547-1832, the infrared colors of this source are typical for a non-evolved source embedded in the dense dark cloud. This region i ...
... cavity. The velocity of the dark cloud is ~2.5 km/s and its distance is estimated as (380-990) pc. The object SNO 85 itself is associated with an IRAS point source IRAS 17547-1832, the infrared colors of this source are typical for a non-evolved source embedded in the dense dark cloud. This region i ...
E-AQA Mark Scheme P1 long answer questions
... There is a clear, balanced and detailed description of the advantages and disadvantages of using solar energy to heat the water rather than using an electric immersion heater, with a minimum of two advantages and two disadvantages from the examples below. ...
... There is a clear, balanced and detailed description of the advantages and disadvantages of using solar energy to heat the water rather than using an electric immersion heater, with a minimum of two advantages and two disadvantages from the examples below. ...
Astron 104 Laboratory #11 The Scale of the Milky Way
... called the Local Group. The following table lists the distances to the centers of three Local Group galaxies. Draw a dot on your picture (if possible) to represent the center of each galaxy. Don’t worry about the direction (left/right/up/down) for each galaxy; just place a dot an appropriate distanc ...
... called the Local Group. The following table lists the distances to the centers of three Local Group galaxies. Draw a dot on your picture (if possible) to represent the center of each galaxy. Don’t worry about the direction (left/right/up/down) for each galaxy; just place a dot an appropriate distanc ...
AY5 Announcements
... (1) More massive stars require higher central temperatures (hydrostatic eqm.) (2) The P-P fusion rate and luminosity is proportional to T4 Therefore, more massive stars will have higher central temperature and higher Luminosity. This is what is seen along the H-R Diagram main sequence. ...
... (1) More massive stars require higher central temperatures (hydrostatic eqm.) (2) The P-P fusion rate and luminosity is proportional to T4 Therefore, more massive stars will have higher central temperature and higher Luminosity. This is what is seen along the H-R Diagram main sequence. ...
2008 - Astronomy Now
... News update Record quintuple planetary system revealed �������� 1, 9 Were the first stars dark?.................................... 1, 10 Rosetta returns home......................................... 1, 10 The naked white dwarfs..................................... 1, 11 Infant galaxies filled the e ...
... News update Record quintuple planetary system revealed �������� 1, 9 Were the first stars dark?.................................... 1, 10 Rosetta returns home......................................... 1, 10 The naked white dwarfs..................................... 1, 11 Infant galaxies filled the e ...
HD 140283: A Star in the Solar Neighborhood that Formed Shortly
... and V − I colors through polynomial fits to a sample of 791 single main-sequence stars with accurate BVI photometry and Hipparcos or USNO parallaxes of 40 mas or higher (d < 25 pc), which is provided online by I. N. Reid2. A correction for metallicity, estimated from each star’s position in B − V vs ...
... and V − I colors through polynomial fits to a sample of 791 single main-sequence stars with accurate BVI photometry and Hipparcos or USNO parallaxes of 40 mas or higher (d < 25 pc), which is provided online by I. N. Reid2. A correction for metallicity, estimated from each star’s position in B − V vs ...
Astronomy 15 - Problem Set Number 4 1) Suppose one were to
... b) A star is found to have a displacement on the plates of almost half a pixel - 10 microns due to parallax, and simultaneously has a yearly displacement of 20 microns due to proper motion. Find its annual proper motion, its distance, and its transverse velocity. c) For this same star, a heliocentri ...
... b) A star is found to have a displacement on the plates of almost half a pixel - 10 microns due to parallax, and simultaneously has a yearly displacement of 20 microns due to proper motion. Find its annual proper motion, its distance, and its transverse velocity. c) For this same star, a heliocentri ...
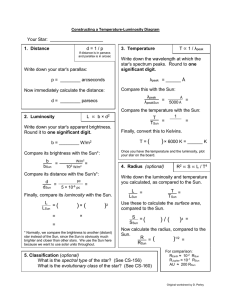
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... Winter Stars – The brightest and most spectacular stars in the sky belong to the winter. Betelgeuse, the ridiculously huge supergiant mentioned in lecture; Meissa, a rare superhot O star in Orion's belt; and dog star Sirius: the brightest of all stars are all winter stars. These stars are already vi ...
... Winter Stars – The brightest and most spectacular stars in the sky belong to the winter. Betelgeuse, the ridiculously huge supergiant mentioned in lecture; Meissa, a rare superhot O star in Orion's belt; and dog star Sirius: the brightest of all stars are all winter stars. These stars are already vi ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.