Section 5.2 - Cells: The Basic Unit of Life ANIMAL CELL
... - acts as the control centre, directing all of the cell's activities. - genetic information is organized into threadlike structures called chromosomes - each chromosome contains many different ...
... - acts as the control centre, directing all of the cell's activities. - genetic information is organized into threadlike structures called chromosomes - each chromosome contains many different ...
Mitosis Investigation
... All new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which involves both replication of the cell's nucleus and the division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis) to form two genetically identical cells. There are two types of nuclear division: mitosis and ...
... All new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which involves both replication of the cell's nucleus and the division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis) to form two genetically identical cells. There are two types of nuclear division: mitosis and ...
Chapter 3 Section 2 - Blue Earth Area Schools
... Follow along steps 1-3 and see how they calculate surface area, volume and the ratio between the two. Answer analysis questions 1-3 ...
... Follow along steps 1-3 and see how they calculate surface area, volume and the ratio between the two. Answer analysis questions 1-3 ...
1-2: What are the properties of matter?
... • Eukaryotic cells have many specialized organs called organelles • ORGANELLES: specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell ...
... • Eukaryotic cells have many specialized organs called organelles • ORGANELLES: specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell ...
2/23/10 Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce
... o Complete division of the cytoplasm forming two new cells o Differs in plant and animal cells Cytokinesis in plants o Cell plate forms o Vesicles line up at equator Derived from Golgi ...
... o Complete division of the cytoplasm forming two new cells o Differs in plant and animal cells Cytokinesis in plants o Cell plate forms o Vesicles line up at equator Derived from Golgi ...
The Cell Cycle
... • It does this by initiating a process that will lead to destruction of its cyclin. (We learn about this destruction in Ch. 19 with proteosomes!) • Destruction is important! This actually will keep driving the cycle past the M phase checkpoint which controls the onset of anaphase ...
... • It does this by initiating a process that will lead to destruction of its cyclin. (We learn about this destruction in Ch. 19 with proteosomes!) • Destruction is important! This actually will keep driving the cycle past the M phase checkpoint which controls the onset of anaphase ...
File
... 11. What is the jelly-like area between the cell membrane and the nucleus in an animal cell? 12. Under a microscope a student observed cells with a boxlike shape, green organelles, and a nucleus off to the side. What type of cells were these? 13. What is the function of the nucleus? 14. What is the ...
... 11. What is the jelly-like area between the cell membrane and the nucleus in an animal cell? 12. Under a microscope a student observed cells with a boxlike shape, green organelles, and a nucleus off to the side. What type of cells were these? 13. What is the function of the nucleus? 14. What is the ...
Unit 3: Cells Study Guide Write the correct letter in the blank provided
... _____ 3. This is the gel like material that holds all the other organelles in place inside the cell. _____ 4. This organelle surrounds plant cells, gives protection and shape to the cell. _____ 5. This organelle is responsible for processing, sorting and delivering proteins. _____ 6. This organelle ...
... _____ 3. This is the gel like material that holds all the other organelles in place inside the cell. _____ 4. This organelle surrounds plant cells, gives protection and shape to the cell. _____ 5. This organelle is responsible for processing, sorting and delivering proteins. _____ 6. This organelle ...
Unit 1 Review
... • Life activity carried on by every living plant and animal • Combine simple molecules to form complex molecules • The absorption and distribution of materials ...
... • Life activity carried on by every living plant and animal • Combine simple molecules to form complex molecules • The absorption and distribution of materials ...
Organelles Day 3
... purpose that allows the cell to function. To be inducted into the biology club, you need to know all the organelles. ...
... purpose that allows the cell to function. To be inducted into the biology club, you need to know all the organelles. ...
Name
... The invention of the microscope in the late 1500s revealed to early scientists a whole new world of tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. The discoveries of scientists from the 1600s through the 1800s led to the cell theory, which is a unifying concept of ...
... The invention of the microscope in the late 1500s revealed to early scientists a whole new world of tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. The discoveries of scientists from the 1600s through the 1800s led to the cell theory, which is a unifying concept of ...
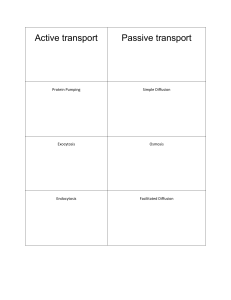
Passive Transport in the Cell
... This is the movement of molecules such as Oxygen, Sugar, and Carbon Dioxide from one region to another. Because these are relatively small molecules, they can pass through the cell membrane until they are equal on the inside and the outside. This is referred to as dynamic ...
... This is the movement of molecules such as Oxygen, Sugar, and Carbon Dioxide from one region to another. Because these are relatively small molecules, they can pass through the cell membrane until they are equal on the inside and the outside. This is referred to as dynamic ...
Name that Organelle Review PPT
... • Helps cell maintain cell shape • Microfilaments are threadlike & made of ACTIN • Microtubules are tubelike & made of TUBULIN ...
... • Helps cell maintain cell shape • Microfilaments are threadlike & made of ACTIN • Microtubules are tubelike & made of TUBULIN ...
Power Point Notes
... 1. The period between cell divisions is known as interphase. 2. During interphase all normal cell functions are taking place. The cell is not dividing. 3. Chromosomes are duplicated during this phase. (but you can’t see them!) ...
... 1. The period between cell divisions is known as interphase. 2. During interphase all normal cell functions are taking place. The cell is not dividing. 3. Chromosomes are duplicated during this phase. (but you can’t see them!) ...
BIO STUDY GUIDE - Biochemistry and Cells
... 8. From your notes/lab, what are some examples of acids and bases? 9. What particles are in an atom? 10. Water molecules are polar. What does this mean? 11. What are the basis building blocks of starch? 12. Which of the four main classes of organic molecules serves as the main source of energy for l ...
... 8. From your notes/lab, what are some examples of acids and bases? 9. What particles are in an atom? 10. Water molecules are polar. What does this mean? 11. What are the basis building blocks of starch? 12. Which of the four main classes of organic molecules serves as the main source of energy for l ...
1. Cells have selectively permeable membranes that regulate what
... 14. Transport proteins move substances into and out of the cell in the process of facilitated diffusion. 15. The process in which a substance is taken into a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane, forming a sphere called a vesicle is endocytosis. 16. Metabolism is the total of all chemical r ...
... 14. Transport proteins move substances into and out of the cell in the process of facilitated diffusion. 15. The process in which a substance is taken into a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane, forming a sphere called a vesicle is endocytosis. 16. Metabolism is the total of all chemical r ...
Mitosis
... becoming visible. Nuclear membrane dissolves The centrioles (an organelle that makes microtubules) appears and migrate to opposite sides. spindle fibers start to form between them http://www.biostudio.com/demo_freeman_dna_coiling.htm ...
... becoming visible. Nuclear membrane dissolves The centrioles (an organelle that makes microtubules) appears and migrate to opposite sides. spindle fibers start to form between them http://www.biostudio.com/demo_freeman_dna_coiling.htm ...
Websearch
... the animation and read the text below the animation on this page. 11. List the stages of mitosis (Notice – there’s an extra phase here…”prometaphase” – sometimes that is added as an “in-between” phase between prophase and metaphase. In this class you are only responsible for knowing PMAT) ...
... the animation and read the text below the animation on this page. 11. List the stages of mitosis (Notice – there’s an extra phase here…”prometaphase” – sometimes that is added as an “in-between” phase between prophase and metaphase. In this class you are only responsible for knowing PMAT) ...
Cell Organelle Riddles
... Cell Riddles Read each description below and then identify the correct vocabulary word. Write your answer on the line provided choosing from the following words: ...
... Cell Riddles Read each description below and then identify the correct vocabulary word. Write your answer on the line provided choosing from the following words: ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.