review for second six weeks common assessment
... 9. How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? 10. Know importance of meiosis 11. Functions of xylem and phloem 12. Describe the type of seed that would be dispersed by wind? insects? water? 13. What is the equation for photosynthesis? Where does it occur? 14. Levels of cell organization and define ...
... 9. How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? 10. Know importance of meiosis 11. Functions of xylem and phloem 12. Describe the type of seed that would be dispersed by wind? insects? water? 13. What is the equation for photosynthesis? Where does it occur? 14. Levels of cell organization and define ...
Cell Cycle & Cancer
... The Cell Cycle • Interphase Cell Growth and Preparation for Division • Mitosis Division of the Nucleus and its DNA • Cytokinesis Division of the Cytoplasm ...
... The Cell Cycle • Interphase Cell Growth and Preparation for Division • Mitosis Division of the Nucleus and its DNA • Cytokinesis Division of the Cytoplasm ...
79099_Mitosis
... Represents the longest time period of the cell cycle Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division ar ...
... Represents the longest time period of the cell cycle Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division ar ...
KEY - Humble ISD
... c. duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane in prokaryotic cells and are separated from each other as the membrane grows d. the chromosomes do not separate along a mitotic spindle network in prokaryotic cells e. the chromosome number is reduced by half in eukaryotic cells but not ...
... c. duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane in prokaryotic cells and are separated from each other as the membrane grows d. the chromosomes do not separate along a mitotic spindle network in prokaryotic cells e. the chromosome number is reduced by half in eukaryotic cells but not ...
Mitosis *. Part II
... • The sporophyte phase is "diploid", and is that part of the life cycle in which meiosis occurs. However, many plant species are thought to arise by polyploidy, and the use of "diploid" in the last sentence was meant to indicate that the greater number of chromosome sets occur in this phase. • The g ...
... • The sporophyte phase is "diploid", and is that part of the life cycle in which meiosis occurs. However, many plant species are thought to arise by polyploidy, and the use of "diploid" in the last sentence was meant to indicate that the greater number of chromosome sets occur in this phase. • The g ...
Mitosis Notes
... • Definition: process by which a cell’s genetic material divides, creating two complete sets of the cell’s genetic material • Result: Two daughter cells that are genetically identical ...
... • Definition: process by which a cell’s genetic material divides, creating two complete sets of the cell’s genetic material • Result: Two daughter cells that are genetically identical ...
mitosis[1] - MissChapman11
... By this stage, the chromatids will have moved to the poles of the cell. Nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes. The cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis. ...
... By this stage, the chromatids will have moved to the poles of the cell. Nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes. The cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis. ...
Stages of Mitosis
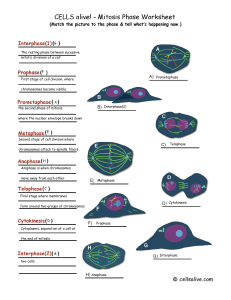
... 1. INTERPHASE: a. this is what the cell looks like in its normal phase b. it is not considered a phase of mitosis c. it is a period of intense metabolic activity prior to mitosis d. it consists of 3 phases: 1. G1- cell prepares for replication and organelles reproduce 2. S- synthesis of DNA, replica ...
... 1. INTERPHASE: a. this is what the cell looks like in its normal phase b. it is not considered a phase of mitosis c. it is a period of intense metabolic activity prior to mitosis d. it consists of 3 phases: 1. G1- cell prepares for replication and organelles reproduce 2. S- synthesis of DNA, replica ...
Mitosis
... cytoskeleton that produces spindle fibers during mitosis ● Spindle fibers form ○ strands of microtubules that help separate chromosomes ...
... cytoskeleton that produces spindle fibers during mitosis ● Spindle fibers form ○ strands of microtubules that help separate chromosomes ...
Cell Division - Mediapolis Community School
... – Growth, DNA replication – preparation for cell division – division of the nucleus and cytoplasm ...
... – Growth, DNA replication – preparation for cell division – division of the nucleus and cytoplasm ...
10-2 Cell Division lecture notes
... 2 phases of cell division: Mitosis is the division of the ___________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Cytokinesis: _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... 2 phases of cell division: Mitosis is the division of the ___________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Cytokinesis: _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm
... of the cleavage furrow a contractile ring of actin microfilaments and the motor protein myosin form. • Contraction of the ring pinches the cell in two. ...
... of the cleavage furrow a contractile ring of actin microfilaments and the motor protein myosin form. • Contraction of the ring pinches the cell in two. ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.













![mitosis[1] - MissChapman11](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012422988_1-3e4c21de847b14cac14c4860c4d1b932-300x300.png)