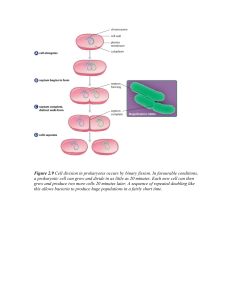
CELL DIVISION
... 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter cells 3. Cytokinesis: Cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell -Prior to cell division, must always have a duplication of genetic material DNA Replication Chromosome: Structure that contains genetic material passed from generation to genera ...
... 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter cells 3. Cytokinesis: Cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell -Prior to cell division, must always have a duplication of genetic material DNA Replication Chromosome: Structure that contains genetic material passed from generation to genera ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
AS Biology – Foundation Genetics questions
... Is it the chromosomes, the genes or the DNA that hold the instructions for making new cells? ...
... Is it the chromosomes, the genes or the DNA that hold the instructions for making new cells? ...
Mitosis - muhlsdk12.org
... Separation of chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated ...
... Separation of chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated ...
Ch. 6 Section 3 Directed Reading/Quiz
... a. Chromosomes move to the center of the cell and line up along the equator. b. A nuclear envelope forms around the chromatids at each pole. c. Chromosomes coil up and become visible. d. The two chromatids move toward opposite poles as the spindle fibers attached to them shorten. ...
... a. Chromosomes move to the center of the cell and line up along the equator. b. A nuclear envelope forms around the chromatids at each pole. c. Chromosomes coil up and become visible. d. The two chromatids move toward opposite poles as the spindle fibers attached to them shorten. ...
Cell Cycle Stages Worksheet
... Write the events in the correct steps of the cell cycle. Stage Events G1 Interphase ...
... Write the events in the correct steps of the cell cycle. Stage Events G1 Interphase ...
Cell Division Homework #2
... Label these structures in the drawings above: cell membrane, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, centrioles, microtubules, spindle, sister chromatids, cleavage furrow. Name the stage in which the following events occur. Interphase is included. ______________2. ...
... Label these structures in the drawings above: cell membrane, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, centrioles, microtubules, spindle, sister chromatids, cleavage furrow. Name the stage in which the following events occur. Interphase is included. ______________2. ...
Bio I - TCS Moodle 2
... dissipates, centrioles migrate to opposite sides of cell, spindle fiber network forms. 2.Metaphase: spindle fibers attach to chromosomes at kinetochores, chromosomes align on metaphase plate. 3. Anaphase: spindle fibers shorten, sister chromatids are pulled apart by contracting fibers, move to oppos ...
... dissipates, centrioles migrate to opposite sides of cell, spindle fiber network forms. 2.Metaphase: spindle fibers attach to chromosomes at kinetochores, chromosomes align on metaphase plate. 3. Anaphase: spindle fibers shorten, sister chromatids are pulled apart by contracting fibers, move to oppos ...
Cell division and mitosis
... Shortest phase of mitosis Centrioles are at poles Chromosomes line up in the middle along equator Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes on the centromere ...
... Shortest phase of mitosis Centrioles are at poles Chromosomes line up in the middle along equator Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes on the centromere ...
File
... 5. Imagine a cell that mutates and loses the function of its kinetochore proteins. What might this do to the cell and its descendents? 6. Can plants (such as African violets) complete cytokinesis by using a cleavage furrow? Explain. 7. Is mitosis the same thing as Cytokinesis? Explain. 8. Imagine an ...
... 5. Imagine a cell that mutates and loses the function of its kinetochore proteins. What might this do to the cell and its descendents? 6. Can plants (such as African violets) complete cytokinesis by using a cleavage furrow? Explain. 7. Is mitosis the same thing as Cytokinesis? Explain. 8. Imagine an ...
Mitosis Diagram
... During S the cell replicates its DNA...so it now has 2 complete sets of DNA. This allows the cell to divide into two daughter cells, each with a complete copy of DNA. During the G2 the cell again undergoes growth and protein synthesis, because it needs enough proteins for 2 cells. ...
... During S the cell replicates its DNA...so it now has 2 complete sets of DNA. This allows the cell to divide into two daughter cells, each with a complete copy of DNA. During the G2 the cell again undergoes growth and protein synthesis, because it needs enough proteins for 2 cells. ...
Topic 2: Cells - Peoria Public Schools
... 1. The cell cycle includes 4 phases: G1, S, G2, and M. 2. Interphase of the cell cycle includes G1, S, and G2. 3. Interphase is the phase in which the cell is carrying out its appointed activity or activities. Metabolic activities such as protein synthesis, DNA replication and organelle reproduction ...
... 1. The cell cycle includes 4 phases: G1, S, G2, and M. 2. Interphase of the cell cycle includes G1, S, and G2. 3. Interphase is the phase in which the cell is carrying out its appointed activity or activities. Metabolic activities such as protein synthesis, DNA replication and organelle reproduction ...
Cell Growth and Division
... grow and to repair damaged tissue • Cells grow, then divide. Why don’t they keep growing? • Large cells do not have enough DNA to function. • Large cells could not diffuse oxygen and nutrients efficiently. *Agar block lab* ...
... grow and to repair damaged tissue • Cells grow, then divide. Why don’t they keep growing? • Large cells do not have enough DNA to function. • Large cells could not diffuse oxygen and nutrients efficiently. *Agar block lab* ...
Mitosis Matching Worksheet
... _______ 6. Chromosome replication takes place. Because of this, each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” chromatids. _______ 7. The DNA starts to unwind in the nucleus. _______ 8. Periods of intense growth ‐ cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles. _______ 9. “In‐ ...
... _______ 6. Chromosome replication takes place. Because of this, each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” chromatids. _______ 7. The DNA starts to unwind in the nucleus. _______ 8. Periods of intense growth ‐ cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles. _______ 9. “In‐ ...
Slide 1
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
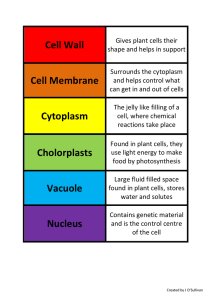
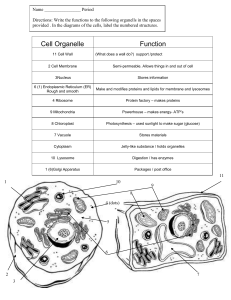
Cell Organelle
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
Quiz – Cytokinesis Part A: True/False Questions 1. Telophase is
... 2. Anaphase is followed by prophase in cell division. 3. Cytokinesis is essential for separation of daughter cell from each other. 4. Myosin II moves along the actin filament using the energy from hydrolysis ...
... 2. Anaphase is followed by prophase in cell division. 3. Cytokinesis is essential for separation of daughter cell from each other. 4. Myosin II moves along the actin filament using the energy from hydrolysis ...
Unit 2 Part1 wksht
... 1. According to the cell theory, all cells carry on ____________________________________________, come from __________________________________ and all organisms are made of _____________. ...
... 1. According to the cell theory, all cells carry on ____________________________________________, come from __________________________________ and all organisms are made of _____________. ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.