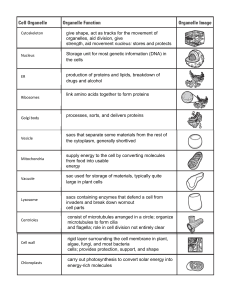
carry out photosynthesis to convert solar energy into energy
... link amino acids together to form proteins ...
... link amino acids together to form proteins ...
Notes for Cell Cycle
... the doubled chromosomes line up at the equator (middle) of the cell moved by the spindle fibers attached to their centromere. ...
... the doubled chromosomes line up at the equator (middle) of the cell moved by the spindle fibers attached to their centromere. ...
Vacuoles
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
Structures and Organelles
... Membrane system of folded sacs and channels Site for protein and lipid synthesis Rough ER- where ribosomes attach Smooth ER- where lipids are synthesized ...
... Membrane system of folded sacs and channels Site for protein and lipid synthesis Rough ER- where ribosomes attach Smooth ER- where lipids are synthesized ...
Mitosis ppt
... When cells begin to divide, the first thing that happens is that the chromatin in the nucleus begins to wind up, separating the strands from each other. ...
... When cells begin to divide, the first thing that happens is that the chromatin in the nucleus begins to wind up, separating the strands from each other. ...
Mitosis
... 3. Spindle apparatus is fully formed Spindle apparatus Centrioles Metaphase plate Centrioles ...
... 3. Spindle apparatus is fully formed Spindle apparatus Centrioles Metaphase plate Centrioles ...
Slide 1
... • The chromosomes are at each end of the cell and nuclear envelops form • The cell divides in two-Cytokinesis • THE END ...
... • The chromosomes are at each end of the cell and nuclear envelops form • The cell divides in two-Cytokinesis • THE END ...
Semester 1 extra practice worksheet-model answers
... Gap 2 (G2): the cell carries out its normal functions and grows further in size. A critical checkpoint must be passed; where DNA copying is checked for errors. The first three stages are collectively called the interphase. Mitosis: 4 STAGES a) Prophase: the chromosomes condense and become visi ...
... Gap 2 (G2): the cell carries out its normal functions and grows further in size. A critical checkpoint must be passed; where DNA copying is checked for errors. The first three stages are collectively called the interphase. Mitosis: 4 STAGES a) Prophase: the chromosomes condense and become visi ...
Cell Cycle Check
... 15. Bacteria are all clones of each other (no recombination). 16. If a skin cell does mitosis it produces clones of itself. 17. The major purpose of metaphase is to separate chromatids. 18. Humans have 92 strands of DNA in metaphase ...
... 15. Bacteria are all clones of each other (no recombination). 16. If a skin cell does mitosis it produces clones of itself. 17. The major purpose of metaphase is to separate chromatids. 18. Humans have 92 strands of DNA in metaphase ...
Curtis Science Dept. Biology Name: Period: Date: Chapter 10: Cell
... The first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus. ...
... The first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus. ...
1. Describe two functions of centromere during mitosis. 2. a) Look at
... iii) In each nucleus at the end of telophase? ...
... iii) In each nucleus at the end of telophase? ...
REG3.2.3.3c UNIDAD EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR ECOMUNDO
... REG3.2.3.3c UNIDAD EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR ECOMUNDO UNIT I II TERM EXAM SUBJECT: Language Arts Study Guide VERSIONS: 1,2, 3 GRADE: 1st Bacc. ...
... REG3.2.3.3c UNIDAD EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR ECOMUNDO UNIT I II TERM EXAM SUBJECT: Language Arts Study Guide VERSIONS: 1,2, 3 GRADE: 1st Bacc. ...
name
... 3. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus. When they are uncoiled and not visible they are called __________________________________________________. 4. After the chromosomes replicate and condense they become visible during Prophase. Label this diagram of a doubled chromosome: ...
... 3. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus. When they are uncoiled and not visible they are called __________________________________________________. 4. After the chromosomes replicate and condense they become visible during Prophase. Label this diagram of a doubled chromosome: ...
Biology Study guide
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
... Stage 1 (G1) – metabolic activity of the cell Synthesis Stage (S) – metabolic activity of the cell, replication of ...
... Stage 1 (G1) – metabolic activity of the cell Synthesis Stage (S) – metabolic activity of the cell, replication of ...
Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell
... NAME: ___________________________ Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell!!! (See chapter 7 in your book to answer these questions) 1. The size of a typical cell is _______________. 2. Who was the first person to observe “cells”? 3. The cell theory states: (3 parts) 4. What is the timeline for the hist ...
... NAME: ___________________________ Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell!!! (See chapter 7 in your book to answer these questions) 1. The size of a typical cell is _______________. 2. Who was the first person to observe “cells”? 3. The cell theory states: (3 parts) 4. What is the timeline for the hist ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.