Study Guide, Section 2
... Label the diagram of the stages of mitosis using lines 13–16. Use these choices: anaphase ...
... Label the diagram of the stages of mitosis using lines 13–16. Use these choices: anaphase ...
Mitosis - Wikispaces
... *MITOSIS* STANDARD HS-LS1-7: USE A MODEL TO ILLUSTRATE THE ROLE OF CELLULAR DIVISION (MITOSIS) AND DIFFERENTIATION IN PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING COMPLEX ORGANISMS. ...
... *MITOSIS* STANDARD HS-LS1-7: USE A MODEL TO ILLUSTRATE THE ROLE OF CELLULAR DIVISION (MITOSIS) AND DIFFERENTIATION IN PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING COMPLEX ORGANISMS. ...
Slide 1
... 2. Mitosis – Cell division 3. Cytokinesis – Splitting How long does it take? • Adult human cell: ~24 hrs • 18-20 hours in interphase • 2 hours in mitosis • Embryonic cells: 30 min. ...
... 2. Mitosis – Cell division 3. Cytokinesis – Splitting How long does it take? • Adult human cell: ~24 hrs • 18-20 hours in interphase • 2 hours in mitosis • Embryonic cells: 30 min. ...
How does the cell know how to divide?
... How does the cell know how to divide? The DNA has the instructions for all of the cell’s activities. ...
... How does the cell know how to divide? The DNA has the instructions for all of the cell’s activities. ...
Mitosis, Cell division and aging
... 3. Which stage or phase of the cell cycle corresponds to each of the descriptions below? a) A new cell wall begins to form. cytokinesis b) The membrane of the nucleus dissolves. prophase (starts to dissolve), metaphase (finished) c) Daughter chromosomes begin to separate. anaphase d) Thick chromosom ...
... 3. Which stage or phase of the cell cycle corresponds to each of the descriptions below? a) A new cell wall begins to form. cytokinesis b) The membrane of the nucleus dissolves. prophase (starts to dissolve), metaphase (finished) c) Daughter chromosomes begin to separate. anaphase d) Thick chromosom ...
Unit 3 Prezi 1
... What has to occur for a cell to divide? What purposes do these divisions serve? How do prokaryotic cells divide? Why does the DNA condense into chromosomes during cell division? Explain the relationship between chromosomes, chromatids and centromeres in a eukaryotic cell. Explain what happens during ...
... What has to occur for a cell to divide? What purposes do these divisions serve? How do prokaryotic cells divide? Why does the DNA condense into chromosomes during cell division? Explain the relationship between chromosomes, chromatids and centromeres in a eukaryotic cell. Explain what happens during ...
Cell Cycle/Cell Division
... up in the middle of the cell) • Highly organized so that both new cells will get exactly the same DNA • Spindle fibers completely attached to centromeres ...
... up in the middle of the cell) • Highly organized so that both new cells will get exactly the same DNA • Spindle fibers completely attached to centromeres ...
Cell Cycle part 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... beginning to disappear. Although not yet visible in the micrograph, the mitotic spindle is starting to form. ...
... beginning to disappear. Although not yet visible in the micrograph, the mitotic spindle is starting to form. ...
Mitosis Notes
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
chapter 12.rtf - HCC Learning Web
... 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) interphase C) telophase D) prophase E) metaphase 2) If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how m ...
... 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) interphase C) telophase D) prophase E) metaphase 2) If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how m ...
The Cell Cycle
... Is an asexual process (without intercourse single parent) Is a multistep process that allows the nucleus to divide creating two daughter cells Has the greatest amount of steps (four) of all the parts of the cell cycle Is a relatively short cycle Is carried out by all human cells (somatic ...
... Is an asexual process (without intercourse single parent) Is a multistep process that allows the nucleus to divide creating two daughter cells Has the greatest amount of steps (four) of all the parts of the cell cycle Is a relatively short cycle Is carried out by all human cells (somatic ...
Chapter 12 – The Cell Cycle – Homework
... 5. Imagine a cell that mutates and loses the function of its kinetochore proteins. What might this do to the cell and its descendents? ...
... 5. Imagine a cell that mutates and loses the function of its kinetochore proteins. What might this do to the cell and its descendents? ...
Onion Root Tip Lab
... Parts of the Onion Root • Region of Maturation- where root hairs develop and cells differentiate ...
... Parts of the Onion Root • Region of Maturation- where root hairs develop and cells differentiate ...
Exam 3 Questions for Monday Feb 4th
... image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IMAGE. You need only label a structure once. The starting cell will have a haploid number of 3 (this could change…be prepared for anything). (The following terms should be included ...
... image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IMAGE. You need only label a structure once. The starting cell will have a haploid number of 3 (this could change…be prepared for anything). (The following terms should be included ...
Exam III Sample Questions
... 5. The Basal Lamina is a specialized form of connective tissue underlying an epithelium. 6. Neural Crest Cells Escape from neural epithelium by downregulating N-cadherin expression 7. The assembly of cohesions and condensins onto sister chromatids is dependent upon M-CDK activity 8. Nucleotide hydro ...
... 5. The Basal Lamina is a specialized form of connective tissue underlying an epithelium. 6. Neural Crest Cells Escape from neural epithelium by downregulating N-cadherin expression 7. The assembly of cohesions and condensins onto sister chromatids is dependent upon M-CDK activity 8. Nucleotide hydro ...
HOMEWORK: REVIEW CELL LIFE CYCLE AND MITOSIS
... 4) Cell division starts with ___________ parent cell and finishes with ____________________________________________. ...
... 4) Cell division starts with ___________ parent cell and finishes with ____________________________________________. ...
Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
... ↑Spindle The spindle apparatus ensure that fiber each new Centrioles → cell receives 1 full copy of the genetic material ...
... ↑Spindle The spindle apparatus ensure that fiber each new Centrioles → cell receives 1 full copy of the genetic material ...
Check answers
... (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Chromatin condenses; Chromosomes first visible Nuclear envelope/Nucleoli disappear Centrosomes appear & move towards poles Mitotic spindle begins to form Microtubules attach to kinetochore proteins on centromeres METAPHASE (= MID ...
... (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Chromatin condenses; Chromosomes first visible Nuclear envelope/Nucleoli disappear Centrosomes appear & move towards poles Mitotic spindle begins to form Microtubules attach to kinetochore proteins on centromeres METAPHASE (= MID ...
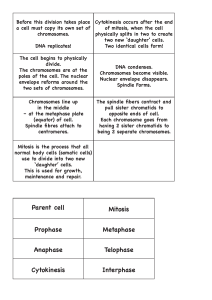
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.