Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
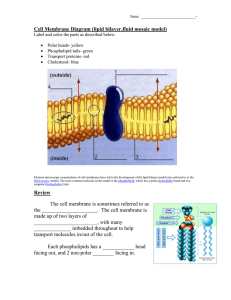
... ________________________, with many ______________ imbedded throughout to help transport molecules in/out of the cell. Each phospholipids has a ____________ head facing out, and 2 non-polar ________ facing in. ...
... ________________________, with many ______________ imbedded throughout to help transport molecules in/out of the cell. Each phospholipids has a ____________ head facing out, and 2 non-polar ________ facing in. ...
Section 10–2 Cell Division (pages 244–249)
... 10. What happens during the S phase? Chromosomes are replicated, and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place. Also, key proteins associated with the chromosomes are synthesized. ...
... 10. What happens during the S phase? Chromosomes are replicated, and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place. Also, key proteins associated with the chromosomes are synthesized. ...
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
... 1. As a cell’s size increases, its amount of DNA also increases. 2. The amount of activity in a cell is related to its volume. 3. The smaller the cell, the smaller its ratio of surface area to volume. 4. The information crisis in a cell is solved by the replication of the DNA before cell division. 5 ...
... 1. As a cell’s size increases, its amount of DNA also increases. 2. The amount of activity in a cell is related to its volume. 3. The smaller the cell, the smaller its ratio of surface area to volume. 4. The information crisis in a cell is solved by the replication of the DNA before cell division. 5 ...
The Cell Cycle2
... In animal cells, the cytoplasm pinches in around the middle of the cell. Eventually the cell divides in two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms across the middle of the cell. The cell plates develop into a new cell membrane. The cell wall forms around the cell membrane. ...
... In animal cells, the cytoplasm pinches in around the middle of the cell. Eventually the cell divides in two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms across the middle of the cell. The cell plates develop into a new cell membrane. The cell wall forms around the cell membrane. ...
Organelle Notes
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
CELL PARTS MATCHING - SD43 Teacher Sites
... THE CELL'S POWERHOUSE, STORES ENERGY IN ATP MOLECULES ...
... THE CELL'S POWERHOUSE, STORES ENERGY IN ATP MOLECULES ...
Name School Class Date Laboratory Investigation on Cells Observing Plant Cells
... piece of the outer cell layer. The layer that you peel off is as thin as a piece of cling film. Place this onto a ...
... piece of the outer cell layer. The layer that you peel off is as thin as a piece of cling film. Place this onto a ...
3-2 Reading Study Questions
... The cell _________ is the normal sequence of development and division of a cell The cell cycle consists of two main ____________. The cell carries out its normal activities during a phase called __________. ____________ is the phase when a eukaryotic cell divides. ____________ is the part of the cel ...
... The cell _________ is the normal sequence of development and division of a cell The cell cycle consists of two main ____________. The cell carries out its normal activities during a phase called __________. ____________ is the phase when a eukaryotic cell divides. ____________ is the part of the cel ...
Cells
... membrane enclosed organelle chromosomes in pairs streaming in the cytoplasm cell division by mitosis complex flagella larger ribosomes complex cytoskeleton cellulose in cell walls DNA bound to histone proteins ...
... membrane enclosed organelle chromosomes in pairs streaming in the cytoplasm cell division by mitosis complex flagella larger ribosomes complex cytoskeleton cellulose in cell walls DNA bound to histone proteins ...
Name: Period: _____ Cell Division Homework 1.) Explain
... 14.) _____ During metaphase nuclear membranes begin to form in the cell. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 15.) _____ During prophase the chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles. ________________________________________________________ ...
... 14.) _____ During metaphase nuclear membranes begin to form in the cell. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 15.) _____ During prophase the chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles. ________________________________________________________ ...
Please
... Stages of Mitosis Telophase - in this final stage, spindle fibers disappear and a nuclear membrane forms around each separated set of chromosomes -cell is ready to divide Cytokinesis -is the separation of the nuclei into two daughter cells -animal cells- cell pinches together and divides -plant cel ...
... Stages of Mitosis Telophase - in this final stage, spindle fibers disappear and a nuclear membrane forms around each separated set of chromosomes -cell is ready to divide Cytokinesis -is the separation of the nuclei into two daughter cells -animal cells- cell pinches together and divides -plant cel ...
Cell Organelle Organelle Function City Part Cell Membrane
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
S3O1 Curr Map
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
Cell Reproduction
... In addition, the _____________ break down, the _________ nucleolus spinder fibers ______ envelope reappears, a new nuclear __________ membrane begins forms, and a new double __________ to form between the two nuclei. ...
... In addition, the _____________ break down, the _________ nucleolus spinder fibers ______ envelope reappears, a new nuclear __________ membrane begins forms, and a new double __________ to form between the two nuclei. ...
Mitosis - TeacherWeb
... •Chromosomes come together and form thick thread like structures •Centrioles separate (in animal cells only) •Spindle fibers grow from the centrioles ...
... •Chromosomes come together and form thick thread like structures •Centrioles separate (in animal cells only) •Spindle fibers grow from the centrioles ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.























