Lecture 026--Cell Division
... Separation of Chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated separate to become individual chromosomes cohesin and separase and securin ...
... Separation of Chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated separate to become individual chromosomes cohesin and separase and securin ...
Mitosis Lab Activity: 1. Diagram a cell in interphase, prophase
... 1. Diagram a cell in interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase concurrent with cytokinesis. ...
... 1. Diagram a cell in interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase concurrent with cytokinesis. ...
mitosis veg prop - Hicksville Public Schools
... The body cells of all organisms have a special way of dividing. The dividing of a cell to form two new cells that are exactly alike is called mitosis. The dividing cell is called the parent cell, & the 2 new cells are called the daughter cells. Before the parent cell divides it makes a copy of its n ...
... The body cells of all organisms have a special way of dividing. The dividing of a cell to form two new cells that are exactly alike is called mitosis. The dividing cell is called the parent cell, & the 2 new cells are called the daughter cells. Before the parent cell divides it makes a copy of its n ...
cell structure review sheet
... Distinguish between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. Distinguish between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism State the three parts of the Cell theory. List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able t ...
... Distinguish between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. Distinguish between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism State the three parts of the Cell theory. List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able t ...
MITOSIS
... • Genes copy themselves by the process known as replication. Chromosomes consist of two identical strands once replication is completed. Each of these strands is called a chromatid. During mitosis the chromatids will separate and each chromatid will become a separate chromosome. ...
... • Genes copy themselves by the process known as replication. Chromosomes consist of two identical strands once replication is completed. Each of these strands is called a chromatid. During mitosis the chromatids will separate and each chromatid will become a separate chromosome. ...
Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of cellulose
... Consists of flattened membranous sacs; receives transport vesicles from the ER, modifies ER produces, produces secretory vesicles ...
... Consists of flattened membranous sacs; receives transport vesicles from the ER, modifies ER produces, produces secretory vesicles ...
Cell Study Guide - Miss Gleason`s Science
... What pathway do proteins take through the cell (protein trafficking) ...
... What pathway do proteins take through the cell (protein trafficking) ...
Name - St. Rose of Lima School
... What are the characteristics classifying a prokaryotic cell? Provides an example _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... What are the characteristics classifying a prokaryotic cell? Provides an example _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
9.1 All cells come from cells.
... and protein molecules 2. Chromosomes-when a cell divides, its chromatin fibers condense, becoming visible as they compact Human Body = Has how many chromosomes? Each chromosome may contain hundreds of genes ...
... and protein molecules 2. Chromosomes-when a cell divides, its chromatin fibers condense, becoming visible as they compact Human Body = Has how many chromosomes? Each chromosome may contain hundreds of genes ...
Notes Chapter 3
... 5. CENTROSOME (central body) - Usually near the G.A. and nucleus. Composed of 2 “cylinders” called CENTRIOLES (each composed of numerous microtubules), which always lie perpendicular to each other. Active involved in cell reproduction – SPINDLE forms from the centrioles 6. VESICLES – tiny sacs in wh ...
... 5. CENTROSOME (central body) - Usually near the G.A. and nucleus. Composed of 2 “cylinders” called CENTRIOLES (each composed of numerous microtubules), which always lie perpendicular to each other. Active involved in cell reproduction – SPINDLE forms from the centrioles 6. VESICLES – tiny sacs in wh ...
Chromosomes
... Stages of Mitosis Interphase • Most of the cell’s life cycle is spent in this phase. • Cell increases in size just before the next phase begins. - ...
... Stages of Mitosis Interphase • Most of the cell’s life cycle is spent in this phase. • Cell increases in size just before the next phase begins. - ...
The Cell Cycle
... The Cell Cycle • Consists of G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis ...
... The Cell Cycle • Consists of G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis ...
Notes: Chapter 11
... b. Chromosomes lie on the metaphase plate – an imaginary plane between the spindle’s two poles. c. Each chromatid’s kinetochore is attached to microtubules d. Entire apparatus of microtubules= spindle 4. Anaphase a. Paired centromeres of each chromosome separate b. New chromosomes begin to move to o ...
... b. Chromosomes lie on the metaphase plate – an imaginary plane between the spindle’s two poles. c. Each chromatid’s kinetochore is attached to microtubules d. Entire apparatus of microtubules= spindle 4. Anaphase a. Paired centromeres of each chromosome separate b. New chromosomes begin to move to o ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound compounds that contain
... part of mitosis where the centromeres split and the two chromatids separate; one chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell while the other chromatid moves to the opposite end part of mitosis where chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rod like appearance; a new nuclear ...
... part of mitosis where the centromeres split and the two chromatids separate; one chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell while the other chromatid moves to the opposite end part of mitosis where chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rod like appearance; a new nuclear ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound
... part of mitosis where the centromeres split and the two chromatids separate; one chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell while the other chromatid moves to the opposite end part of mitosis where chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rod like appearance; a new nuclear ...
... part of mitosis where the centromeres split and the two chromatids separate; one chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell while the other chromatid moves to the opposite end part of mitosis where chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rod like appearance; a new nuclear ...
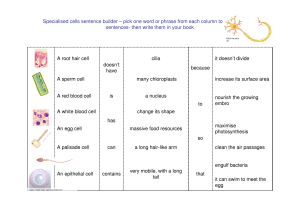
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
Unit_biology_2_Cells
... Cells and simple cell transport Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: a) Most human and animal cells have the following parts: ■ a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell ■ cytoplasm, in which most of the chemical reactions take place ■ a ce ...
... Cells and simple cell transport Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: a) Most human and animal cells have the following parts: ■ a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell ■ cytoplasm, in which most of the chemical reactions take place ■ a ce ...
Cell Organelle Packet
... 1. Which organelles are enclosed by a double bound membrane? 2. What are the three parts of the cell theory? Who(m) is credited with the theory? 3. Compare prokaryotic to eukaryotic cells in terms of organelles in common and difference. 4. Explain the endomembrane system. 5. What challenges face a c ...
... 1. Which organelles are enclosed by a double bound membrane? 2. What are the three parts of the cell theory? Who(m) is credited with the theory? 3. Compare prokaryotic to eukaryotic cells in terms of organelles in common and difference. 4. Explain the endomembrane system. 5. What challenges face a c ...
topic 5 -part 3 guided notes -plant vs animal cells - student
... TOPIC 5: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PART 3: PLANT VS. ANIMAL CELLS Plants and animals differ in their cell makeup. Structures Common to Both Plant and Animal Cells 1. cell membrane 2. nucleus 3. nuclear envelope 4. DNA 5. nucleolus 6. ribosomes ...
... TOPIC 5: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PART 3: PLANT VS. ANIMAL CELLS Plants and animals differ in their cell makeup. Structures Common to Both Plant and Animal Cells 1. cell membrane 2. nucleus 3. nuclear envelope 4. DNA 5. nucleolus 6. ribosomes ...
Cell Organelles
... Smooth ER has different functions for different cells. Storage of enzymes, and the production and storage of ...
... Smooth ER has different functions for different cells. Storage of enzymes, and the production and storage of ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.