Cell Structure and Function Guided Notes
... a. He reasoned that all cells come from other pre-existing cells by __________________________________________. 6. The cell theory states: a. All living things are ____________________________________________________. b. Cells are the basic unit of ___________________________________________________ ...
... a. He reasoned that all cells come from other pre-existing cells by __________________________________________. 6. The cell theory states: a. All living things are ____________________________________________________. b. Cells are the basic unit of ___________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 7_The Cell
... Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes (membrane-bound organelles). The nucleus is a distinct central organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA). Organelles are specialized structures that carry out specific cell functions. They enable cell functions ...
... Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes (membrane-bound organelles). The nucleus is a distinct central organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA). Organelles are specialized structures that carry out specific cell functions. They enable cell functions ...
Cell membranes MOVE!
... • II. Sizes and shapes • A. Size – varies from microscopic to small • B. Shape – many varieties ...
... • II. Sizes and shapes • A. Size – varies from microscopic to small • B. Shape – many varieties ...
topic-4.doc
... Nuclear area (nucleoid): contains bacterial chromosome o circular (most), double-stranded DNA which is attached to the plasma membrane o in replicating cell can be as much as 20% of cell volume o segregates during division Ribosomes: sites of protein synthesis o composed of protein and rRNA o thousa ...
... Nuclear area (nucleoid): contains bacterial chromosome o circular (most), double-stranded DNA which is attached to the plasma membrane o in replicating cell can be as much as 20% of cell volume o segregates during division Ribosomes: sites of protein synthesis o composed of protein and rRNA o thousa ...
Ch. 2-2: The Organelles of the Cell ER, Golgi Complex, Lysosomes
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ________________ 5. RIbosomes do not h ...
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ________________ 5. RIbosomes do not h ...
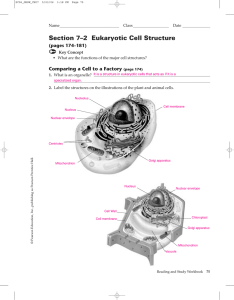
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... A flowchart can help you remember the order in which events occur. On a separate sheet of paper, create a flowchart that describes how proteins are made in the cell. You will find that the steps of this process are explained on pages 176–178. For more information about flowcharts, see Organizing Inf ...
... A flowchart can help you remember the order in which events occur. On a separate sheet of paper, create a flowchart that describes how proteins are made in the cell. You will find that the steps of this process are explained on pages 176–178. For more information about flowcharts, see Organizing Inf ...
Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for
... Cell membranes present a unique interface that governs numerous biological events in physiology as well as in disease pathogenesis; exploiting this interface for therapeutic development promises novel treatment modalities with biomimetic functionalities. Herein I report a nanoparticle functionalizat ...
... Cell membranes present a unique interface that governs numerous biological events in physiology as well as in disease pathogenesis; exploiting this interface for therapeutic development promises novel treatment modalities with biomimetic functionalities. Herein I report a nanoparticle functionalizat ...
Wellness and Illness
... Cells that do replicate (mitosis) accumulate different damage • DNA damaged every S phase (mostly deletions) • After several hundred rounds of mitosis these cells may function abnormally due to accumulation of mutations – digestive – respiratory – integumentary ...
... Cells that do replicate (mitosis) accumulate different damage • DNA damaged every S phase (mostly deletions) • After several hundred rounds of mitosis these cells may function abnormally due to accumulation of mutations – digestive – respiratory – integumentary ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... of telomerase, an enzyme that repairs the ends of chromosomes Cancer cells show metastasis, an invasion of other tissues ...
... of telomerase, an enzyme that repairs the ends of chromosomes Cancer cells show metastasis, an invasion of other tissues ...
Cellular Reproduction
... Recall that all cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. All substances moving into or out of the cell must cross the plasma membrane. The surface area of the cell is the area covered by the plasma membrane. The volume of a cell is the space taken by the inner contents. Because cells are small, th ...
... Recall that all cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. All substances moving into or out of the cell must cross the plasma membrane. The surface area of the cell is the area covered by the plasma membrane. The volume of a cell is the space taken by the inner contents. Because cells are small, th ...
Your Name Date
... Biology Word Study – Chapter 3 – Cell Structure and Function Directions: Study the following words by reading and rereading them each evening so you will be prepared for the word study test each week. You may use one 4” x 6” index card to write as many words and definitions on as possible for the te ...
... Biology Word Study – Chapter 3 – Cell Structure and Function Directions: Study the following words by reading and rereading them each evening so you will be prepared for the word study test each week. You may use one 4” x 6” index card to write as many words and definitions on as possible for the te ...
What`s on the Test - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Describe paradigm shifts that occurred during the development of the Cell Theory. Describe conflicts that took place during the development of the Cell Theory. Match the names of the main contributors to the Cell Theory with a description of what they did. ...
... Describe paradigm shifts that occurred during the development of the Cell Theory. Describe conflicts that took place during the development of the Cell Theory. Match the names of the main contributors to the Cell Theory with a description of what they did. ...
video slide
... (b) Dinoflagellates. In unicellular protists called dinoflagellates, the nuclear envelope remains intact during cell division, and the chromosomes attach to the nuclear envelope. Microtubules pass through the nucleus inside cytoplasmic tunnels, reinforcing the spatial orientation of the nucleus, whi ...
... (b) Dinoflagellates. In unicellular protists called dinoflagellates, the nuclear envelope remains intact during cell division, and the chromosomes attach to the nuclear envelope. Microtubules pass through the nucleus inside cytoplasmic tunnels, reinforcing the spatial orientation of the nucleus, whi ...
Cells in Anatomy
... are not all the same All cells share general structures All cells have three main regions Nucleus Cytosol (cytoplasm) Plasma membrane ...
... are not all the same All cells share general structures All cells have three main regions Nucleus Cytosol (cytoplasm) Plasma membrane ...
CELL MEMBRANE: Structure and Function
... an area of higher to lower concentration… or the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. ...
... an area of higher to lower concentration… or the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. ...
Diffusion and Osmosis
... Diffusion • Definition: movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration • What is concentration? • Concentration is an amount. • Example: What does it mean if a pool has a high concentration of chlorine? ...
... Diffusion • Definition: movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration • What is concentration? • Concentration is an amount. • Example: What does it mean if a pool has a high concentration of chlorine? ...
M001 Signalling to the translation initiation machinery Nahum
... Mnk-1, which is activated by both Erk and p38 MAPK. eIF4E activity is also controlled by phosphorylation of 4E-BPs (eIF4Ebinding proteins). 4E-BPs repress cap-dependent translation by binding to eIF4E. Upon their phosphorylation, 4E-BPs dissociate from eIF4E. The signalling pathway that leads to pho ...
... Mnk-1, which is activated by both Erk and p38 MAPK. eIF4E activity is also controlled by phosphorylation of 4E-BPs (eIF4Ebinding proteins). 4E-BPs repress cap-dependent translation by binding to eIF4E. Upon their phosphorylation, 4E-BPs dissociate from eIF4E. The signalling pathway that leads to pho ...
THE CELL
... Organelles that contain digestive enzymes which break down large particles for removal from the cell ...
... Organelles that contain digestive enzymes which break down large particles for removal from the cell ...
The Cell Theory - CGW-Life-Science
... How Has The Cell Theory Been Used? The basic discovered truths about cells, listed in the Cell Theory, are the basis for things such as: Disease/Health/Medical Research and Cures(AIDS, Cancer, Vaccines, Cloning, Stem Cell ...
... How Has The Cell Theory Been Used? The basic discovered truths about cells, listed in the Cell Theory, are the basis for things such as: Disease/Health/Medical Research and Cures(AIDS, Cancer, Vaccines, Cloning, Stem Cell ...
Chapter 4
... 2 kinds of microbodies: Peroxisomes - have enzymes which transfer H from various substrates to O (produce H2O2 as a byproduct) Glyoxysomes - contain enzymes to convert fats to sugar (in plants) ...
... 2 kinds of microbodies: Peroxisomes - have enzymes which transfer H from various substrates to O (produce H2O2 as a byproduct) Glyoxysomes - contain enzymes to convert fats to sugar (in plants) ...
Tenocyte alignment is dependant upon cell density and tensional
... prior to loading. These flasks were placed on our custom made motorised tensional loading jig within our culture incubator. While one end is fixed in a static clamp, the flasks are subjected to cyclic unidirectional loading by the motor. Loading strains of approximately 3% and 6% at 1 Hz cyclical lo ...
... prior to loading. These flasks were placed on our custom made motorised tensional loading jig within our culture incubator. While one end is fixed in a static clamp, the flasks are subjected to cyclic unidirectional loading by the motor. Loading strains of approximately 3% and 6% at 1 Hz cyclical lo ...
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division
... Budding- a small projection grows on the surface of the parent organism, forming a separate new individual. Fragmentation- a parent organism splits into pieces, each of which can grow into a new organism. ...
... Budding- a small projection grows on the surface of the parent organism, forming a separate new individual. Fragmentation- a parent organism splits into pieces, each of which can grow into a new organism. ...
PDF
... vivo. E. Jane Albert Hubbard, Hillel Kugler and colleagues now use available data to build a computational model of germline development in C. elegans (see p. 47). In this model, germline cells move, divide, respond to signals, progress through mitosis and meiosis, and differentiate according to var ...
... vivo. E. Jane Albert Hubbard, Hillel Kugler and colleagues now use available data to build a computational model of germline development in C. elegans (see p. 47). In this model, germline cells move, divide, respond to signals, progress through mitosis and meiosis, and differentiate according to var ...
PDF
... vivo. E. Jane Albert Hubbard, Hillel Kugler and colleagues now use available data to build a computational model of germline development in C. elegans (see p. 47). In this model, germline cells move, divide, respond to signals, progress through mitosis and meiosis, and differentiate according to var ...
... vivo. E. Jane Albert Hubbard, Hillel Kugler and colleagues now use available data to build a computational model of germline development in C. elegans (see p. 47). In this model, germline cells move, divide, respond to signals, progress through mitosis and meiosis, and differentiate according to var ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.