Mitosis
... Observe your preparation under the low power (X10) of a microscope Search the slide to find cells in various stages of cell division, once you have located cells in division, change to high power (X40) & try to observe several stages of division. Record the number of cells in each stage. Count at le ...
... Observe your preparation under the low power (X10) of a microscope Search the slide to find cells in various stages of cell division, once you have located cells in division, change to high power (X40) & try to observe several stages of division. Record the number of cells in each stage. Count at le ...
Cells Test What do I need to know???? Know the parts of a plant
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
Lecture 2: Cellular signalling and cell division
... Cell division: The fundamental principle of life Interphase: cells look normal and just grow insize as observed under microscope. But many molecular events take place in this phase and this phase further subdivided into following subdivisions: G1 phase: Starts after completion of mitosis and ends b ...
... Cell division: The fundamental principle of life Interphase: cells look normal and just grow insize as observed under microscope. But many molecular events take place in this phase and this phase further subdivided into following subdivisions: G1 phase: Starts after completion of mitosis and ends b ...
Cell Organelle Notes worksheet
... One of a set of structures found in the nucleus; made of DNA, plus some protein ...
... One of a set of structures found in the nucleus; made of DNA, plus some protein ...
Mitosis Essay - msvictorialin
... Mitosis Essay Prepare to write an in class essay about the following topic: Describe the process of cell division in somatic cells. Include a description of what happens in each phase of mitosis. ...
... Mitosis Essay Prepare to write an in class essay about the following topic: Describe the process of cell division in somatic cells. Include a description of what happens in each phase of mitosis. ...
Mitotic Cell Division Lab
... show the stages of mitotic cell division for BOTH plants and animals arranged in correct order. Stage and phase labels are provided. Lab sheets should have the names of all lab partners listed as well as the class period. Each student is responsible for turning in the completed follow-up questions. ...
... show the stages of mitotic cell division for BOTH plants and animals arranged in correct order. Stage and phase labels are provided. Lab sheets should have the names of all lab partners listed as well as the class period. Each student is responsible for turning in the completed follow-up questions. ...
Unit: Genetics Lesson: Cell Cycle
... cycle – Interphase, Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Interphase encompasses the phases of G1 (Growth 1), S (DNA Synthesis) and G2 (Growth 2) phase. Mitosis encompasses the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis (cytoplasm divides) Let’s see what this look like! ...
... cycle – Interphase, Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Interphase encompasses the phases of G1 (Growth 1), S (DNA Synthesis) and G2 (Growth 2) phase. Mitosis encompasses the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis (cytoplasm divides) Let’s see what this look like! ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
... 1. Normal cells contain check points to regulate the cell cycle, & stop at appropriate check points. 2. Cancerous cells do not respond to check points and continue rapidly through the cell cycle. This results in masses of undefined cells called tumors. 3. Cancer cells do not mature; they become more ...
... 1. Normal cells contain check points to regulate the cell cycle, & stop at appropriate check points. 2. Cancerous cells do not respond to check points and continue rapidly through the cell cycle. This results in masses of undefined cells called tumors. 3. Cancer cells do not mature; they become more ...
Unit: Genetics Lesson: Cell Cycle
... cycle – Interphase, Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Interphase encompasses the phases of G1 (Growth 1), S (DNA Synthesis) and G2 (Growth 2) phase. Mitosis encompasses the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis (cytoplasm divides) Let’s see what this look like! ...
... cycle – Interphase, Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Interphase encompasses the phases of G1 (Growth 1), S (DNA Synthesis) and G2 (Growth 2) phase. Mitosis encompasses the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis (cytoplasm divides) Let’s see what this look like! ...
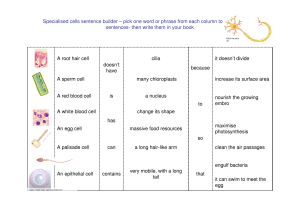
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
Exam 3 Questions for Monday Feb 4th
... image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IMAGE. You need only label a structure once. The starting cell will have a haploid number of 3 (this could change…be prepared for anything). (The following terms should be included ...
... image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IMAGE. You need only label a structure once. The starting cell will have a haploid number of 3 (this could change…be prepared for anything). (The following terms should be included ...
MITOSIS (2n = _____)
... All the cells of the body (except the sex cells) are produced by mitotic division. Mitosis involves a complex series of changes in the nuclei of the body cells (also called somatic cells) that produce daughter cells with exactly the same number and type of chromosomes as the original parent cell ...
... All the cells of the body (except the sex cells) are produced by mitotic division. Mitosis involves a complex series of changes in the nuclei of the body cells (also called somatic cells) that produce daughter cells with exactly the same number and type of chromosomes as the original parent cell ...
The Cell Cycle
... 1. Interphase – Cell grows and develops until it reaches maximum capacity. Chromosomes replicate so that each consists of two identical strands known as chromatids. The strands are joined together by a centromere. 2. Mitosis – a process of four phases in which the nucleus of eukaryotic cell divides ...
... 1. Interphase – Cell grows and develops until it reaches maximum capacity. Chromosomes replicate so that each consists of two identical strands known as chromatids. The strands are joined together by a centromere. 2. Mitosis – a process of four phases in which the nucleus of eukaryotic cell divides ...
File
... 38. it wraps around proteins to become more compact 39. to code for traits; direct cell activities 40. what connects the middle part of a duplicated chromosome 41. 46 (23 pairs) 42. in Body cells = 2n = double number 43. in sex cells = n = number of chromosomes in sperm or eggs 44. your body cells h ...
... 38. it wraps around proteins to become more compact 39. to code for traits; direct cell activities 40. what connects the middle part of a duplicated chromosome 41. 46 (23 pairs) 42. in Body cells = 2n = double number 43. in sex cells = n = number of chromosomes in sperm or eggs 44. your body cells h ...
Cell Division
... – Interphase: G1, S, G2 – Mitosis – genetic material of cell divides – Cytokineses – cell membrane/ wall divides ...
... – Interphase: G1, S, G2 – Mitosis – genetic material of cell divides – Cytokineses – cell membrane/ wall divides ...
chromosome
... Mitosis (cell begins to divide)DNA tightens into chromosomes, nuclear membrane breaks down and disappears • Centrosomes-dark spots that appear next to the nucleus and begin to move to opposite end of the cell-if an animal-then has a pair of centrioles • Spindle fibers made of microtubules, form bet ...
... Mitosis (cell begins to divide)DNA tightens into chromosomes, nuclear membrane breaks down and disappears • Centrosomes-dark spots that appear next to the nucleus and begin to move to opposite end of the cell-if an animal-then has a pair of centrioles • Spindle fibers made of microtubules, form bet ...
The Cell Cycle
... Interphase extends from the end of one mitosis to the beginning of the next mitosis After interphase, mitosis proceeds in five stages Cytokinesis completes cell division by dividing the cytoplasm between daughter cells ...
... Interphase extends from the end of one mitosis to the beginning of the next mitosis After interphase, mitosis proceeds in five stages Cytokinesis completes cell division by dividing the cytoplasm between daughter cells ...
cell cycle and mitosis powerpoint 2015
... • Chromatin fibers condense • Nuclear membrane breaks down • Spindle of microtubules forms from centrioles [animals only] • Attach to chromatids on centromere ...
... • Chromatin fibers condense • Nuclear membrane breaks down • Spindle of microtubules forms from centrioles [animals only] • Attach to chromatids on centromere ...
Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.