Observing the Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tips
... In this lab, you will examine the dividing root-tip cells of an onion. You will examine the specimen to identify the various phases of the cell cycle, to see which phases cells spend more time in, and you will answer related analysis questions to further your understanding of the eukaryotic cell cyc ...
... In this lab, you will examine the dividing root-tip cells of an onion. You will examine the specimen to identify the various phases of the cell cycle, to see which phases cells spend more time in, and you will answer related analysis questions to further your understanding of the eukaryotic cell cyc ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... themselves. • Actively dividing cells go through a cycle: a repeating sequence of cellular growth and division. ...
... themselves. • Actively dividing cells go through a cycle: a repeating sequence of cellular growth and division. ...
In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation
... Time when a cell’s metabolic activity is very high and the cell performs various functions ...
... Time when a cell’s metabolic activity is very high and the cell performs various functions ...
Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell Wall Ribosome Reticulum
... dark, round, no membrane, can be attached to the E.R. ...
... dark, round, no membrane, can be attached to the E.R. ...
AQA B2 ESQ - Mitosis and Meiosis 1
... What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? ...
... What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? ...
Bio392-Chapter 10-2 - Cell Division- this one!!
... (1) Double-stranded DNA. (2) Chromatin strand (DNA with histones). (3) Chromatin during interphase with centromere. (4) Condensed chromatin during prophase. (Two copies of the DNA molecule are now present) (5) Chromosome chromosome during metaphase. chromatin ...
... (1) Double-stranded DNA. (2) Chromatin strand (DNA with histones). (3) Chromatin during interphase with centromere. (4) Condensed chromatin during prophase. (Two copies of the DNA molecule are now present) (5) Chromosome chromosome during metaphase. chromatin ...
Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7 “I can…” state discuss
... cell and the cell theory. identify similarities and differences between cells and viruses. construct a graphic organizer comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. identify the cell organelles and state their functions. construct a cell model (i.e., form and function model, cell ana ...
... cell and the cell theory. identify similarities and differences between cells and viruses. construct a graphic organizer comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. identify the cell organelles and state their functions. construct a cell model (i.e., form and function model, cell ana ...
Chapter 10
... • Gather and synthesize nutrients – ex. Make the 6 billion nucleotides needed to replicate the DNA. Acquire/synthesize enough amino acids to build all the required proteins to divide the cell, etc… Cells can hang in this subphase for a very long time like certain muscle cells or forever like cardiac ...
... • Gather and synthesize nutrients – ex. Make the 6 billion nucleotides needed to replicate the DNA. Acquire/synthesize enough amino acids to build all the required proteins to divide the cell, etc… Cells can hang in this subphase for a very long time like certain muscle cells or forever like cardiac ...
Document
... centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. D. Telophase: the fourth stage of mitosis. * During ________________, two distinct daughter cells are formed. The cells ...
... centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. D. Telophase: the fourth stage of mitosis. * During ________________, two distinct daughter cells are formed. The cells ...
Cell Division Assignment
... 2. From this page, navigate to the treatment section. Find the following information on one of the following cancer treatments: chemotherapy or radiation therapy. (8pts) *Tip : Use the ‘Related Information’ menu on the left side of the page to help guide you to the appropriate information. a. Descri ...
... 2. From this page, navigate to the treatment section. Find the following information on one of the following cancer treatments: chemotherapy or radiation therapy. (8pts) *Tip : Use the ‘Related Information’ menu on the left side of the page to help guide you to the appropriate information. a. Descri ...
Name - St. Rose of Lima School
... What are the characteristics classifying a prokaryotic cell? Provides an example _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... What are the characteristics classifying a prokaryotic cell? Provides an example _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... What are the phases of the Cell Cycle and briefly explain what occurs during each phase (start with interphase and end with cytokinesis)? Interphase: the cell grows and carries out its usual functions, DNA replicates Prophase: DNA of replicated chromosomes twists into coils; membrane around nucleus ...
... What are the phases of the Cell Cycle and briefly explain what occurs during each phase (start with interphase and end with cytokinesis)? Interphase: the cell grows and carries out its usual functions, DNA replicates Prophase: DNA of replicated chromosomes twists into coils; membrane around nucleus ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... What are the phases of the Cell Cycle and briefly explain what occurs during each phase (start with interphase and end with cytokinesis)? Interphase: the cell grows and carries out its usual functions, DNA replicates Prophase: DNA of replicated chromosomes twists into coils; membrane around nucleus ...
... What are the phases of the Cell Cycle and briefly explain what occurs during each phase (start with interphase and end with cytokinesis)? Interphase: the cell grows and carries out its usual functions, DNA replicates Prophase: DNA of replicated chromosomes twists into coils; membrane around nucleus ...
ADVANCED BIOLOGY Exam III (Chapter 3: Cell Structure and
... cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6 ...
... cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6 ...
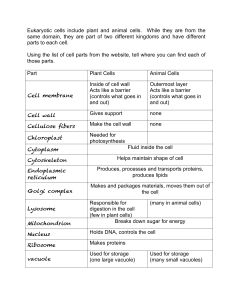
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
Important organells in a Cell 2
... Unicellular organisms: Made of only one cell. Multicellular: Made up of more than one cell eg Humans. ...
... Unicellular organisms: Made of only one cell. Multicellular: Made up of more than one cell eg Humans. ...
Bell Work Question - Firelands Elementary School
... The centrioles move to opposite side of the cell and stretch out spindle fibers. Spindle fibers organize the chromosomes. Chromosomses (DNA) line up along the center of the animal cell. ...
... The centrioles move to opposite side of the cell and stretch out spindle fibers. Spindle fibers organize the chromosomes. Chromosomses (DNA) line up along the center of the animal cell. ...
Cell Content Statement 1 Study Guide
... (Use “The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life” Packet) Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuoles Nucleus Chromosomes Chloroplasts Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Mitochondria ...
... (Use “The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life” Packet) Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuoles Nucleus Chromosomes Chloroplasts Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Mitochondria ...
Haploid cells - Belle Vernon Area School District
... They are made to repair, replace and growth Asexual reproduction---offsprings are EXACTLY the same as parent. ...
... They are made to repair, replace and growth Asexual reproduction---offsprings are EXACTLY the same as parent. ...
INVESTIGATIVE SCIENCE
... 3. Describe the difference between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis. Use the terms “chromosomes” and “chromatids” in your explanation. ...
... 3. Describe the difference between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis. Use the terms “chromosomes” and “chromatids” in your explanation. ...
eprint_12_11727_866
... cytoplasm and then segregated so that each daughter cell receives a copy of the original DNA (if you start with 46 in the parent cell, you should end up with 46 chromosomes in each daughter cell). To do this cells utilize microtubules (referred to as the spindle apparatus) to "pull" chromosomes into ...
... cytoplasm and then segregated so that each daughter cell receives a copy of the original DNA (if you start with 46 in the parent cell, you should end up with 46 chromosomes in each daughter cell). To do this cells utilize microtubules (referred to as the spindle apparatus) to "pull" chromosomes into ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.