Ecology - An Introduction Ecology comes from Greek root words
... orbit around the sun. At any given place on earth (latitude) the angle at which sunlight strikes the surface changes with the season. Our map latitude is ~42° N. That’s also ‘solar latitude’ at the equinoxes. But on June 21 our ‘solar latitude’ is ~19° and on December 21 it’s ~65°. ...
... orbit around the sun. At any given place on earth (latitude) the angle at which sunlight strikes the surface changes with the season. Our map latitude is ~42° N. That’s also ‘solar latitude’ at the equinoxes. But on June 21 our ‘solar latitude’ is ~19° and on December 21 it’s ~65°. ...
Cycles
... sun, as well as water, carbon and other essential nutrients Food Chains populations are affected by populations below (food source) and above (food source for others) ...
... sun, as well as water, carbon and other essential nutrients Food Chains populations are affected by populations below (food source) and above (food source for others) ...
Evolution Notes
... A. Species usually produce more offspring than the environment can support. B. This creates competition to survive and reproduce. C. Natural variation found in species allows for change. D. Natural selection explains how two populations of the same species that are isolated can become two different ...
... A. Species usually produce more offspring than the environment can support. B. This creates competition to survive and reproduce. C. Natural variation found in species allows for change. D. Natural selection explains how two populations of the same species that are isolated can become two different ...
Document
... C. Water—the major ingredient of the fluid inside the cells of all organisms D. Soil—a mixture of mineral and rock particles, the remains of dead organisms, water, and air E. Sunlight—the source of energy for most life on Earth F. Most organisms’ body temperatures should stay within the range of 0°C ...
... C. Water—the major ingredient of the fluid inside the cells of all organisms D. Soil—a mixture of mineral and rock particles, the remains of dead organisms, water, and air E. Sunlight—the source of energy for most life on Earth F. Most organisms’ body temperatures should stay within the range of 0°C ...
Ecology Review Packet
... 2. True or False: Human activity uses as much energy as all of Earth’s other multicellular species combined. ...
... 2. True or False: Human activity uses as much energy as all of Earth’s other multicellular species combined. ...
Principles of Ecology
... Which are biotic factors in a forest environment? A. plants and microscopic organisms living B. pH and salt concentration of the soil C. sunlight, soil type and soil nutrients D. temperature, air currents and rainfall ...
... Which are biotic factors in a forest environment? A. plants and microscopic organisms living B. pH and salt concentration of the soil C. sunlight, soil type and soil nutrients D. temperature, air currents and rainfall ...
parasitism
... • If the presence or absence of a factor limits the growth of the ecosystems elements, it is called a limiting factor . • One of the features of an ecosystem is that its growth is limited under normal conditions by competition for resources within the system and by external factors such as environme ...
... • If the presence or absence of a factor limits the growth of the ecosystems elements, it is called a limiting factor . • One of the features of an ecosystem is that its growth is limited under normal conditions by competition for resources within the system and by external factors such as environme ...
Chapter 10 review, page 246 1-5, 8, 10
... 5. Generalist is opposite to specialist. Specialists eat or do only one thing, or one type of thing, while generalists are good at many things and can eat lots of different stuff. 8. Eco means home, an ecosystem provides a home to the living things in the community that live in it. 10 Because a biom ...
... 5. Generalist is opposite to specialist. Specialists eat or do only one thing, or one type of thing, while generalists are good at many things and can eat lots of different stuff. 8. Eco means home, an ecosystem provides a home to the living things in the community that live in it. 10 Because a biom ...
Humans in the Biosphere
... habitat and wildlife. Conservation focuses on protecting ecosystems, which will ensure that the natural habitat and the interactions of many different species are preserved at the same time ...
... habitat and wildlife. Conservation focuses on protecting ecosystems, which will ensure that the natural habitat and the interactions of many different species are preserved at the same time ...
Natural Selection Note
... The survival of an organism depends on its ability to sense and respond to the external environment. In all environments, organisms with similar needs compete for the same resources. These two facts fuel the process of natural selection. Natural selection is a process by which organisms with traits ...
... The survival of an organism depends on its ability to sense and respond to the external environment. In all environments, organisms with similar needs compete for the same resources. These two facts fuel the process of natural selection. Natural selection is a process by which organisms with traits ...
Unit 12 Notes PPT
... 3. The part of the earth that can support life is the _________. 4. All the living and non-living factors in an area make up the: a) population b) ecosystem c) community ...
... 3. The part of the earth that can support life is the _________. 4. All the living and non-living factors in an area make up the: a) population b) ecosystem c) community ...
Chapter 5
... Chapter 5 Habitat and Niche • The “Where” and the “How”. • Habitat: • “Where” organisms lives. • Niche: • Includes space, food, temperature, conditions for mating, etc. • Also takes into account behavior at various seasons or times of day. ...
... Chapter 5 Habitat and Niche • The “Where” and the “How”. • Habitat: • “Where” organisms lives. • Niche: • Includes space, food, temperature, conditions for mating, etc. • Also takes into account behavior at various seasons or times of day. ...
BIOGEOGRAPHIC PROCESSES
... ECOSYSTEM PROCESSES Ecosystem: an organized system made up of plants, animals, and inorganic components which are linked together by flows of energy and materials. examples… ...
... ECOSYSTEM PROCESSES Ecosystem: an organized system made up of plants, animals, and inorganic components which are linked together by flows of energy and materials. examples… ...
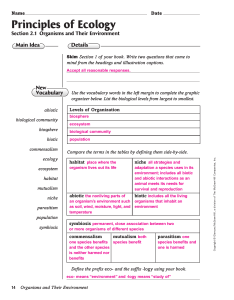
Science Notebook Chapter 2 - Answer Key
... Use the vocabulary words in the left margin to complete the graphic organizer below. List the biological levels from largest to smallest. Levels of Organization biosphere ecosystem ...
... Use the vocabulary words in the left margin to complete the graphic organizer below. List the biological levels from largest to smallest. Levels of Organization biosphere ecosystem ...
Chapter 22 - Darwinian Evolution
... higher rate than other individuals • Natural selection increases the adaptation of organisms to their environment over time • If an environment changes over time, natural selection may result in adaptation to these new conditions and may give rise to new species ...
... higher rate than other individuals • Natural selection increases the adaptation of organisms to their environment over time • If an environment changes over time, natural selection may result in adaptation to these new conditions and may give rise to new species ...
concepts for episode 1 - Austin Community College
... The populations of species that live and interact in a particular area comprise a community. Each species interacts uniquely with both its biotic and abiotic environments, producing an ecosystem. Populations, communities, and ecosystems change over time and space in a variety of ways. I. ...
... The populations of species that live and interact in a particular area comprise a community. Each species interacts uniquely with both its biotic and abiotic environments, producing an ecosystem. Populations, communities, and ecosystems change over time and space in a variety of ways. I. ...
BIO 112-STUDY GUIDE
... 1). What is science and what are the two main types and how do they differ? 2). What are the main components of the scientific method? 3). What are different ways of inquiry besides the scientific method and what makes science different from these other ways of inquiry? 4). Be able to write a hypoth ...
... 1). What is science and what are the two main types and how do they differ? 2). What are the main components of the scientific method? 3). What are different ways of inquiry besides the scientific method and what makes science different from these other ways of inquiry? 4). Be able to write a hypoth ...
Evolution - HHS Biology-Blattman
... organism’s fitness. Organisms with the best traits suited for their environment will survive, those not best suited will die. This is called survival of the fittest. ...
... organism’s fitness. Organisms with the best traits suited for their environment will survive, those not best suited will die. This is called survival of the fittest. ...
AP Environmental Science Biodiversity Key Terms
... inhibited or destroyed and the other is unaffected. There are two basic modes: competition, in which a larger or stronger organism excludes a smaller or weaker one from living space or deprives it of food, and antibiosis, in which one organism is unaffected but the other is damaged or killed by a ch ...
... inhibited or destroyed and the other is unaffected. There are two basic modes: competition, in which a larger or stronger organism excludes a smaller or weaker one from living space or deprives it of food, and antibiosis, in which one organism is unaffected but the other is damaged or killed by a ch ...
Life Science I 83.101.102 Dr. Ekaterina (Kate) Vorotnikova Office
... still share certain characteristics from common finch ancestor – body shape, nesting behavior, etc. ...
... still share certain characteristics from common finch ancestor – body shape, nesting behavior, etc. ...
ANSWERS Biology Interim Study Guide
... 33. What type of curve is this called? S Curve 34. What is the definition of carrying capacity? The maximum number of organisms an ecosystem can successfully handle (like an elevator) What is it on the graph above? ...
... 33. What type of curve is this called? S Curve 34. What is the definition of carrying capacity? The maximum number of organisms an ecosystem can successfully handle (like an elevator) What is it on the graph above? ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.