* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems and Energy Transfers2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
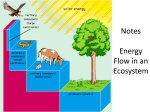
Ecosystems and Energy Transfers WONG HONG CHING Index • 1. Definition of key words • 2. Energy transfers in ecosystems • 3. Ecological pyramids 1. Definition of key words • Ecosystem • Population • Community • Habitat • Niche • Environment Ecosystem • Ecosystem stands for Ecological system. • It is an ecological unit which includes all living organisms and the abiotic factors that surround the organisms, results from the dynamic interactions abiotic and biotic factors. • The abiotic factors: • • • • • • Temperature pH Light intensity Oxygen level Humidity Rainfall • The biotic factors: • • • Animals Plants Micro-organisms Population & Community • Population refers to all the organisms of the same species in a area. • Community refers to all living organisms of different species living in a given area. • Living organisms interact with each other and are interconnected by food chains or food webs. Habitat • Habitat refers to the place where the communities live. • Examples of habitats: • • • • Forest Sea Rock shore Soil Niche • It is a word which is used to describe the relational position of a species in an area. • It refers to the roles of an organism in an area. • Different species have different roles, niches. • Roles: • • • • What it eats Where it lives When it is active When it eats Environment • Environment is the conditions surrounding the organisms. • The conditions include both abiotic factors and biotic factors. • The abiotic factors: • • • • • • Temperature Rainfall pH Light intensity Oxygen level Humidity • The biotic factors: • • Predation by other organisms Competition of nutrients, food Energy transfers Cycle • First step: • Solar energy Plants (Act as producers) • Second step: • Producers’ energy Primary consumer (herbivores) • Third step: • Primary consumers’ energy Secondary consumers (carnivores) • Forth step: • Secondary consumers’ energy Tertiary consumers • Final step: • When tertiary consumers die, the energy and nutrients are returned to the soil by saprotrophic organisms which feed on dead organisms. • Decomposers: Start the cycle again Energy Transfers in Ecosystem • Is the energy totally transferred between different trophic levels? • The answer is no. • Only 10% energy is transferred between different trophic level. WHY?? • 30% of energy is used in respiration. • 60% of energy is lost in excretion of waste products, like faeces, urine, gas. • Amount of energy stored and transferred to another trophic level: • 100% - 30% - 60% = 10% • No food chain can exceed more than 5 links. • Otherwise, the consumers at the end of food chain cannot get enough food and energy. Ecological Pyramids • What is ecological pyramids? • They are the graphs which are used to show the relationship between energy and trophic levels of an area. • Three types of pyramids: • Pyramid of number • Pyramid of biomass • Pyramid of energy Feature: Primary producers are at the bottom. Pyramid of number • Feature: • It is a ecological pyramid which shows the number of organisms in different trophic levels. • Advantage: • Just counting the number of organisms, is easy to produce. • Disadvantages: • The pyramid shape is messed up by small amount of big producers (like trees) and large amount of tertiary producers (like fleas). Abnormal cases of pyramids of number • Small amount of large producers. • Large amount of small tertiary consumers. Pyramid of biomass • It is a ecological pyramid which measures the dry mass of organisms in different trophic levels. • The unit of dry mass is kg/m2 • Advantage: • Pretty accurate, often have a normal pyramid shape. • Disadvantages: • Difficult to get the data. (Need to kill the organism and evaporate all of it’s water inside the body) • If the producers have small sizes, short life and reproduces quickly, then the pyramid shape is distorted. Pyramid of energy • It is a ecological pyramid which measures the amount of energy in the organisms in different trophic levels. • The unit is kJ/m-2/yr-1 • It is the most accurate among other pyramids. • However, it is very difficult to measure the amount of energy in the organism. Bibliography • http://ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topics/frogs/chain _reaction/index.cfm • http://www.arcytech.org/java/population/facts_foo dchain.html