Chapter 6
... to provide a more favorable pathway for the transformation of one to another. • Increase likelihood that reactants can interact productively. • CANNOT promote reactions where G>0. ...
... to provide a more favorable pathway for the transformation of one to another. • Increase likelihood that reactants can interact productively. • CANNOT promote reactions where G>0. ...
Multiple Choice Enzymes and Resp Answers
... C. The substrate molecules are moving faster. D. There are more substrate molecules to catalyse the reaction. ...
... C. The substrate molecules are moving faster. D. There are more substrate molecules to catalyse the reaction. ...
C483 Summer 2015 Exam 2 Name 1. 20 pts Fill in the blanks (2
... B. ______________ An increase in cholesterol levels would cause the melting point of a lipid bilayer to increase. C. ______________ Integral proteins are generally reversibly associated with the cell membrane. ...
... B. ______________ An increase in cholesterol levels would cause the melting point of a lipid bilayer to increase. C. ______________ Integral proteins are generally reversibly associated with the cell membrane. ...
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2009
... b. prokaryotic cells generally have a larger surface-to-volume ratio than do eukaryotic cells. c. the Krebs Cycle operates faster in prokaryotic cells than in eukaryotic cells. d. eukaryotic cells use ATP to transport respiration substrates into and out of mitochondria. 25. The metabolic pathway tha ...
... b. prokaryotic cells generally have a larger surface-to-volume ratio than do eukaryotic cells. c. the Krebs Cycle operates faster in prokaryotic cells than in eukaryotic cells. d. eukaryotic cells use ATP to transport respiration substrates into and out of mitochondria. 25. The metabolic pathway tha ...
Enzyme
... Metabolic Pathways • A metabolic pathway has many steps – That begin with a specific molecule and end with a product – That are each catalyzed by a specific enzyme ...
... Metabolic Pathways • A metabolic pathway has many steps – That begin with a specific molecule and end with a product – That are each catalyzed by a specific enzyme ...
Photosynthesis - Crestwood Local Schools
... Energy from these photons zaps the e- and gives it more energy *this energy is used in 2 different processes in the light reactions: a.) Making ATP: ~ excited e- get replaced by splitting H2O molecules - H donates its e- and is left with H+ - O isn't used anymore so it leaves as O2 gas ~ excited e- ...
... Energy from these photons zaps the e- and gives it more energy *this energy is used in 2 different processes in the light reactions: a.) Making ATP: ~ excited e- get replaced by splitting H2O molecules - H donates its e- and is left with H+ - O isn't used anymore so it leaves as O2 gas ~ excited e- ...
BIO 220 Chapter 5 lecture outline Metabolism definition Collision
... 5. Describe the general structure and characteristics of an enzyme. 6. Explain the mechanism by which enzymes speed up chemical reactions. 7. Why would a particular enzyme be able to bind to only one or a small number of substrates? 8. What is the function of each type of enzyme listed in table 5.1 ...
... 5. Describe the general structure and characteristics of an enzyme. 6. Explain the mechanism by which enzymes speed up chemical reactions. 7. Why would a particular enzyme be able to bind to only one or a small number of substrates? 8. What is the function of each type of enzyme listed in table 5.1 ...
Screening Applications
... “sandwich-type” expression immunoassay, using as a label an expressible DNA fragment encoding firefly luciferase. The DNA label contains a T7 RNA polymerase promoter, a firefly luciferase-encoding sequence and a poly(dA/dT) tail. The 3´-end of the DNA label is biotinylated and complexed with streptavidi ...
... “sandwich-type” expression immunoassay, using as a label an expressible DNA fragment encoding firefly luciferase. The DNA label contains a T7 RNA polymerase promoter, a firefly luciferase-encoding sequence and a poly(dA/dT) tail. The 3´-end of the DNA label is biotinylated and complexed with streptavidi ...
Test 2a
... (8 points)Tell me about the different types of catalysis you see occurring in this mechanism. In step 1 His 12 is acting as a general base to remove a proton from the 2' OH of the ribose, and His 119 is acitng as a general acid to donate its proton to the phosphate group between the two ribose sugar ...
... (8 points)Tell me about the different types of catalysis you see occurring in this mechanism. In step 1 His 12 is acting as a general base to remove a proton from the 2' OH of the ribose, and His 119 is acitng as a general acid to donate its proton to the phosphate group between the two ribose sugar ...
Cell Resp. Power Point Brief SV
... TWO WAYS TO MAKE ATP 1) ______________________ Phosphorylation: An enzyme transfers a __________ from a substrate (a molecule) to ADP, yielding ATP: ex: 1,3 Bisphosphate glycerate loses a phosphate to ADP-----> ATP 2) ______________________ Phosphorylation: Energy from redox reactions in electrontr ...
... TWO WAYS TO MAKE ATP 1) ______________________ Phosphorylation: An enzyme transfers a __________ from a substrate (a molecule) to ADP, yielding ATP: ex: 1,3 Bisphosphate glycerate loses a phosphate to ADP-----> ATP 2) ______________________ Phosphorylation: Energy from redox reactions in electrontr ...
Enzymes - Solon City Schools
... An egg becomes hard boiled when placed in hot water. What is similar about these two events? ...
... An egg becomes hard boiled when placed in hot water. What is similar about these two events? ...
Document
... Dihydrolipoamide Acyltransferase (E2) • Transfer catalyzed by E1 • Serves as an linker to “swing” substrate through subunits • Mechanism of redox ...
... Dihydrolipoamide Acyltransferase (E2) • Transfer catalyzed by E1 • Serves as an linker to “swing” substrate through subunits • Mechanism of redox ...
A green glow
... phenomena simultaneously? To do so, scientists would have to produce proteins which give off different coloured types of fluorescence. How? Fluorescence also exists in corals and sea anemones which express the fluorescent proteins – FP – that are similar to GFP but glow blue, yellow or orange-red. C ...
... phenomena simultaneously? To do so, scientists would have to produce proteins which give off different coloured types of fluorescence. How? Fluorescence also exists in corals and sea anemones which express the fluorescent proteins – FP – that are similar to GFP but glow blue, yellow or orange-red. C ...
Enzymes - Solon City Schools
... a. Reactions require energy to begin…enzymes lower the amount of energy required. ...
... a. Reactions require energy to begin…enzymes lower the amount of energy required. ...
SUCCINYL-CoA SYNTHETASE from a prokaryote (Lot 140901b)
... The enzyme is supplied as an ammonium sulphate suspension and should be stored at 4°C. For assay, this enzyme should be diluted in 100 mM glycylglycine buffer, pH 8.4 containing 10 mM MgCl2. Swirl to mix the enzyme suspension immediately prior to use. ...
... The enzyme is supplied as an ammonium sulphate suspension and should be stored at 4°C. For assay, this enzyme should be diluted in 100 mM glycylglycine buffer, pH 8.4 containing 10 mM MgCl2. Swirl to mix the enzyme suspension immediately prior to use. ...
Lecture 8
... • The entropy of the universe must increase in a spontaneous process, and protein folding is a spontaneous process – When water molecules surround a nonpolar compound, they are restricted in the number of hydrogen bonds then can form which represents a lower entropy – By having the hydrophobic resid ...
... • The entropy of the universe must increase in a spontaneous process, and protein folding is a spontaneous process – When water molecules surround a nonpolar compound, they are restricted in the number of hydrogen bonds then can form which represents a lower entropy – By having the hydrophobic resid ...
Exam II answer key
... Fatty acid CoA thioester must be transported to the mitochnodria, but it cannot pass through membranes. The fatty acid is temporarily transesterified with carnitine, which is transported and then transesterified back to CoA thioester. d) What two properties make triacylglycerols more efficient than ...
... Fatty acid CoA thioester must be transported to the mitochnodria, but it cannot pass through membranes. The fatty acid is temporarily transesterified with carnitine, which is transported and then transesterified back to CoA thioester. d) What two properties make triacylglycerols more efficient than ...
Exam II
... Fatty acid CoA thioester must be transported to the mitochnodria, but it cannot pass through membranes. The fatty acid is temporarily transesterified with carnitine, which is transported and then transesterified back to CoA thioester. d) What two properties make triacylglycerols more efficient than ...
... Fatty acid CoA thioester must be transported to the mitochnodria, but it cannot pass through membranes. The fatty acid is temporarily transesterified with carnitine, which is transported and then transesterified back to CoA thioester. d) What two properties make triacylglycerols more efficient than ...
Photosynthesis- Photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR)
... pH stroma goes up from 7 Æ 8 Mg2+ increases in stroma NADPH allosteric activator Rubisco Activase catalyzes carbamate formation – CO2 required ...
... pH stroma goes up from 7 Æ 8 Mg2+ increases in stroma NADPH allosteric activator Rubisco Activase catalyzes carbamate formation – CO2 required ...
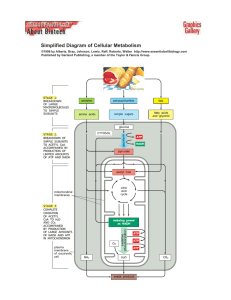
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
emboj7600663-sup
... with a rotating anode (RU-300, Rigaku) and an R-AXIS IV detector (Molecular Structure Corporation). Diffraction data for ADP- and ATP-bound complexes were collected with beamlines 19ID and 19BM in the Structural Biology Center at the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne, IL). The data were processed wit ...
... with a rotating anode (RU-300, Rigaku) and an R-AXIS IV detector (Molecular Structure Corporation). Diffraction data for ADP- and ATP-bound complexes were collected with beamlines 19ID and 19BM in the Structural Biology Center at the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne, IL). The data were processed wit ...
ENZYMES: THE MAJESTIC MOLECULES OF LIFE Part
... Structure of the Active centre: There are distinguished, in the active centre, a contact site (anchor site) for binding a substrate, and a catalytic site at which the conversion of the bound substrate takes place. However, this functional differentiation is somewhat arbitrary, since the binding of ...
... Structure of the Active centre: There are distinguished, in the active centre, a contact site (anchor site) for binding a substrate, and a catalytic site at which the conversion of the bound substrate takes place. However, this functional differentiation is somewhat arbitrary, since the binding of ...
CHAPTER 10 REVIEW SHEET Briefly describe metabolism. What
... 27. Exemplify how the Gibbs free energy change for ATP hydrolysis in vivo is greater than the standard Gibbs free energy change given [ATP] = 3.8 mM, [ADP] = 0.9 mM and [Pi] = 5.2 mM for a particular organism. Assume 25°C and pH = 7.0. ATP ADP + Pi ...
... 27. Exemplify how the Gibbs free energy change for ATP hydrolysis in vivo is greater than the standard Gibbs free energy change given [ATP] = 3.8 mM, [ADP] = 0.9 mM and [Pi] = 5.2 mM for a particular organism. Assume 25°C and pH = 7.0. ATP ADP + Pi ...
Structure of bacterial luciferase
... [3 subunit is folded alone, it forms a homodimer which is insensitive to proteases and does not unfold even after prolonged incubation in 5 M urea [39"'], conditions that would cause rapid unfolding of the native heterodimer [40-42]. These biochemical studies, both with the proteolyzed enzyine and w ...
... [3 subunit is folded alone, it forms a homodimer which is insensitive to proteases and does not unfold even after prolonged incubation in 5 M urea [39"'], conditions that would cause rapid unfolding of the native heterodimer [40-42]. These biochemical studies, both with the proteolyzed enzyine and w ...
Exam 2 Practice - Nicholls State University
... be used for energy production or they can be stored for later use. What molecule can serve as a regulator of this process? a. glucose b. pyruvate c. lactic acid d. ATP 23. The actual yield of ATP from each molecule of glucose is about 20% less than the theoretical yield under ideal conditions. Which ...
... be used for energy production or they can be stored for later use. What molecule can serve as a regulator of this process? a. glucose b. pyruvate c. lactic acid d. ATP 23. The actual yield of ATP from each molecule of glucose is about 20% less than the theoretical yield under ideal conditions. Which ...
Luciferase

Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes used in bioluminescence and is distinct from a photoprotein. The name is derived from Lucifer, the root of which means 'light-bearer' (lucem ferre). One example is the firefly luciferase (EC 1.13.12.7) from the firefly Photinus pyralis. ""Firefly luciferase"" as a laboratory reagent often refers to P. pyralis luciferase although recombinant luciferases from several other species of fireflies are also commercially available.