Cumulative Vocabulary List Organism: A living thing Cell: The basic
... Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river, formed from sediments carried by river Sand Dune: Hills of sand, formed by the wind Fault: A crack in Earth’s crust Matter: Anything that takes up space Physical Change: When matter changes without creating a new substance Chemical Change: When mat ...
... Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river, formed from sediments carried by river Sand Dune: Hills of sand, formed by the wind Fault: A crack in Earth’s crust Matter: Anything that takes up space Physical Change: When matter changes without creating a new substance Chemical Change: When mat ...
Biology
... found within each cell. Explain how variation in organelle number and type can be used to indicate the function of the cell. 6. Using the evidence that you have collected, identify an organelle other than the cell nucleus that you feel is the next most critical in the functioning of a cell. Construc ...
... found within each cell. Explain how variation in organelle number and type can be used to indicate the function of the cell. 6. Using the evidence that you have collected, identify an organelle other than the cell nucleus that you feel is the next most critical in the functioning of a cell. Construc ...
Name__________________________ Date_______________
... ______ 12. Passive transport L. A smaller part of a cell, that each has a special function ______ 13. Active transport M. Made in muscle cells when there is no oxygen ______ 14. Photosynthesis N. The smallest living thing ______ 15. Respiration O. Glucose and oxygen are turned into ATP, water, and C ...
... ______ 12. Passive transport L. A smaller part of a cell, that each has a special function ______ 13. Active transport M. Made in muscle cells when there is no oxygen ______ 14. Photosynthesis N. The smallest living thing ______ 15. Respiration O. Glucose and oxygen are turned into ATP, water, and C ...
Year 12 Induction Task Induction task: The Ultrastructure of Cells
... found within each cell. Explain how variation in organelle number and type can be used to indicate the function of the cell. 6. Using the evidence that you have collected, identify an organelle other than the cell nucleus that you feel is the next most critical in the functioning of a cell. Construc ...
... found within each cell. Explain how variation in organelle number and type can be used to indicate the function of the cell. 6. Using the evidence that you have collected, identify an organelle other than the cell nucleus that you feel is the next most critical in the functioning of a cell. Construc ...
79099_Mitosis
... Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division are assembled. ...
... Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division are assembled. ...
7.2 - Cell Structure - Office of Instructional Technology
... enzymes that break down large molecules and organelles that are no longer useful ...
... enzymes that break down large molecules and organelles that are no longer useful ...
Active Transport
... large quantities need to pass through the cell These situations use vesicle transport Two kinds 1.Endocytosis 2.Exocytosis ...
... large quantities need to pass through the cell These situations use vesicle transport Two kinds 1.Endocytosis 2.Exocytosis ...
Cell Membrane
... Some integral proteins have receptors on their surface to recognize & take in hormones, ...
... Some integral proteins have receptors on their surface to recognize & take in hormones, ...
Section: Eukaryotic Cells
... ______19. Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ______20. Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ______21. Chl ...
... ______19. Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ______20. Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ______21. Chl ...
Section 7.1 Guided Notes
... – Is the cell _______________________________________________ !! – Regulates what _________________________________ and _____________________________________ the cell. – The cell membrane is ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
... – Is the cell _______________________________________________ !! – Regulates what _________________________________ and _____________________________________ the cell. – The cell membrane is ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
General Biology I (BIOLS 102)
... Extremely thin filaments like a twisted pearl necklace Dense web just under plasma membrane maintains cell shape Support for microvilli in intestinal cells Intracellular traffic control For moving stuff around within cell Cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells ...
... Extremely thin filaments like a twisted pearl necklace Dense web just under plasma membrane maintains cell shape Support for microvilli in intestinal cells Intracellular traffic control For moving stuff around within cell Cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells ...
Cell notes File
... Surrounds the cell membrane and protects cell. Adds stiffness to cell. Plant cells have a cell wall and cell membrane. (Animals only have a cell membrane.) ...
... Surrounds the cell membrane and protects cell. Adds stiffness to cell. Plant cells have a cell wall and cell membrane. (Animals only have a cell membrane.) ...
Study Guide
... 1. Stores material within the cell 2. Controls what moves in and out of the nucleus 3. The sites of protein synthesis 4. Considered the roadways of the cell 5. The region inside the cell except for the nucleus 6. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 7. Site ...
... 1. Stores material within the cell 2. Controls what moves in and out of the nucleus 3. The sites of protein synthesis 4. Considered the roadways of the cell 5. The region inside the cell except for the nucleus 6. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 7. Site ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide
... e. Anton van Leeuwenhoek 4. Name all organelles found in a plant cell and explain the role of each. 5. Name all organelles found in an animal cell and explain the role of each. 6. Draw and label the parts of an ATP molecule. What is it used for? 7. Draw and label the parts of the FMMOCM—know structu ...
... e. Anton van Leeuwenhoek 4. Name all organelles found in a plant cell and explain the role of each. 5. Name all organelles found in an animal cell and explain the role of each. 6. Draw and label the parts of an ATP molecule. What is it used for? 7. Draw and label the parts of the FMMOCM—know structu ...
Plant and Animal Cell Parts
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
Cell Wall
... Not all cells are alike! They vary in… A) size B) shape C) internal organization SIZE: range from .2m – 0.2um (most are 10-50um) -not all are microscopic (most are) ex: giraffe’s nerve cells extend 6.5 ft. down it’s leg!! ...
... Not all cells are alike! They vary in… A) size B) shape C) internal organization SIZE: range from .2m – 0.2um (most are 10-50um) -not all are microscopic (most are) ex: giraffe’s nerve cells extend 6.5 ft. down it’s leg!! ...
Animal Cell - TeacherWeb
... packages, modifies, and transports proteins from rough ER found in salivary glands, pancreas ...
... packages, modifies, and transports proteins from rough ER found in salivary glands, pancreas ...
Cell Organelle Notes A. Cell Wall
... 1. Release energy from stored food molecules 2. Use food to form ATP (Molecule that is used as energy in cell) 3. Enclosed by two membranes (inner folds and outer) Chemical reactions 4. Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells ...
... 1. Release energy from stored food molecules 2. Use food to form ATP (Molecule that is used as energy in cell) 3. Enclosed by two membranes (inner folds and outer) Chemical reactions 4. Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells ...
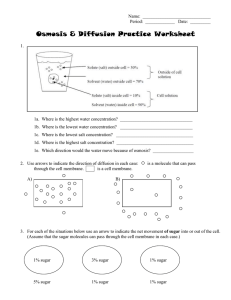
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 1e. Which direction would the water move because of osmosis? __________________ 2. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: through the cell membrane. is a cell membrane. A) ...
... 1e. Which direction would the water move because of osmosis? __________________ 2. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: through the cell membrane. is a cell membrane. A) ...
science words chapter 3
... hereditary material that controls all the activities of a cell, contains the information to make new cells, and provides instructions for making proteins ...
... hereditary material that controls all the activities of a cell, contains the information to make new cells, and provides instructions for making proteins ...
Cell powerpoint - Valhalla High School
... All cells arise from pre-existing living cells. This means that life doesn’t spontaneous appear from non-living matter. ...
... All cells arise from pre-existing living cells. This means that life doesn’t spontaneous appear from non-living matter. ...
Basic Cellular Review Powerpoint
... but not both • Depend on the energy of the host cell • Has protective coat which makes them hard to control; antibiotics have no effect • Bacteriophage: virus which invades bacteria • Examples of viral diseases: measles, ...
... but not both • Depend on the energy of the host cell • Has protective coat which makes them hard to control; antibiotics have no effect • Bacteriophage: virus which invades bacteria • Examples of viral diseases: measles, ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑