Questions for each cell structure
... How many ribosomes in an average cell? Why so many? What two organelles have ribosomes independent of the cell’s? Is there a difference between a free floating ribosome and one attached to the ER? Cytoskeleton: What are the major filaments/ structures that make up the cytoskeleton? How are they arra ...
... How many ribosomes in an average cell? Why so many? What two organelles have ribosomes independent of the cell’s? Is there a difference between a free floating ribosome and one attached to the ER? Cytoskeleton: What are the major filaments/ structures that make up the cytoskeleton? How are they arra ...
Cell Trafficking
... Integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are cell surface receptors mediating biological functions such as cell survival, proliferation and cell migration. Integrins, through direct binding to extracellular molecules, provide a physical link between the cell cytoskeleton and the surrounding en ...
... Integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are cell surface receptors mediating biological functions such as cell survival, proliferation and cell migration. Integrins, through direct binding to extracellular molecules, provide a physical link between the cell cytoskeleton and the surrounding en ...
Cell structure
... It spreads through the whole of the cytoplasm as a 3D network of parallel flattened sacs, called cisternae, all the cavities are inter-linked and this is what is known as the ER. It also links with the nuclear membrane and may link to the Golgi body. The outside of the ER may be encrusted with ribos ...
... It spreads through the whole of the cytoplasm as a 3D network of parallel flattened sacs, called cisternae, all the cavities are inter-linked and this is what is known as the ER. It also links with the nuclear membrane and may link to the Golgi body. The outside of the ER may be encrusted with ribos ...
Cell Booklet By Ferris Williams Illinois State Standard 12.A.4b
... Illinois State Standard 12.A.4b- Describe the structures and the organization of cells and tissues that underlie basic life functions including nutrition, respiration, cellular transport, biosynthesis and reproduction. Objective: ...
... Illinois State Standard 12.A.4b- Describe the structures and the organization of cells and tissues that underlie basic life functions including nutrition, respiration, cellular transport, biosynthesis and reproduction. Objective: ...
Bioenergetics Structures and Functions of Cells
... A simple analysis of “odd one out”. Identify the structure which does not belong to the group. 1. capsule; flagella; pili; nucleoid; desmosome; 2. cell membrane; DNA; ribosome; peroxisome; cytosol 3. cell wall; plasmodesma; huge vacuole; chloroplast; ribosome 4. lysosomes; nucleus; mitochondria; chl ...
... A simple analysis of “odd one out”. Identify the structure which does not belong to the group. 1. capsule; flagella; pili; nucleoid; desmosome; 2. cell membrane; DNA; ribosome; peroxisome; cytosol 3. cell wall; plasmodesma; huge vacuole; chloroplast; ribosome 4. lysosomes; nucleus; mitochondria; chl ...
Name____________________ The World of Cells Organelle
... In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? ...
... In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? ...
Astronomy Review
... • What is the function of a lysosome? • Cellular digestion, breaksdown items in the cell that are no longer needed, can destroy organelles as well. ...
... • What is the function of a lysosome? • Cellular digestion, breaksdown items in the cell that are no longer needed, can destroy organelles as well. ...
pass through the cell membrane
... For a cell to maintain its internal environment, it has to be selective in the materials it allows to cross its cell membrane. Transport: How molecules and fluids pass through the cell membrane. ...
... For a cell to maintain its internal environment, it has to be selective in the materials it allows to cross its cell membrane. Transport: How molecules and fluids pass through the cell membrane. ...
The Cell Notes
... All the scientists previously mentioned contributed to the Cell Theory which states: – All living things are composed of cells – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms – New cells are produced from pre-existing cells ...
... All the scientists previously mentioned contributed to the Cell Theory which states: – All living things are composed of cells – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms – New cells are produced from pre-existing cells ...
CHAPTER 6 LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... 17. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion and explain the importance of compartmentalization in mitochondrial function. 18. Distinguish among amyloplasts, chromoplasts, and chloroplasts. 19. Identify the three functional compartments of a chloroplast. Explain the importance of compartmentalizati ...
... 17. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion and explain the importance of compartmentalization in mitochondrial function. 18. Distinguish among amyloplasts, chromoplasts, and chloroplasts. 19. Identify the three functional compartments of a chloroplast. Explain the importance of compartmentalizati ...
Centrosome - English at the Shore Spot
... Animal or Plant Cell? • Centrosomes are found in both • Centrioles are only in animal cells • Plants still perform • Why? Cilia and flagella for cells are surface features used for cell movement, cells in plants aren’t required to move around like those in animal cells ...
... Animal or Plant Cell? • Centrosomes are found in both • Centrioles are only in animal cells • Plants still perform • Why? Cilia and flagella for cells are surface features used for cell movement, cells in plants aren’t required to move around like those in animal cells ...
Cell Processes Review
... When vesicles are formed at the endoplasmic reticulum of Golgi complex and they carry large particles to the cell membrane to exit the cell, this is called ...
... When vesicles are formed at the endoplasmic reticulum of Golgi complex and they carry large particles to the cell membrane to exit the cell, this is called ...
File
... Hypertonic: solute concentrations outside are higher than inside the cell. When hypertonic, water moves to the outside of the cell and the cell shrivels up ...
... Hypertonic: solute concentrations outside are higher than inside the cell. When hypertonic, water moves to the outside of the cell and the cell shrivels up ...
Cell Notes - gst boces
... Controls the cells activities Energy center or "powerhouse" of the cell (Mr. Capp) Turns food into useable energy Storage tanks of the cell for food, water, and waste They are little bundles of chlorophyll. It is where green plants make their own food. The green coloring matter in plants. Processes, ...
... Controls the cells activities Energy center or "powerhouse" of the cell (Mr. Capp) Turns food into useable energy Storage tanks of the cell for food, water, and waste They are little bundles of chlorophyll. It is where green plants make their own food. The green coloring matter in plants. Processes, ...
Cell Foldable
... Prokaryote Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled – cell wall, pilli/flagella, cytoplasm, 70s ribosome, nucleoid region(and DNA), plasmid. Eukaryote – Plant Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled ...
... Prokaryote Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled – cell wall, pilli/flagella, cytoplasm, 70s ribosome, nucleoid region(and DNA), plasmid. Eukaryote – Plant Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled ...
Cell Structure
... When you are sick your mitochondria have less infoldings, so you feel weak. As you get better the infoldings increase and you get more energy. ...
... When you are sick your mitochondria have less infoldings, so you feel weak. As you get better the infoldings increase and you get more energy. ...
Cell Foldable
... Prokaryote Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled – cell wall, pilli/flagella, cytoplasm, 70s ribosome, nucleoid region(and DNA), plasmid. Eukaryote – Plant Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled ...
... Prokaryote Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled – cell wall, pilli/flagella, cytoplasm, 70s ribosome, nucleoid region(and DNA), plasmid. Eukaryote – Plant Cell – Must be drawn to scale compared to the other cells. Organelles included and labeled ...
1. Cell Structure - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... Called the basic unit of life because it is the simplest unit capable of independent existence and reproduction All organisms are constructed out of cells - unicellular organism = 1 cell - multicellular organism = more than 1 cell Cells of all organisms contain organelles which carry out certain ...
... Called the basic unit of life because it is the simplest unit capable of independent existence and reproduction All organisms are constructed out of cells - unicellular organism = 1 cell - multicellular organism = more than 1 cell Cells of all organisms contain organelles which carry out certain ...
Cytoplasm (inside of cell)
... 1. They are all bound by a thin plasma membrane. 2. All cells have DNA. 3. All cells have ribosomes. Cytoplasm-the entire contents of a cell ...
... 1. They are all bound by a thin plasma membrane. 2. All cells have DNA. 3. All cells have ribosomes. Cytoplasm-the entire contents of a cell ...
Bell Work
... • Gathers simple molecules and combines them to make molecules that are more complex • Big molecules are made into vesicles • builds lysosomes (cell digestion machines) • In plants, creates complex sugars and sends them off in secretory vesicles. ...
... • Gathers simple molecules and combines them to make molecules that are more complex • Big molecules are made into vesicles • builds lysosomes (cell digestion machines) • In plants, creates complex sugars and sends them off in secretory vesicles. ...
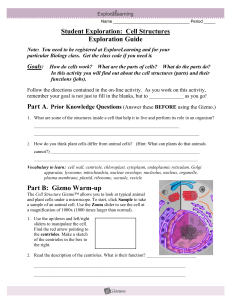
HW Cell Structures Gizmo Gizmo Cell Structures final
... 1. Use the up/down and left/right sliders to manipulate the cell. Find the red arrow pointing to the centrioles. Make a sketch of the centrioles in the box to the right. 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ ______________________________________ ...
... 1. Use the up/down and left/right sliders to manipulate the cell. Find the red arrow pointing to the centrioles. Make a sketch of the centrioles in the box to the right. 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ ______________________________________ ...
3 ch - CELLS
... Resting membrane potential – the point where K+ potential is balanced by the membrane potential range -50 to -100 millivolts (mV). The Cells become polarized which results from Na+ and K+ concentration gradients across the membrane. This is a steady state – maintained by active transport of ions Cel ...
... Resting membrane potential – the point where K+ potential is balanced by the membrane potential range -50 to -100 millivolts (mV). The Cells become polarized which results from Na+ and K+ concentration gradients across the membrane. This is a steady state – maintained by active transport of ions Cel ...
Journal Entry #12
... Which organelle would be responsible for breaking down the excess hydrogen peroxide that gets produced in the cell as a result of photosynthesis? b) The muscle cells in a man’s arms are being used to lift weights at the gym. What organelle would be in charge of creating the energy to make this possi ...
... Which organelle would be responsible for breaking down the excess hydrogen peroxide that gets produced in the cell as a result of photosynthesis? b) The muscle cells in a man’s arms are being used to lift weights at the gym. What organelle would be in charge of creating the energy to make this possi ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑