Cell High School - Solon City Schools
... • If the school was a cell, the building itself or the walls would be the cell membrane. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and the environment. The building walls are surrounding the whole building and are a boundary between the school and outside. Also, the cell membrane uses selec ...
... • If the school was a cell, the building itself or the walls would be the cell membrane. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and the environment. The building walls are surrounding the whole building and are a boundary between the school and outside. Also, the cell membrane uses selec ...
Actin dynamics - Journal of Cell Science
... monomer and Arp2/3 complex (shown in red), an assembly of seven subunits including two actin-related proteins. Arp2/3 complex then initiates the growth of a new actin filament as a branch on the side of an older actin filament. The branch grows rapidly at its barbed end by addition of actin-profilin ...
... monomer and Arp2/3 complex (shown in red), an assembly of seven subunits including two actin-related proteins. Arp2/3 complex then initiates the growth of a new actin filament as a branch on the side of an older actin filament. The branch grows rapidly at its barbed end by addition of actin-profilin ...
PDF
... neuron (CSDn) in Drosophila, suggest K. VijayRaghavan and colleagues, the answer to this question is neuronal activity and Wnt signalling (see p. 1351). The dendrites of the CSDn grow extensively in the antennal lobe during early pupal development but then shrink to form the final adult structure. T ...
... neuron (CSDn) in Drosophila, suggest K. VijayRaghavan and colleagues, the answer to this question is neuronal activity and Wnt signalling (see p. 1351). The dendrites of the CSDn grow extensively in the antennal lobe during early pupal development but then shrink to form the final adult structure. T ...
Curriculum - Rivers2Lake
... Bring students outside and put them into groups. Depending on how much rope/time/students you have, you can divide them into two groups and have one group complete an animal cell (red rope) and the other complete a plant cell (green rope) with the matching red and green cards for animal cell parts a ...
... Bring students outside and put them into groups. Depending on how much rope/time/students you have, you can divide them into two groups and have one group complete an animal cell (red rope) and the other complete a plant cell (green rope) with the matching red and green cards for animal cell parts a ...
Biology
... h. teach someone else the concepts discussed i. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells 2. summarize the principles of the cell theory 3. differentiate between a prokaryotic an ...
... h. teach someone else the concepts discussed i. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells 2. summarize the principles of the cell theory 3. differentiate between a prokaryotic an ...
Year 8 Information Evening Presentation
... rectangular shape of the plant cell. Made of cellulose. A substance. A green dye which absorbs sunlight. A plant organelle. Only found in plants. Photosynthesis (making food) happens here. Using common features to group animals and plants eg vertebrates/invertebrates, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphi ...
... rectangular shape of the plant cell. Made of cellulose. A substance. A green dye which absorbs sunlight. A plant organelle. Only found in plants. Photosynthesis (making food) happens here. Using common features to group animals and plants eg vertebrates/invertebrates, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphi ...
Biology Cell unit
... structure when examining cork under the microscope Named these structures cells, meaning “storage rooms” ...
... structure when examining cork under the microscope Named these structures cells, meaning “storage rooms” ...
Comparing Organelles to Body Systems
... • A barrier between the cytoplasm and the outside of the cell • Pulls needed matter through the membrane • Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
... • A barrier between the cytoplasm and the outside of the cell • Pulls needed matter through the membrane • Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
a. Cell membrane
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. humans b. squid c. spiders d. all of the above 3. Which of the following is true of membranes? a. Folded membranes decrease surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum i ...
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. humans b. squid c. spiders d. all of the above 3. Which of the following is true of membranes? a. Folded membranes decrease surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum i ...
Cell_Structure_post
... • Double membrane organelle – central cavity filled with matrix – inner membrane folds = cristae • large surface area for chemical reactions of cellular respiration ...
... • Double membrane organelle – central cavity filled with matrix – inner membrane folds = cristae • large surface area for chemical reactions of cellular respiration ...
Membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus that contains DNA
... The organelles of a cell help it function similar to how a school, city, or team functions. Your Job: Choose a topic that you are familiar with, and create 10 comparisons that relate to the organelles of a cell. An example: A cell is like a city. The nucleus is like city hall because they both st ...
... The organelles of a cell help it function similar to how a school, city, or team functions. Your Job: Choose a topic that you are familiar with, and create 10 comparisons that relate to the organelles of a cell. An example: A cell is like a city. The nucleus is like city hall because they both st ...
name date ______ period - Ms. Shunkwiler`s Wiki!
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following are TRUE of a cell membranes (choose more than one)? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following are TRUE of a cell membranes (choose more than one)? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through ...
CP Bio Study Guide
... Stores water for the cell. Plant cells have one large central. Animal cells small and numerous. Transports membrane and secretory proteins inside of a cell from the nucleus to the Golgi Body via transport vesicles. Nucleolus 1. List the 4 structures that are common to all cells (both prokaryotic and ...
... Stores water for the cell. Plant cells have one large central. Animal cells small and numerous. Transports membrane and secretory proteins inside of a cell from the nucleus to the Golgi Body via transport vesicles. Nucleolus 1. List the 4 structures that are common to all cells (both prokaryotic and ...
Cell Jeopardy
... A devise that uses a lens or a system of lenses to produce a greatly magnified image. Used to see objects that are invisible to the naked eye, such as cells, bacteria, ...
... A devise that uses a lens or a system of lenses to produce a greatly magnified image. Used to see objects that are invisible to the naked eye, such as cells, bacteria, ...
Candy Factory
... Complete the chart below based on what we learned about a candy factory. Remember the “Candy Factory” is the cell. Candy Factory Role ...
... Complete the chart below based on what we learned about a candy factory. Remember the “Candy Factory” is the cell. Candy Factory Role ...
Cells
... Cytoplasm is the material between the cell’s nucleus and the cell membrane. It fills the entire cell. It contains a large variety of organelles and nutrients. The cytoplasm consists of an outer ectoplasm and an inner endoplasm. ...
... Cytoplasm is the material between the cell’s nucleus and the cell membrane. It fills the entire cell. It contains a large variety of organelles and nutrients. The cytoplasm consists of an outer ectoplasm and an inner endoplasm. ...
Unit 5: Cells Objectives Chapter 4 Distinguish between the detail
... gap junctions, anchoring junctions, plasmodesmata 7. Describe the components of the endomembrane system that would be involved in secreting a protein hormone into the blood. (what are they and how do they play a role in this process). Describe how they would produce a lipid that is secreted. How wou ...
... gap junctions, anchoring junctions, plasmodesmata 7. Describe the components of the endomembrane system that would be involved in secreting a protein hormone into the blood. (what are they and how do they play a role in this process). Describe how they would produce a lipid that is secreted. How wou ...
cell biology review sheet
... 8. You should be familiar with the molecules that compose the cell membrane and be able to diagrams and describe why the membrane form in the manner that it does (with relation to water) as well as the functions of the various components of the cell membrane. 9. You should be able to estimate the si ...
... 8. You should be familiar with the molecules that compose the cell membrane and be able to diagrams and describe why the membrane form in the manner that it does (with relation to water) as well as the functions of the various components of the cell membrane. 9. You should be able to estimate the si ...
Deconstructing the cell wall polysaccharide matrix of the
... The fungal cell wall is vital for the protection of fungal cells and for determining cell shape and function. This is of particular importance for pathogenic fungi, many of which elaborate specialised infection structures to invade their hosts. In spite of its importance, we know little about the st ...
... The fungal cell wall is vital for the protection of fungal cells and for determining cell shape and function. This is of particular importance for pathogenic fungi, many of which elaborate specialised infection structures to invade their hosts. In spite of its importance, we know little about the st ...
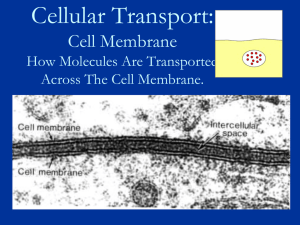
cell membrane
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
• Individual chromosomes are made up of 2 identical strands of
... up of 2 identical strands of genetic information. Chromosomes become visible and shorten and thicken Nuclear membrane fades Spindle forms Double-stranded chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell and attach to the spindle at the Centromere. ...
... up of 2 identical strands of genetic information. Chromosomes become visible and shorten and thicken Nuclear membrane fades Spindle forms Double-stranded chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell and attach to the spindle at the Centromere. ...
Cell Unit Study Guide
... You should be able to do the following: 1. Identify and provide examples of the traits of living things. 2. List and describe the levels of organization from smallest to largest. 3. Identify the three parts of cell theory. 4. Determine if a cell is a eukaryote or prokaryote given limited information ...
... You should be able to do the following: 1. Identify and provide examples of the traits of living things. 2. List and describe the levels of organization from smallest to largest. 3. Identify the three parts of cell theory. 4. Determine if a cell is a eukaryote or prokaryote given limited information ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑