Jeff Errington L-form bacteria: life without walls or a division machine
... fragments of the wall are recognised as danger signals by our innate immune systems. The wall was probably present in the last common ancestor of the bacteria and thus in the first recognisable cells on earth. It is thus shocking that many bacteria seem to be able to switch almost effortlessly into ...
... fragments of the wall are recognised as danger signals by our innate immune systems. The wall was probably present in the last common ancestor of the bacteria and thus in the first recognisable cells on earth. It is thus shocking that many bacteria seem to be able to switch almost effortlessly into ...
Biology Microbes / Classification 2012 – 2013 #4
... Bacterial anatomy A. Cell Wall = not like that of a plant 1. Gram + have typical cell wall - stain purple 2. Gram - have an extra lipid layer ...
... Bacterial anatomy A. Cell Wall = not like that of a plant 1. Gram + have typical cell wall - stain purple 2. Gram - have an extra lipid layer ...
The plant cell. - Napa Valley College
... 2) Energy-‐ releasing and biosynthe?c reac?ons take place within the cells 3) Cells arise from other cells 4) Hereditary informa?on pass from one genera?on to the other ...
... 2) Energy-‐ releasing and biosynthe?c reac?ons take place within the cells 3) Cells arise from other cells 4) Hereditary informa?on pass from one genera?on to the other ...
20 September - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... osmotic pressure? 4. Peptidoglycan a. List components of peptidoglycan (PG) subunit and explain how they are connected. b. ...
... osmotic pressure? 4. Peptidoglycan a. List components of peptidoglycan (PG) subunit and explain how they are connected. b. ...
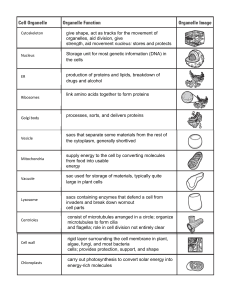
Cell Analogies Worksheet
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
The Magic Universe of Cells Directions
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
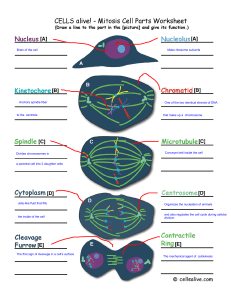
Mitosis-Cell Division
... a. Prophase- The ______ phase of mitosis. It is the “_________” phase of mitosis. 1. The ___________ coils to become ____________ ...
... a. Prophase- The ______ phase of mitosis. It is the “_________” phase of mitosis. 1. The ___________ coils to become ____________ ...
science chapter 1 questions
... of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes themto other parts of the cell. 2b. the endoplasmic reticulum carry proteins form one part to another 2c. the ...
... of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes themto other parts of the cell. 2b. the endoplasmic reticulum carry proteins form one part to another 2c. the ...
carry out photosynthesis to convert solar energy into energy
... sacs that separate some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm, generally shortlived ...
... sacs that separate some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm, generally shortlived ...
Cells and Microscope Test Study Guide
... Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things Know what make ...
... Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things Know what make ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... plants, but I guess that’s enough. ...
... plants, but I guess that’s enough. ...
Vancomycin - Clemson University
... Glycopeptide antibiotic Used to treat gram-positive bacteria Inhibits bacterial cell wall production Resistant strains have been identified ...
... Glycopeptide antibiotic Used to treat gram-positive bacteria Inhibits bacterial cell wall production Resistant strains have been identified ...
What Part of the Cell am I?
... I’m a series of tubes found throughout the cell, I transport proteins and other things as well. What am I? ...
... I’m a series of tubes found throughout the cell, I transport proteins and other things as well. What am I? ...
http://en
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.