Biology Study guide
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
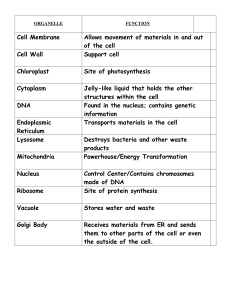
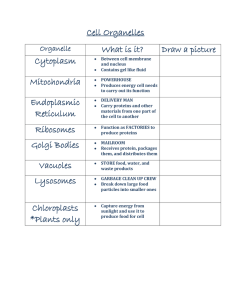
... plant), what their function is, and a real life example of each(analogy): cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. b. What are the differences between an animal cel ...
... plant), what their function is, and a real life example of each(analogy): cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. b. What are the differences between an animal cel ...
Chapter 17 - Damien Rutkoski
... gathers them into groups whose members are similar to one another ...
... gathers them into groups whose members are similar to one another ...
You will be shown some cartoons. From those cartoons, you will
... Write the equation for photosynthesis. Summarize the process (in 1-2 sentences) and identify the cell part, organelle, in which it takes place. ...
... Write the equation for photosynthesis. Summarize the process (in 1-2 sentences) and identify the cell part, organelle, in which it takes place. ...
sgCh1Cell
... Name _______________________________Date______________ Block ______________ Science Chapter 1 (Study Guide) Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek obs ...
... Name _______________________________Date______________ Block ______________ Science Chapter 1 (Study Guide) Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek obs ...
Document
... 4. What happens to plant cells when they do not have enough water? Why? 5. If there is more water in the soil and less in a plant’s roots, which way will the water move? What is this process called? ...
... 4. What happens to plant cells when they do not have enough water? Why? 5. If there is more water in the soil and less in a plant’s roots, which way will the water move? What is this process called? ...
Cell organelle powerpoint
... Mitochondrion is like a crankshaft because it helps turn the motor and give it power ...
... Mitochondrion is like a crankshaft because it helps turn the motor and give it power ...
Organelles – Who Am I?
... 8. I make ribosomes, after all the workbench needs to be made before it can be used to make proteins. 9. I process, package, and ship proteins. 10. I surround the cell and control what enters and leaves the cell. 11. Found only in plant cells, I’m green as can be. I make food for the plant using the ...
... 8. I make ribosomes, after all the workbench needs to be made before it can be used to make proteins. 9. I process, package, and ship proteins. 10. I surround the cell and control what enters and leaves the cell. 11. Found only in plant cells, I’m green as can be. I make food for the plant using the ...
Ch 3 - Fort Bend ISD
... • Have a membrane surrounding their DNA, forming a NUCLEUS • Contain numerous internal membranes that have specific functions, called ORGANELLES ...
... • Have a membrane surrounding their DNA, forming a NUCLEUS • Contain numerous internal membranes that have specific functions, called ORGANELLES ...
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
... Cilia and flagella are hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement. ...
... Cilia and flagella are hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement. ...
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
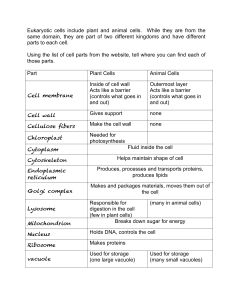
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
CELL: the smallest unit of life. CHLOROPHYLL: a material in plants
... BIOTIC FACTOR: a living part of the ecosystem. ABIOTIC FACTORS: a nonliving part of the ecosystem ENVIRONMENT: all the living and nonliving things that surround an organism. TISSUE: similar cells acting to perform a specific function; four basic types of tissue are muscle, connective, nerve, and epi ...
... BIOTIC FACTOR: a living part of the ecosystem. ABIOTIC FACTORS: a nonliving part of the ecosystem ENVIRONMENT: all the living and nonliving things that surround an organism. TISSUE: similar cells acting to perform a specific function; four basic types of tissue are muscle, connective, nerve, and epi ...
Cell Analogy Sheet
... Cell Analogy Sheet Purpose: To show mastery of each organelles function and role within a cell. Directions: Students will make their own unified analogy for the functions and roles of cell organelles. 1. Cell wall is: a plant cells outermost organelle. It is in charge of protecting the cell, as well ...
... Cell Analogy Sheet Purpose: To show mastery of each organelles function and role within a cell. Directions: Students will make their own unified analogy for the functions and roles of cell organelles. 1. Cell wall is: a plant cells outermost organelle. It is in charge of protecting the cell, as well ...
The Cell School to Home LESSON 2 1.
... 1. Write a clue that could be used to describe each of the following cell structures. Then share your clues with your learning partner to see whether he or she can guess each answer. The first clue is provided as an example. ...
... 1. Write a clue that could be used to describe each of the following cell structures. Then share your clues with your learning partner to see whether he or she can guess each answer. The first clue is provided as an example. ...
The Parts of A Cell - Lemoore Elementary School
... Standard 7.1a Students know cells function similarly in all living organisms. ...
... Standard 7.1a Students know cells function similarly in all living organisms. ...
Cells how to post it activity
... 1. Think of a place you could draw that would represent the cell and all of its organelles. EX: A drawing of a basketball court with teams playing basketball, match up the cell words with the drawing. Don’t use our classroom since that is the analogy I will use in class (coach – nucleus, gym walls – ...
... 1. Think of a place you could draw that would represent the cell and all of its organelles. EX: A drawing of a basketball court with teams playing basketball, match up the cell words with the drawing. Don’t use our classroom since that is the analogy I will use in class (coach – nucleus, gym walls – ...
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
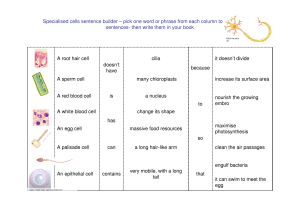
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
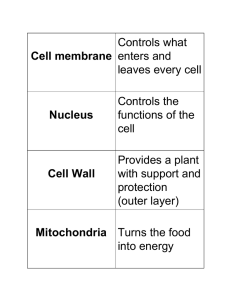
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.