GCE Science TRP
... (a) Which term best describes a sequence of more than two and less than 20 amino acids joined together? A ...
... (a) Which term best describes a sequence of more than two and less than 20 amino acids joined together? A ...
Cell growth comparison of Porvair Sciences tissue culture
... or close dyes (XTT, MTS, WSTs) to formazan dyes, giving a purple colour. A main application allows assessing the viability (cell counting) and the proliferation of cells (cell culture assays). ...
... or close dyes (XTT, MTS, WSTs) to formazan dyes, giving a purple colour. A main application allows assessing the viability (cell counting) and the proliferation of cells (cell culture assays). ...
Mitosis
... The Cell Cycle During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells, each of which begins the cycle again. Consists of four stages: G1 S G2 Mitosis ...
... The Cell Cycle During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells, each of which begins the cycle again. Consists of four stages: G1 S G2 Mitosis ...
Cell Unit Jeopardy
... This word specifically describes what happens to a plant cell such as elodea under these conditions. ...
... This word specifically describes what happens to a plant cell such as elodea under these conditions. ...
Two identical daughter cells are produced
... around each of the two identical groups of chromosomes at opposite ends of the cell and, in each new nucleus. ...
... around each of the two identical groups of chromosomes at opposite ends of the cell and, in each new nucleus. ...
Name
... On a sheet of large unlined drawing paper, draw a typical plant cell and animal cell side by side. You will need to include the proper organelles and other cell parts in each drawing. The drawing should be colored, neat, and the parts labeled properly. You will be comparing the cell to a school (jus ...
... On a sheet of large unlined drawing paper, draw a typical plant cell and animal cell side by side. You will need to include the proper organelles and other cell parts in each drawing. The drawing should be colored, neat, and the parts labeled properly. You will be comparing the cell to a school (jus ...
Cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm
... chromosome which consists of a circular DNA molecule and associated proteins. • While bacteria do not have as many genes or DNA molecules as long as those in eukaryotes, their circular chromosome is still highly folded and coiled in the cell. ...
... chromosome which consists of a circular DNA molecule and associated proteins. • While bacteria do not have as many genes or DNA molecules as long as those in eukaryotes, their circular chromosome is still highly folded and coiled in the cell. ...
Guided Notes The Cell
... – Distribution of vesicles to final destinations (secretion, membranes, etc.) Lysosomes and Peroxisomes = “Garbage Disposal of the Cell” ...
... – Distribution of vesicles to final destinations (secretion, membranes, etc.) Lysosomes and Peroxisomes = “Garbage Disposal of the Cell” ...
partsofthecell2
... • Network of canals used to transport and store substances • A pathway between the nucleus and cell membrane ...
... • Network of canals used to transport and store substances • A pathway between the nucleus and cell membrane ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 7. Compare and contrast the structures of plant and animal cells. 8. Relate the processes of photosynthesis and respiration to specific cell organelles. 9. Explain the structure and function of a cell’s plasma membrane. 10. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. 11. Di ...
... 7. Compare and contrast the structures of plant and animal cells. 8. Relate the processes of photosynthesis and respiration to specific cell organelles. 9. Explain the structure and function of a cell’s plasma membrane. 10. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. 11. Di ...
Randolph-Henry Biology Benchmark Test Six Weeks #1
... Do not write on this test booklet!!!! Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark on your answer sheet. _____1. Which of the sciences is the study of Plants? a. zoology b. botany c. mycology d. ecology _____2. Which scientist is considered to be the father of modern genetics? a. Darwin b. Paste ...
... Do not write on this test booklet!!!! Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark on your answer sheet. _____1. Which of the sciences is the study of Plants? a. zoology b. botany c. mycology d. ecology _____2. Which scientist is considered to be the father of modern genetics? a. Darwin b. Paste ...
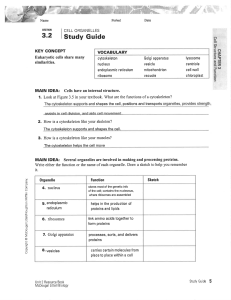
3.2 Study Guide KEY
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that is flex¡ble and ¡nteracts w¡th the env¡ronmênt only certa¡n cells have a cell wâll wh¡ch ìs rigid and provides shape and support toEells ...
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that is flex¡ble and ¡nteracts w¡th the env¡ronmênt only certa¡n cells have a cell wâll wh¡ch ìs rigid and provides shape and support toEells ...
TRANSPORT
... – Distance involved (short-fast, long-slow) – Surface Area involved (large-fast, smallslow) ...
... – Distance involved (short-fast, long-slow) – Surface Area involved (large-fast, smallslow) ...
Cells!
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
Cells Alive - The Biology Corner
... page, or hit your back button). For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. ...
... page, or hit your back button). For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. ...
Onion Cell Scientific Diagram (sorry, it`s a bit blurry) Notice: all labels
... 1.The structures identified were the nucleus, nuclear membrane, cytoplasm and cell wall. The nucleus was a spherical structure in the cell that was stained yellow by the iodine. It was surrounded by the nuclear membrane. The cell wall was the outermost layer of the cell that defined the cell's recta ...
... 1.The structures identified were the nucleus, nuclear membrane, cytoplasm and cell wall. The nucleus was a spherical structure in the cell that was stained yellow by the iodine. It was surrounded by the nuclear membrane. The cell wall was the outermost layer of the cell that defined the cell's recta ...
Click on each organelle to learn its function
... packages molecules including proteins for export from the cell. ...
... packages molecules including proteins for export from the cell. ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.