Bio07_TR_U03_CH07.QXD
... 16. The portion of the cell outside the nucleus is called the 17. Eukaryotes contain structures that act as if they are specialized organs. These structures are called 18. Molecules tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. This process i ...
... 16. The portion of the cell outside the nucleus is called the 17. Eukaryotes contain structures that act as if they are specialized organs. These structures are called 18. Molecules tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. This process i ...
slide show on “microorganisms”
... *A single large cup shaped chloroplast is also present at the broader end of the chlamydomonas. *Two liquid filled spaces called, contractile vacuole are found at the anterior end of the cell. *A tiny orange-red pigment spot called eye-spot, which is photo receptive organ is present at the later sid ...
... *A single large cup shaped chloroplast is also present at the broader end of the chlamydomonas. *Two liquid filled spaces called, contractile vacuole are found at the anterior end of the cell. *A tiny orange-red pigment spot called eye-spot, which is photo receptive organ is present at the later sid ...
Cell Membrane /cell wall nucleus cytoplasm mitochondria
... helps support its shape. It is where all of the chemicals come in and out of the cell, so the cell can function and live. Plants (and fungi) also have cell wall that gives the cell a stronger structure and helps to filter things coming inside and outside of the body. ...
... helps support its shape. It is where all of the chemicals come in and out of the cell, so the cell can function and live. Plants (and fungi) also have cell wall that gives the cell a stronger structure and helps to filter things coming inside and outside of the body. ...
What is a cell?
... but also contain some additional organelles. Plants gain all their energy from sunlight; cells in their leaves contain many chloroplasts to convert this into a useful form. chloroplast vacuole Every plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall, and contains one or more permanent vacuoles. 8 of 10 ...
... but also contain some additional organelles. Plants gain all their energy from sunlight; cells in their leaves contain many chloroplasts to convert this into a useful form. chloroplast vacuole Every plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall, and contains one or more permanent vacuoles. 8 of 10 ...
Cytology Basics Review
... 11. Use a green colored pencil to put a bullet in front of the organelle(s) that are only found in plant cells 12. Use a brown colored pencil to put a bullet in front of the organelle(s) that are only found in animal cells 13. Make a key so that you can remember the significance of these colors ...
... 11. Use a green colored pencil to put a bullet in front of the organelle(s) that are only found in plant cells 12. Use a brown colored pencil to put a bullet in front of the organelle(s) that are only found in animal cells 13. Make a key so that you can remember the significance of these colors ...
Cell analogy project
... labels. You must include these structures in your cell: Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane (envelope) Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth) Ribosomes Cytoplasm Lysosome Golgi bodies Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondrion Centrioles Chromatin Cell wall Remember that not all of these parts are in both ...
... labels. You must include these structures in your cell: Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane (envelope) Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth) Ribosomes Cytoplasm Lysosome Golgi bodies Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondrion Centrioles Chromatin Cell wall Remember that not all of these parts are in both ...
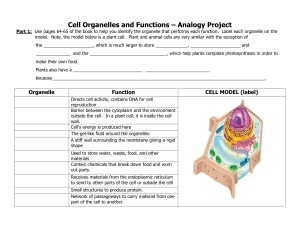
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store _____________, ____________________ and ______________ and the _______________________________, which help plants complete photosynthesi ...
... model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store _____________, ____________________ and ______________ and the _______________________________, which help plants complete photosynthesi ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound compounds that contain
... changing it into food the small openings on the underside of a leaf that allow 4 stomata carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to leave the leaf the process by which cells break down food to release 5 respiration energy using oxygen process through which different gases are transferred in 6 gas exchang ...
... changing it into food the small openings on the underside of a leaf that allow 4 stomata carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to leave the leaf the process by which cells break down food to release 5 respiration energy using oxygen process through which different gases are transferred in 6 gas exchang ...
Study Guide for the LS
... the pigment in vacuoles is what gives some plants their color and makes vegetables crispy if they are full of water cytoplasm: jelly-like fluid inside of the cell nucleolus: stores the materials that will be used later to make ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Be able to identify and label all of the ...
... the pigment in vacuoles is what gives some plants their color and makes vegetables crispy if they are full of water cytoplasm: jelly-like fluid inside of the cell nucleolus: stores the materials that will be used later to make ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Be able to identify and label all of the ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound
... changing it into food the small openings on the underside of a leaf that allow 4 stomata carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to leave the leaf the process by which cells break down food to release energy 5 respiration using oxygen process through which different gases are transferred in 6 gas exchang ...
... changing it into food the small openings on the underside of a leaf that allow 4 stomata carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to leave the leaf the process by which cells break down food to release energy 5 respiration using oxygen process through which different gases are transferred in 6 gas exchang ...
1-2 Looking Inside Cells
... ONLY IN PLANTS These give plants their green color Green due to Chlorophyll ...
... ONLY IN PLANTS These give plants their green color Green due to Chlorophyll ...
Slide 1
... • Make a Cell–Using household items make a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell that meets the criteria listed below. (Sample items: cereal, balloons, gummi worms, mints, fruit slices, dried fruit, matches, gum balls, peanuts, rope licorice, jelly beans, sesame seeds, other candies, too ...
... • Make a Cell–Using household items make a three-dimensional model of a plant or animal cell that meets the criteria listed below. (Sample items: cereal, balloons, gummi worms, mints, fruit slices, dried fruit, matches, gum balls, peanuts, rope licorice, jelly beans, sesame seeds, other candies, too ...
Taxonomy!! - BHSBiologyMatt
... The belong to the kingdom MONERA All bacteria have NO NUCLEUS, which means that their DNA could be floating all around the cytoplasm. ...
... The belong to the kingdom MONERA All bacteria have NO NUCLEUS, which means that their DNA could be floating all around the cytoplasm. ...
Assignment
... Write and perform a rap or song that explains the structure and functions of either plant or animal cells or a cell process. It must inform the audience about the cell type and organelles found in that cell or cell process and what it does and why it is important for the life of the cell. Make 3-D m ...
... Write and perform a rap or song that explains the structure and functions of either plant or animal cells or a cell process. It must inform the audience about the cell type and organelles found in that cell or cell process and what it does and why it is important for the life of the cell. Make 3-D m ...
Phagocytosis - mrswalmsley
... Solid particle comes into contact with cell membrane. Cell membrane moves around particle using pseudopods (“false feet”) and engulfs (swallows) ...
... Solid particle comes into contact with cell membrane. Cell membrane moves around particle using pseudopods (“false feet”) and engulfs (swallows) ...
• SWBAT create and label cell diagrams in order to compare and
... and chloroplasts in your answer. ...
... and chloroplasts in your answer. ...
8.3 Cell surface area
... ways so there is lots of cell membrane surface to increase sites for diffusion and activity. ...
... ways so there is lots of cell membrane surface to increase sites for diffusion and activity. ...
Mitosis
... D Japanese knotweed is a plant that may cause great damage to an environment. One was first introduced to the UK as an exotic garden plant during the nineteenth century. It has since invaded the environment. It is a problem because there are no natural pests of it here, to keep the growth ion check. ...
... D Japanese knotweed is a plant that may cause great damage to an environment. One was first introduced to the UK as an exotic garden plant during the nineteenth century. It has since invaded the environment. It is a problem because there are no natural pests of it here, to keep the growth ion check. ...
Cell Theory and the Cell - The Naked Science Society
... Term “cell” was coined in 1665 by Robert Hooke when he looked at a slice of dried cork. He also observed that: 1. All living things are comprised of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest “living” unit in an organisms. 3. Cells come from previously existing cells. ...
... Term “cell” was coined in 1665 by Robert Hooke when he looked at a slice of dried cork. He also observed that: 1. All living things are comprised of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest “living” unit in an organisms. 3. Cells come from previously existing cells. ...
Animal Plant
... I. B. Cell Theory The cell is the basic living unit of structure and function. – All organisms are composed of one or more cells. ...
... I. B. Cell Theory The cell is the basic living unit of structure and function. – All organisms are composed of one or more cells. ...
Investigation 2 power point
... • The blastula then inlayers a deep cavity called the archenteron. This layer will later function as the gut. • From here, different layers of cells from. • The fist of these layers is the ectoderm. This layer will later function as the outer layer of skin, hair, nails, and nervous ...
... • The blastula then inlayers a deep cavity called the archenteron. This layer will later function as the gut. • From here, different layers of cells from. • The fist of these layers is the ectoderm. This layer will later function as the outer layer of skin, hair, nails, and nervous ...
Cell Division - AKNS Students Blogspot
... divided during cell division in eukaryotes. • Summarize the events of interphase. • Describe the stages of mitosis. • Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells. • Explain how cell division is controlled. ...
... divided during cell division in eukaryotes. • Summarize the events of interphase. • Describe the stages of mitosis. • Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells. • Explain how cell division is controlled. ...
Cell Analogy Analogy to a School
... convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. Analogy: Solar panels on top of the school that help to generate power Found only in plants ...
... convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. Analogy: Solar panels on top of the school that help to generate power Found only in plants ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.