No Slide Title
... • No nuclear membrane • No membrane bound organelles • Cell wall • Single loop of DNA ...
... • No nuclear membrane • No membrane bound organelles • Cell wall • Single loop of DNA ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems - Blair Community Schools
... A. Living things respond to their environment B. The maintenance of stable internal conditions in a changing environment C. D. Cell Membrane ...
... A. Living things respond to their environment B. The maintenance of stable internal conditions in a changing environment C. D. Cell Membrane ...
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
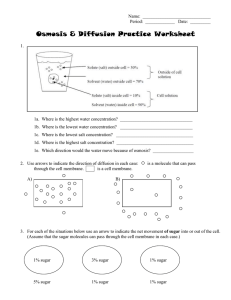
... 3. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
... 3. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
Cell organelles you need to know for unit test
... 5. Chloroplasts- Chloroplasts are specialized organelles that convert the sun’s energy into chemical energy, a sugar called glucose, during the process of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll found in the chloroplasts absorbs the light energy. Plants use this sugar to carry out the functions of the cell. ...
... 5. Chloroplasts- Chloroplasts are specialized organelles that convert the sun’s energy into chemical energy, a sugar called glucose, during the process of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll found in the chloroplasts absorbs the light energy. Plants use this sugar to carry out the functions of the cell. ...
Cells - Ms. Brandon`s Classroom
... Endoplasmic Reticulum – a maze of passageways in within the cytoplasm which carry proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another. Ribosomes – Attached to the outer surface of the endoplasmic reticulum, they are small, grainlike bodies, or some are found floating in the cytoplasm.R ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum – a maze of passageways in within the cytoplasm which carry proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another. Ribosomes – Attached to the outer surface of the endoplasmic reticulum, they are small, grainlike bodies, or some are found floating in the cytoplasm.R ...
Cell Structure We will be looking at two types of cells in this unit. The
... Cell Structure We will be looking at two types of cells in this unit. The first cell is the cell. The second type of cell is the have little structures inside of them called ...
... Cell Structure We will be looking at two types of cells in this unit. The first cell is the cell. The second type of cell is the have little structures inside of them called ...
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have
... From Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants, Buchanan, Gruissem and Jones ...
... From Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants, Buchanan, Gruissem and Jones ...
Parts of the Cell: Cellular Organelles 1. Nucleus • The central core of
... of protein synthesis. It acts as a transport system for proteins and lipids. Rough ER (RER) have ribosomes attached, Smooth ER (SER) do not. 11. Mitochondria • The POWER HOUSE of the cell. It is responsible for producing all of the energy to run the cell, and therefore you. It has a double membrane ...
... of protein synthesis. It acts as a transport system for proteins and lipids. Rough ER (RER) have ribosomes attached, Smooth ER (SER) do not. 11. Mitochondria • The POWER HOUSE of the cell. It is responsible for producing all of the energy to run the cell, and therefore you. It has a double membrane ...
Ch. 19 GN - Jamestown Public Schools
... - Chemoautotrophs - _________________ that can perform ___________________ o Like photoautotrophs, they make _________ carbon molecules from _______ dioxide o However, they do not require ________ as a __________ source o They use ___________ directly from ___________ reactions involving __________, ...
... - Chemoautotrophs - _________________ that can perform ___________________ o Like photoautotrophs, they make _________ carbon molecules from _______ dioxide o However, they do not require ________ as a __________ source o They use ___________ directly from ___________ reactions involving __________, ...
I can: Name and identify the following structures found in the cell
... mitochondria and ribosomes. State the functions of the structures found in the ultrastructure of an animal cell. Name and identify the following structures found in the ultrastructure of a plant cell: nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, cell wall, sap vacuole, chloroplast, mitochondria and ribosomes. ...
... mitochondria and ribosomes. State the functions of the structures found in the ultrastructure of an animal cell. Name and identify the following structures found in the ultrastructure of a plant cell: nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, cell wall, sap vacuole, chloroplast, mitochondria and ribosomes. ...
7.2 Cell structureGS
... 8. Which structures of the cytoskeleton are found in animal cells but not in plant cells? What is the role of these structures? ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 8. Which structures of the cytoskeleton are found in animal cells but not in plant cells? What is the role of these structures? ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ...
Paper 6-LSPT 202-BIOLOGY-II THEORY Marks: 100 Cell and
... Unit 2. Cell as a unit of Life (Ch 6 Campbell) (10 Periods) The Cell Theory; Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Cell size and shape; Eukaryotic Cell components Unit 3. Cell Organelles (Ch 15, 16, 17,18,19,20 Sheeler) (22 Periods) • Mitochondria: Structure, marker enzymes, composition; mitochondrial b ...
... Unit 2. Cell as a unit of Life (Ch 6 Campbell) (10 Periods) The Cell Theory; Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Cell size and shape; Eukaryotic Cell components Unit 3. Cell Organelles (Ch 15, 16, 17,18,19,20 Sheeler) (22 Periods) • Mitochondria: Structure, marker enzymes, composition; mitochondrial b ...
Organellez Lyrics REMIX FINAL
... Maybe DNA rings a bell, these rod-shaped bundles, Are called chromosomes, a fundamental, Component, contain the genetic code, For all living things, whether young or old. An envelope, a boundary, or container, The plasma membrane has a double layer, Of fatty lipids, like a chemical sandwich, That re ...
... Maybe DNA rings a bell, these rod-shaped bundles, Are called chromosomes, a fundamental, Component, contain the genetic code, For all living things, whether young or old. An envelope, a boundary, or container, The plasma membrane has a double layer, Of fatty lipids, like a chemical sandwich, That re ...
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
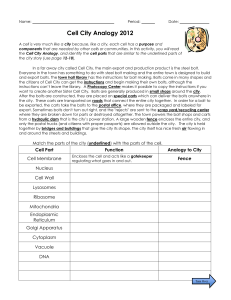
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
FXM Rev Unit C Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... bombarding a specimen with a beam of electrons that are then reflected to a receiver. These are undifferentiated (unspecialized) cells. They are found in high concentration in bone marrow. Then divide through mitosis and produce different types of specialized cells. This is “cell stuff”. It is the m ...
... bombarding a specimen with a beam of electrons that are then reflected to a receiver. These are undifferentiated (unspecialized) cells. They are found in high concentration in bone marrow. Then divide through mitosis and produce different types of specialized cells. This is “cell stuff”. It is the m ...
cells - Perry Local Schools
... Tough, rigid outer covering that protect the cell and give it shape Only found in plant cells, fungi and bacteria support = brick wall ...
... Tough, rigid outer covering that protect the cell and give it shape Only found in plant cells, fungi and bacteria support = brick wall ...
Chapter 5: Cell Transport
... 1. Hypotonic solution: Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell (water conc. is greater than that inside); cell gains water *Cells may burst = cytolysis; *In a plant cell, the cell membrane is push out against the cell wall = turgor pressure ...
... 1. Hypotonic solution: Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell (water conc. is greater than that inside); cell gains water *Cells may burst = cytolysis; *In a plant cell, the cell membrane is push out against the cell wall = turgor pressure ...
Science 10 Assignment U3L6 (20 marks)
... 7. A cell have the dimensions of 2um x 2 um x 3 um. Determine the surface area, volume and surface area to volume ratio of the cell. Show all of your work (9 marks) ...
... 7. A cell have the dimensions of 2um x 2 um x 3 um. Determine the surface area, volume and surface area to volume ratio of the cell. Show all of your work (9 marks) ...
the role of corneal epithelial stem in health and
... To get at the mechanism of these affects, we have a cell culture model we are using to study cell adhesion and ...
... To get at the mechanism of these affects, we have a cell culture model we are using to study cell adhesion and ...
part of the eye
... Bacteria, which is made up of _______ _______, are known to be the simplest organisms. ...
... Bacteria, which is made up of _______ _______, are known to be the simplest organisms. ...
Cell Organelles
... • Do not have structures surrounded by membranes • Few internal structures • One-celled organisms, Bacteria ...
... • Do not have structures surrounded by membranes • Few internal structures • One-celled organisms, Bacteria ...
The Plant Cell
... and the protoplast - the contents of the cell • The protoplast consists of the cytoplasm and a nucleus • The cytoplasm includes distinct membrane-bound organelles such as plastids and mitochondria; systems of membranes (endoplasmic reticulum and dictyosomes); nonmembranous entities such as ribosomes ...
... and the protoplast - the contents of the cell • The protoplast consists of the cytoplasm and a nucleus • The cytoplasm includes distinct membrane-bound organelles such as plastids and mitochondria; systems of membranes (endoplasmic reticulum and dictyosomes); nonmembranous entities such as ribosomes ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.