7-2 - Kleins
... frame work of a cell that is made of protein filaments and helps maintain shape and cell ...
... frame work of a cell that is made of protein filaments and helps maintain shape and cell ...
What structures of living things are cells involved?
... involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
... involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
Cell Booklet Requirements HONORS BIOLOGY
... Parts: Ribosomes, Pili, DNA, Rotary Motor/Flagella, Plasma Membrane, Capsule, Cell Wall ...
... Parts: Ribosomes, Pili, DNA, Rotary Motor/Flagella, Plasma Membrane, Capsule, Cell Wall ...
Ch. 6 Section 3 Directed Reading/Quiz
... a. Chromosomes move to the center of the cell and line up along the equator. b. A nuclear envelope forms around the chromatids at each pole. c. Chromosomes coil up and become visible. d. The two chromatids move toward opposite poles as the spindle fibers attached to them shorten. ...
... a. Chromosomes move to the center of the cell and line up along the equator. b. A nuclear envelope forms around the chromatids at each pole. c. Chromosomes coil up and become visible. d. The two chromatids move toward opposite poles as the spindle fibers attached to them shorten. ...
8 Cells_Simile_assignment-1
... parts in the factory, so the cytoplasm is the where all the organelles and activity are found in the cell. Just as the assembly line is the place where the workers to their job in the factory, so the ER is the place where the ribosomes do their job of assembling proteins. Just as the finishing and p ...
... parts in the factory, so the cytoplasm is the where all the organelles and activity are found in the cell. Just as the assembly line is the place where the workers to their job in the factory, so the ER is the place where the ribosomes do their job of assembling proteins. Just as the finishing and p ...
Cells - Life Learning Cloud
... • All living organisms are composed of cells. • The simplest organisms are made of one single cell. • More complex organisms like animals and plants are made of many cells and are called multicellular organisms. • In multicellular organisms there are many different types of cells that are speciali ...
... • All living organisms are composed of cells. • The simplest organisms are made of one single cell. • More complex organisms like animals and plants are made of many cells and are called multicellular organisms. • In multicellular organisms there are many different types of cells that are speciali ...
Document
... including other cells • Pili- join bacterial cells in preparation for the transfer of DNA from one cell to another ...
... including other cells • Pili- join bacterial cells in preparation for the transfer of DNA from one cell to another ...
plant transport cd
... into the sieve tube elements. The companion cell is closely associated with a phloem sieve tube element to which it is linked by many plasmodesmata. ...
... into the sieve tube elements. The companion cell is closely associated with a phloem sieve tube element to which it is linked by many plasmodesmata. ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... Chloroplast- converts energy from the sun into glucose and oxygen (these two things are used by living things to make ATP). Mitochondria- makes ATP through cellular respiration. ...
... Chloroplast- converts energy from the sun into glucose and oxygen (these two things are used by living things to make ATP). Mitochondria- makes ATP through cellular respiration. ...
Cells - Quia
... 22 The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (9) ...
... 22 The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (9) ...
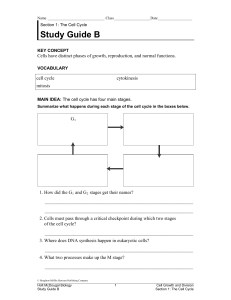
Study Guide B
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
Slide 1
... Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. These membranes also regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells. Ribosomes - non-membraneous, spherical bodies composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and protein enzymes. It is the site of protein synt ...
... Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. These membranes also regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells. Ribosomes - non-membraneous, spherical bodies composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and protein enzymes. It is the site of protein synt ...
Cell Organelles
... ‘rough’ because it is studded with ribosomes Smooth ER - storage and metabolism of carbohydrates, synthesis and transport of lipids ...
... ‘rough’ because it is studded with ribosomes Smooth ER - storage and metabolism of carbohydrates, synthesis and transport of lipids ...
Cell unit vocab - Allen County Schools
... Meiosis—a cell division that creates sperm or egg Mitosis—a cell division that creates identical cells (skin making skin) Nucleus—the control center of a cell Cell membrane—the outer covering of an animal cell that controls what enters and exits the cell Cell wall—an extra covering of a PLANT cell t ...
... Meiosis—a cell division that creates sperm or egg Mitosis—a cell division that creates identical cells (skin making skin) Nucleus—the control center of a cell Cell membrane—the outer covering of an animal cell that controls what enters and exits the cell Cell wall—an extra covering of a PLANT cell t ...
Animal Cell Structure and functions
... Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. These membranes also regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells. Ribosomes - non non--membraneous, spherical bodies composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and protein enzymes. It is the site of protein ...
... Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. These membranes also regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells. Ribosomes - non non--membraneous, spherical bodies composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and protein enzymes. It is the site of protein ...
Cell Biology Unit Study Guide
... What is the function of the nucleus? (a) stores DNA, (b) controls most of the cell’s processes, and (c) contains the information needed to make proteins ...
... What is the function of the nucleus? (a) stores DNA, (b) controls most of the cell’s processes, and (c) contains the information needed to make proteins ...
Review- Cell Transport
... Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes Eukaryotic organelles o Structure, function, location o Presence in an animal, plant, and/or prokaryotic cell o Plant vs Animal Cell Plasma Membrane 1. The plasma membrane is known as the __________________ model. 2. The three parts that make up the structure of the pl ...
... Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes Eukaryotic organelles o Structure, function, location o Presence in an animal, plant, and/or prokaryotic cell o Plant vs Animal Cell Plasma Membrane 1. The plasma membrane is known as the __________________ model. 2. The three parts that make up the structure of the pl ...
DNA THE BASICS AND BEYOND Name Per
... 8. Give a way the two are similar. 9. Give a way that they are different Somatic Nuclear Transfer 10. Somatic cell nuclear transfer (_________), also called _________ transfer, uses a different approach than artificial embryo twinning but it __________ the same ____________ Somatic Cell 11. A ______ ...
... 8. Give a way the two are similar. 9. Give a way that they are different Somatic Nuclear Transfer 10. Somatic cell nuclear transfer (_________), also called _________ transfer, uses a different approach than artificial embryo twinning but it __________ the same ____________ Somatic Cell 11. A ______ ...
REGULATION OF CDK7 ACTIVITY THROUGH A PI (3)-KINASE/ PKC- MEDIATED CELL PROLIFERATION CASCADE
... and proliferation in glioblastoma. PKC-ι is highly over expressed in human glioma and benign and malignant meningioma however little is understood about its role in glioma cell proliferation. Several upstream molecular aberrations and/or loss of PTEN have been implicated to constitutively activate P ...
... and proliferation in glioblastoma. PKC-ι is highly over expressed in human glioma and benign and malignant meningioma however little is understood about its role in glioma cell proliferation. Several upstream molecular aberrations and/or loss of PTEN have been implicated to constitutively activate P ...
Paste or tape this function sheet to the back of your labeled animal
... covers the nucleus and is composed of a double layer of lipids and proteins area within the nucleus where the ribosomes are made (little nucleus) tiny organelles which generate energy from organic compounds to ATP (THE POWERHOUSE) the primary site for protein synthesis (making) in the cell; found in ...
... covers the nucleus and is composed of a double layer of lipids and proteins area within the nucleus where the ribosomes are made (little nucleus) tiny organelles which generate energy from organic compounds to ATP (THE POWERHOUSE) the primary site for protein synthesis (making) in the cell; found in ...
REVIEW FOR TEST 2: Cytology
... 2. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Distinguish between the nucleus and a nucleoid. 3. List advantages to a small cell size. Why are there upper and lower limits? 4. The shape of the cell is related to its ____. 5. List the contributions of: a. Robert Hooke b. Antonie van Leeuwe ...
... 2. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Distinguish between the nucleus and a nucleoid. 3. List advantages to a small cell size. Why are there upper and lower limits? 4. The shape of the cell is related to its ____. 5. List the contributions of: a. Robert Hooke b. Antonie van Leeuwe ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.