Marine Microbiology
... inorganic nutrients by marine heterotrophic bacteria, bacterivory: interactions between bacteria and their grazers, symbiosis and mixotrophy among pelagic microorganisms, marine viruses and their ecological impact, the Global Ocean Survey of Marine Metagenomics, single cell activity in marine bacter ...
... inorganic nutrients by marine heterotrophic bacteria, bacterivory: interactions between bacteria and their grazers, symbiosis and mixotrophy among pelagic microorganisms, marine viruses and their ecological impact, the Global Ocean Survey of Marine Metagenomics, single cell activity in marine bacter ...
File
... As photosynthesizers, algae need light, water, and carbon dioxide for food production and growth, but they do not generally require organic compounds from the environment. As a result of photosynthesis, algae produce oxygen and carbohydrates that are then utilized by other organisms, including anima ...
... As photosynthesizers, algae need light, water, and carbon dioxide for food production and growth, but they do not generally require organic compounds from the environment. As a result of photosynthesis, algae produce oxygen and carbohydrates that are then utilized by other organisms, including anima ...
taxonomy powerpoint
... environments (similar to those of early earth) – Complex metabolic ability (many are chemosynthetic) – First organisms similar to Archaea? ...
... environments (similar to those of early earth) – Complex metabolic ability (many are chemosynthetic) – First organisms similar to Archaea? ...
Diversity of Living Things
... • Chitin cell walls • Use organic chemicals for energy (consumers/heterotrophs) • Decomposers (important in ecosystems) • Moulds – consist of masses of mycelia, which are composed of filaments called hyphae – Reproduce asexually (spores) • Yeasts – Round shape – Reproduce asexually (budding) ...
... • Chitin cell walls • Use organic chemicals for energy (consumers/heterotrophs) • Decomposers (important in ecosystems) • Moulds – consist of masses of mycelia, which are composed of filaments called hyphae – Reproduce asexually (spores) • Yeasts – Round shape – Reproduce asexually (budding) ...
Test Date - Humble ISD
... 2. Adaptations for Genetic Variation Conjugation – a form of “sexual reproduction”. Involves direct transfer of a __________________ from one bacteria to another via ________________. Transformation – Direct uptake of DNA from surroundings Transduction – Use of viral ________________________ t ...
... 2. Adaptations for Genetic Variation Conjugation – a form of “sexual reproduction”. Involves direct transfer of a __________________ from one bacteria to another via ________________. Transformation – Direct uptake of DNA from surroundings Transduction – Use of viral ________________________ t ...
Viruses
... • Infection or disease originating outside of the body • Include pathogenic organisms that invade body, radiation, ...
... • Infection or disease originating outside of the body • Include pathogenic organisms that invade body, radiation, ...
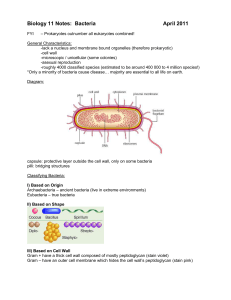
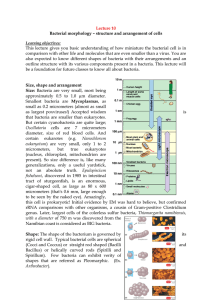
Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of
... Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of cells Learning objectives: ...
... Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of cells Learning objectives: ...
Life in a different time frame
... expanded There is a log-log linear decrease with depth Higher in the surface sediment and relatively lower at several hundred ...
... expanded There is a log-log linear decrease with depth Higher in the surface sediment and relatively lower at several hundred ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (3 x 15= 45) 26. Discuss in detail about the salient features of viruses and their classification. 27. Write detailed notes on the ultrastructure of a bacterial cell. 28. Give a detailed account of a) transformation and b) transduction. 29. Explain about the symptoms, pathogen, disease cycle and con ...
... (3 x 15= 45) 26. Discuss in detail about the salient features of viruses and their classification. 27. Write detailed notes on the ultrastructure of a bacterial cell. 28. Give a detailed account of a) transformation and b) transduction. 29. Explain about the symptoms, pathogen, disease cycle and con ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... The plasma membrane of archaea differs markedly from those of bacteria and eukaryotes. Archaea reproduce asexually by binary fission. Archaeal Metabolism Some archaea are heterotrophs, while others are autotrophs. 28.3 Protists Protists are eukaryotes. For the most part, protists are unicellular and ...
... The plasma membrane of archaea differs markedly from those of bacteria and eukaryotes. Archaea reproduce asexually by binary fission. Archaeal Metabolism Some archaea are heterotrophs, while others are autotrophs. 28.3 Protists Protists are eukaryotes. For the most part, protists are unicellular and ...
Section 6.3 Bacteria
... * Whales die when they drink the water or eat fish filled with the toxins. Salt Water Blooms are called Red Tides: * Red pigment in some salt water algae make the water look red. * Dinoflagellates and diatoms are common algae forming red tide. * Blooms usually occur when nutrients (food) and tempera ...
... * Whales die when they drink the water or eat fish filled with the toxins. Salt Water Blooms are called Red Tides: * Red pigment in some salt water algae make the water look red. * Dinoflagellates and diatoms are common algae forming red tide. * Blooms usually occur when nutrients (food) and tempera ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... What is the collective term for all the filaments that make up the vegetative part of a fungus? ...
... What is the collective term for all the filaments that make up the vegetative part of a fungus? ...
Kingdoms and Domains Section 18-3
... small subunit of ribosomal RNA that occurs in all living things. Three domains: 1. Bacteria 2. Archaea ...
... small subunit of ribosomal RNA that occurs in all living things. Three domains: 1. Bacteria 2. Archaea ...
Worksheet - characteristics of bacteria - OISE-IS
... Bacteria are usually unicellular prokaryotes. Bacteria reproduced by binary fission or conjugation. Bacteria can survive harsh conditions by forming endospores. ...
... Bacteria are usually unicellular prokaryotes. Bacteria reproduced by binary fission or conjugation. Bacteria can survive harsh conditions by forming endospores. ...
Chapter 17 Section 2
... -these amino acids were what gave rise to life forms Life’s Origin -about 200-300 million years after Earth cooled enough to carry liquid water, bacteria was common How? -proteinoid microspheres were produced -not cells, but have some characteristics of living systems -scientists believe over time ...
... -these amino acids were what gave rise to life forms Life’s Origin -about 200-300 million years after Earth cooled enough to carry liquid water, bacteria was common How? -proteinoid microspheres were produced -not cells, but have some characteristics of living systems -scientists believe over time ...
Bacteria and Virus test review
... 18. __________________________Bacterial cells covered with a hard covering that helps them withstand bad conditions 19. __________________________An injection of a weakened or dead virus or bacteria that stimulates antibody production ...
... 18. __________________________Bacterial cells covered with a hard covering that helps them withstand bad conditions 19. __________________________An injection of a weakened or dead virus or bacteria that stimulates antibody production ...
lec3
... Process destroys all forms of microbial life , including bacteria ,viruses , spores , fungi . ...
... Process destroys all forms of microbial life , including bacteria ,viruses , spores , fungi . ...
(for quiz): Taxonomy
... The science of grouping organisms according to their presumed natural relationships. ARISTOTLE ◦ First to classify organisms more than 2000 years ago. ◦ Classified all organisms into TWO groups Plants Further classified by stem differences. Animals Further classified based on where animals w ...
... The science of grouping organisms according to their presumed natural relationships. ARISTOTLE ◦ First to classify organisms more than 2000 years ago. ◦ Classified all organisms into TWO groups Plants Further classified by stem differences. Animals Further classified based on where animals w ...
Virus and Heterotrophic Microplankton
... bacterial communities revealed that the communities are highly variable over space and time despite the fact that some groups like the SAR 11 cluster are ubiquitously present. Protists exert grazing pressure on prokaryotes and this bacterivory is probably to a larger extent species-dependent than as ...
... bacterial communities revealed that the communities are highly variable over space and time despite the fact that some groups like the SAR 11 cluster are ubiquitously present. Protists exert grazing pressure on prokaryotes and this bacterivory is probably to a larger extent species-dependent than as ...