Answers to Science Semester 1Review Possible hazards in the lab
... surface temperature and absolute magnitude. f.) Black hole are objects so massive and dense that even light cannot escape its gravity. g.) Neutron star is a star that has collapsed under gravity to the point that the electrons and protons have smashed together to form neutrons. h.) Pulsar star is a ...
... surface temperature and absolute magnitude. f.) Black hole are objects so massive and dense that even light cannot escape its gravity. g.) Neutron star is a star that has collapsed under gravity to the point that the electrons and protons have smashed together to form neutrons. h.) Pulsar star is a ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster A stellar association is a group ...
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster A stellar association is a group ...
2 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... the zenith at an altitude of 63°. What is the star's declination? What is the declination of a star which passes through Provo's zenith? ...
... the zenith at an altitude of 63°. What is the star's declination? What is the declination of a star which passes through Provo's zenith? ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
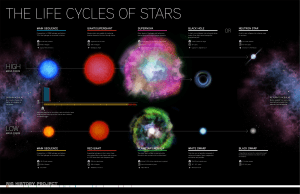
Lifecycle of a Star
... A white dwarf may only be the size of Earth, but it has a mass equal to ½ of the Sun. ...
... A white dwarf may only be the size of Earth, but it has a mass equal to ½ of the Sun. ...
Concise pioneers of astronomy
... most celebrated as the first to propose a sun-centered universe. He is also famed for his pioneering attempt to determine the sizes and distances of the sun and moon. According to his contemporary, Archimedes, Aristarchus was the first to propose not only a heliocentric universe, but also one larger ...
... most celebrated as the first to propose a sun-centered universe. He is also famed for his pioneering attempt to determine the sizes and distances of the sun and moon. According to his contemporary, Archimedes, Aristarchus was the first to propose not only a heliocentric universe, but also one larger ...
Astronomy Unit Period
... __________ 4. Which of the following statements is true about a star? a. A star’s outer layers are hot and thin. b. A star’s outer layers are hot and dense. c. A star’s inner layers are cool and dense. d. A star’s inner layers are hot and dense. __________ 5. Some of the light that radiates from a s ...
... __________ 4. Which of the following statements is true about a star? a. A star’s outer layers are hot and thin. b. A star’s outer layers are hot and dense. c. A star’s inner layers are cool and dense. d. A star’s inner layers are hot and dense. __________ 5. Some of the light that radiates from a s ...
STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... with parallax**** • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the ma ...
... with parallax**** • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the ma ...
Proxima
... Centaurus is known as a “myth” constellation. It’s the 9th largest constellation in the sky Proxima is the 3rd star in Centaurus Contains 2 of the brightest stars (Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri) It contains 11 stars ...
... Centaurus is known as a “myth” constellation. It’s the 9th largest constellation in the sky Proxima is the 3rd star in Centaurus Contains 2 of the brightest stars (Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri) It contains 11 stars ...
Montage of Jupiter and the Galilean satellites
... supergiants at the very top; giants just below them; and finally mainsequence stars. The relative sizes of the stars are shown correctly within each luminosity class, but not between them. The colors are those as perceived by the eye looking at these stars through a telescope. ...
... supergiants at the very top; giants just below them; and finally mainsequence stars. The relative sizes of the stars are shown correctly within each luminosity class, but not between them. The colors are those as perceived by the eye looking at these stars through a telescope. ...
Pretty Pictures of the Cosmos
... with the Hubble Space Telescope, distant galaxies form a dramatic backdrop for disrupted spiral galaxy Arp 188, the Tadpole Galaxy. The cosmic Tadpole is a mere 420 million light-years distant toward the northern constellation Draco. Its eye-catching tail is about 280 thousand light-years long and f ...
... with the Hubble Space Telescope, distant galaxies form a dramatic backdrop for disrupted spiral galaxy Arp 188, the Tadpole Galaxy. The cosmic Tadpole is a mere 420 million light-years distant toward the northern constellation Draco. Its eye-catching tail is about 280 thousand light-years long and f ...
Brichler-powerpoint
... relationship between the surface temperature and the absolute brightness of stars. ...
... relationship between the surface temperature and the absolute brightness of stars. ...
Death of Stars
... fusion of four Hydrogen nuclei to form a He nucleus and conversion of mass to energy The energy appears as K.E of the particles formed, high energy gamma rays and neutrinos The temperature of the star’s core ...
... fusion of four Hydrogen nuclei to form a He nucleus and conversion of mass to energy The energy appears as K.E of the particles formed, high energy gamma rays and neutrinos The temperature of the star’s core ...
SETI: First Considerations (PowerPoint)
... Numbers of Stars The Milky Way is forming about one new star a year, and an ‘average’ star (like the Sun) might last about ten billion years. In the ‘steady state,’ there will be at least several billion radiating stars out there. Stars much more massive than the Sun burn up their fuel very quickly, ...
... Numbers of Stars The Milky Way is forming about one new star a year, and an ‘average’ star (like the Sun) might last about ten billion years. In the ‘steady state,’ there will be at least several billion radiating stars out there. Stars much more massive than the Sun burn up their fuel very quickly, ...
Life Cycle of a Star worksheet
... Learning Goal: I can describe the life cycle of various types of stars. All stars start as a ______________. A ______________ is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together. The contracting cloud is then called a ___________. A protostar is the earli ...
... Learning Goal: I can describe the life cycle of various types of stars. All stars start as a ______________. A ______________ is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together. The contracting cloud is then called a ___________. A protostar is the earli ...
6-Where to Survey - The Challenger Learning Center
... Just as galaxies have structure, our Milky Way has structure. We have a central bulge with a bar through it, arms that spiral outward from the center, and a halo of material surrounding the outer limits. The center of our galaxy has a supermassive black hole. We have between 200 to 400 billion star ...
... Just as galaxies have structure, our Milky Way has structure. We have a central bulge with a bar through it, arms that spiral outward from the center, and a halo of material surrounding the outer limits. The center of our galaxy has a supermassive black hole. We have between 200 to 400 billion star ...
Astronomy 1010 final review sample topics
... a.) a large number of stars; they are attracted to each other by gravity b.) a planet and one or more moons; they are attracted to each other by gravity c.) the sum total of all matter and energy that exists; the material is attracted to each other by gravity d.) a star, and a collection of planets, ...
... a.) a large number of stars; they are attracted to each other by gravity b.) a planet and one or more moons; they are attracted to each other by gravity c.) the sum total of all matter and energy that exists; the material is attracted to each other by gravity d.) a star, and a collection of planets, ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.