* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Air mass (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
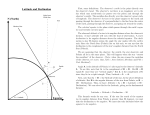
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #2 (Website) Winter 2015 A-1. A star is in the southwestern part of the sky, one-third of the distance from the horizon to the zenith. What is its azimuth? What is its altitude? A-2. An observer notes that the stars neither rise nor set but move right to left, parallel to her horizon. What is her location? A-3. An observer views a star that crossed the celestial meridian 2 hours 20 minutes earlier. His sidereal clock says 15 hours 28 minutes. What is the right ascension of the star? A-4. As viewed from Provo (latitude = +40°), a star transits (crosses the celestial meridian) south of the zenith at an altitude of 63°. What is the star's declination? What is the declination of a star which passes through Provo's zenith? A-5. An observer notes that the sun spends 12 hours per day above his horizon regardless of the month of the year. What is his location? A-6. The track of a star which rises directly in the east is shown with respect to an observer's horizon. The observer's location is (a) near but not at the north pole, (b) at an intermediate northern latitude, (c) near but slightly north of the equator, (d) on the equator, (e) near but slightly south of the equator, (f) at an intermediate southern latitude, (g) near but not at the south pole.