Binary Star Systems
... And, gravity allows us to see comets up close and personal (not always a good thing). ...
... And, gravity allows us to see comets up close and personal (not always a good thing). ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... circle (i.e. within the confines of this building), the NEAREST next star would be in CORTLAND! (3) A parsec is real big! (4) Miles – km analogy Practice Problem #1 & #2 2) Proper Motion and Radial Velocity A) Stars are not truly fixed in the sky, but move in two ways B) Towards or away from the Sun ...
... circle (i.e. within the confines of this building), the NEAREST next star would be in CORTLAND! (3) A parsec is real big! (4) Miles – km analogy Practice Problem #1 & #2 2) Proper Motion and Radial Velocity A) Stars are not truly fixed in the sky, but move in two ways B) Towards or away from the Sun ...
Are constellations just mythic figures in the sky?
... A neat trick for when you become a Sailor • Polaris is the North Star • It is directly above the North Pole on the Celestial Sphere • The North Star is always the same degrees of declination as you position in latitude • This is one of the modes of maritime navigation before GPS (Beware of technolo ...
... A neat trick for when you become a Sailor • Polaris is the North Star • It is directly above the North Pole on the Celestial Sphere • The North Star is always the same degrees of declination as you position in latitude • This is one of the modes of maritime navigation before GPS (Beware of technolo ...
Final Exam Prep
... overall grade. Therefore, they can make a difference between an A and a B, a B and C etc; so please try to pass!! Our final covers just the second semester topics of Astronomy and Meteorology. Detailed topics and correlation to the Text Book are listed below. Good Luck and start reviewing!! A) ASTRO ...
... overall grade. Therefore, they can make a difference between an A and a B, a B and C etc; so please try to pass!! Our final covers just the second semester topics of Astronomy and Meteorology. Detailed topics and correlation to the Text Book are listed below. Good Luck and start reviewing!! A) ASTRO ...
WINNING STORY - Atlantis Short Story Contest
... I was slowly floating, completely at ease, when I realized I had just gone past the two most conspicuous of the stars that make up the Orion constellation. I was taken aback by how large, mighty and bright they were. From people’s viewpoint on Earth, it looks like these celestial bodies are located ...
... I was slowly floating, completely at ease, when I realized I had just gone past the two most conspicuous of the stars that make up the Orion constellation. I was taken aback by how large, mighty and bright they were. From people’s viewpoint on Earth, it looks like these celestial bodies are located ...
Stars - winterk
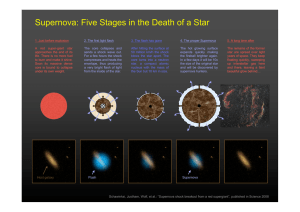
... followed by an outward projection of particles • Depending of the star’s size, its collapse is either in the form of a planetary nebula or a supernova • After that, it then becomes one of the following: 1) White dwarf (small/medium-sized stars) 2) Neutron star (large stars) 3) Black hole (extremely ...
... followed by an outward projection of particles • Depending of the star’s size, its collapse is either in the form of a planetary nebula or a supernova • After that, it then becomes one of the following: 1) White dwarf (small/medium-sized stars) 2) Neutron star (large stars) 3) Black hole (extremely ...
Intro to Fixed Stars
... white in color) in the constellation Leo and one of the brightest stars in the night sky, lying approximately 79 light years from Earth. Regulus is a multiple star system composed of four stars that are organized into two pairs. Keywords: “Nobility, ambition, alertness, great power, status, leadersh ...
... white in color) in the constellation Leo and one of the brightest stars in the night sky, lying approximately 79 light years from Earth. Regulus is a multiple star system composed of four stars that are organized into two pairs. Keywords: “Nobility, ambition, alertness, great power, status, leadersh ...
Distance measures - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... be made for atmospheric refraction and the effects of "seeing". Also stars actually do appear to move across the sky relative to other stars in a definite direction over time. This is called proper motion and must be accounted for when determining parallaxes. If you study the parallax diagram you wi ...
... be made for atmospheric refraction and the effects of "seeing". Also stars actually do appear to move across the sky relative to other stars in a definite direction over time. This is called proper motion and must be accounted for when determining parallaxes. If you study the parallax diagram you wi ...
September 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... The chart above is from Richard Fleet’s Graphdark application and shows graphically the availability of the planets during September. Along the top of the chart is the key to the colour of each planet on the chart. The vertical bars above a planet line indicate the planet will be visible from the ti ...
... The chart above is from Richard Fleet’s Graphdark application and shows graphically the availability of the planets during September. Along the top of the chart is the key to the colour of each planet on the chart. The vertical bars above a planet line indicate the planet will be visible from the ti ...
Stellar evolution
... - Shells appear as a nebula around star, called "Planetary Nebula" (awful, historical name, nothing to do with planets. ...
... - Shells appear as a nebula around star, called "Planetary Nebula" (awful, historical name, nothing to do with planets. ...
January 2015 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... The image above shows the process of star formation as it is happening in the ‘Eagle Nebula’ which is part of Messier 16 (M16) in the constellation of Serpens. The red dots shining in the pillars are new stars starting to ‘peep’ out of the gas and dust clouds of the nebula. The pillars are being sha ...
... The image above shows the process of star formation as it is happening in the ‘Eagle Nebula’ which is part of Messier 16 (M16) in the constellation of Serpens. The red dots shining in the pillars are new stars starting to ‘peep’ out of the gas and dust clouds of the nebula. The pillars are being sha ...
Tour of the Universe
... ● 6 of the planets have moons orbiting them. Them bigger ones have more moons than the smaller ones. ● Earth's moon was formed 4.5 billion years ago from material ejected when a collision occurred between a Marssize object and the Earth. Asteroids ● Rocky objects orbiting the Sun with million ...
... ● 6 of the planets have moons orbiting them. Them bigger ones have more moons than the smaller ones. ● Earth's moon was formed 4.5 billion years ago from material ejected when a collision occurred between a Marssize object and the Earth. Asteroids ● Rocky objects orbiting the Sun with million ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.