Star Life Cycle
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
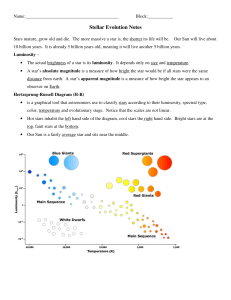
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
Planetary Configurations
... • Recall escape speed: • The Sch. Radius (RS) is the distance at which vesc=c for a BH: ...
... • Recall escape speed: • The Sch. Radius (RS) is the distance at which vesc=c for a BH: ...
Astronomy Unit Test Review Sheet
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
formation2
... Here are the evolutionary tracks for various mass stars. Stars that never have convection do not have the down turn. Also the very massive stars form fast, due to their large gravity. ...
... Here are the evolutionary tracks for various mass stars. Stars that never have convection do not have the down turn. Also the very massive stars form fast, due to their large gravity. ...
Introduction to Celestial Spheres (Professor Powerpoint)
... Looking toward the south you’ll see stars rise in the south east, go to the highest point and set in the southwest, a shorter arc across the sky. ...
... Looking toward the south you’ll see stars rise in the south east, go to the highest point and set in the southwest, a shorter arc across the sky. ...
Movements of Objects in Space
... 3. The Earth and all the other planets are orbiting the Sun, all in the same direction, and all in roughly the same plane (i.e. it's like they are all laid out on a large dinner plate with the Sun at the center). The outer planets orbit more slowly than the inner planets. 4. The stars appear station ...
... 3. The Earth and all the other planets are orbiting the Sun, all in the same direction, and all in roughly the same plane (i.e. it's like they are all laid out on a large dinner plate with the Sun at the center). The outer planets orbit more slowly than the inner planets. 4. The stars appear station ...
Document
... a. white dwarfs are not that common. b. white dwarfs are not dense enough. c. white dwarfs do not have magnetic fields. d. a white dwarf spinning that fast would fly apart 26. The primary reason for the 22 year sunspot cycle is a. Orbit of Jupiter, b. Alignment of the planets every 22 years. c. magn ...
... a. white dwarfs are not that common. b. white dwarfs are not dense enough. c. white dwarfs do not have magnetic fields. d. a white dwarf spinning that fast would fly apart 26. The primary reason for the 22 year sunspot cycle is a. Orbit of Jupiter, b. Alignment of the planets every 22 years. c. magn ...
Sample Answer Sheet for The 10 Tourist Wonders of the
... Website: http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2005/37/image/a/ Justification: Massive stars end their lives in huge explosions that astronomers call supernovae. As much as 90% of the star’s material can be thrown off during the explosion and, in the process, new (heavier) elements are m ...
... Website: http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2005/37/image/a/ Justification: Massive stars end their lives in huge explosions that astronomers call supernovae. As much as 90% of the star’s material can be thrown off during the explosion and, in the process, new (heavier) elements are m ...
Final Exam Practice Part I
... 16. A massive star (25 times the size of our sun) is like an onion. It has layers of various elements. Why do those layers form? 17. Why can’t a star like our sun ever become a black hole? 18. Why isn’t our sun blue? 19. Draw a high energy wave and a low energy wave. Label them? 20. Which of the wav ...
... 16. A massive star (25 times the size of our sun) is like an onion. It has layers of various elements. Why do those layers form? 17. Why can’t a star like our sun ever become a black hole? 18. Why isn’t our sun blue? 19. Draw a high energy wave and a low energy wave. Label them? 20. Which of the wav ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
Chapter 21 notes - Clinton Public Schools
... Section 5: The Expanding Universe: How the universe was formed: Astronomers believe the universe was incredibly hot and dense, exploded in what astronomers called the Big Bang. According to the big bang theory, the universe formed in an instant, billion of years ago, in an enormous explosion. Since ...
... Section 5: The Expanding Universe: How the universe was formed: Astronomers believe the universe was incredibly hot and dense, exploded in what astronomers called the Big Bang. According to the big bang theory, the universe formed in an instant, billion of years ago, in an enormous explosion. Since ...
3 Nightly Motions
... For a star rising in northeastern sky: Stars first rise in the northeast, rise very high into the sky as they approach the meridian, and then set in the northwestern sky. ...
... For a star rising in northeastern sky: Stars first rise in the northeast, rise very high into the sky as they approach the meridian, and then set in the northwestern sky. ...
galaxy.
... Sine the apparent magnitude can be measured directly, determining the period of a Cepheid variable gives a precise measurement of its distance. Using present-day data, it is about 700,000 pc from us. It can be seen with the naked eye. ...
... Sine the apparent magnitude can be measured directly, determining the period of a Cepheid variable gives a precise measurement of its distance. Using present-day data, it is about 700,000 pc from us. It can be seen with the naked eye. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.