answers
... distant objects ever found. All of the objects are galaxies of stars except for E, which is a single nearby star. Which object is more luminous? A) E B) F C) they are about the same B) The two objects look equally bright, but are very different. The star is much closer and much less luminous. The ga ...
... distant objects ever found. All of the objects are galaxies of stars except for E, which is a single nearby star. Which object is more luminous? A) E B) F C) they are about the same B) The two objects look equally bright, but are very different. The star is much closer and much less luminous. The ga ...
Astronomy_Stars_n_Galaxies_PowerPoint
... Most of the objects in space that astronomers study are too far away to visit. So in order to decide what a distant star or galaxy is made of, how hot it is, and how far away it is, astronomers study the light (electromagnetic radiation) that the object gives off. ...
... Most of the objects in space that astronomers study are too far away to visit. So in order to decide what a distant star or galaxy is made of, how hot it is, and how far away it is, astronomers study the light (electromagnetic radiation) that the object gives off. ...
Cosmology 2 - schoolphysics
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
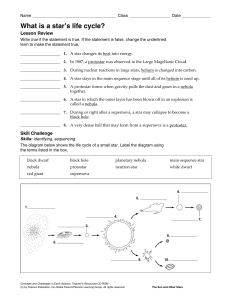
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
Characteristics of Stars
... nuclear fusion is happening at their cores… they create their own light • Have different characteristics which allow many different ‘varieties’ of stars to exist ...
... nuclear fusion is happening at their cores… they create their own light • Have different characteristics which allow many different ‘varieties’ of stars to exist ...
Stellar Evolution: After the Main Sequence
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of Population II stars, then ejected into space and incorporated into a later ste ...
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of Population II stars, then ejected into space and incorporated into a later ste ...
ASTRONOMY 313
... 8. Astronomers investigate a region of nebulosity in the Milky Way by obtaining a spectrum of the cloud and find that the spectrum exhibits bright emission lines, most of which coincide in wavelength with those expected for lines of the Balmer series of hydrogen. What type of nebula is the cloud and ...
... 8. Astronomers investigate a region of nebulosity in the Milky Way by obtaining a spectrum of the cloud and find that the spectrum exhibits bright emission lines, most of which coincide in wavelength with those expected for lines of the Balmer series of hydrogen. What type of nebula is the cloud and ...
ems 6 - LincolnLions.org
... Cloud expanded into clumps Clumps evolved into galaxies Universe is still expanding outward ...
... Cloud expanded into clumps Clumps evolved into galaxies Universe is still expanding outward ...
(HR) Diagrams
... Remember that the SMALLER the MV number, the MORE LUMINOUS the star is, in absolute terms. A star with MV = –5.0 is MUCH more luminous than an MV = 1.0 star. To put it another way, a star with MV = –5.0 appears SPECTACULARLY more bright – IF SEEN FROM THE SAME DISTANCE – than a star with MV = 1.0. F ...
... Remember that the SMALLER the MV number, the MORE LUMINOUS the star is, in absolute terms. A star with MV = –5.0 is MUCH more luminous than an MV = 1.0 star. To put it another way, a star with MV = –5.0 appears SPECTACULARLY more bright – IF SEEN FROM THE SAME DISTANCE – than a star with MV = 1.0. F ...
May 2014
... contains two remarkable deep sky objects. Largest of globular star clusters, Omega Centauri (originally classified as a star), and Centaurus A, a powerfully radiating disturbed galaxy. They are both visible from Southern California. But farther south are Alpha and Beta Centauri, two first magnitude ...
... contains two remarkable deep sky objects. Largest of globular star clusters, Omega Centauri (originally classified as a star), and Centaurus A, a powerfully radiating disturbed galaxy. They are both visible from Southern California. But farther south are Alpha and Beta Centauri, two first magnitude ...
HR Diagram
... H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R dia ...
... H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R dia ...
1_Introduction
... Which of my assumptions is wrong? I assumed every star is visible from Earth. Since stars are opaque spheres, distant stars can hide behind nearby stars. ...
... Which of my assumptions is wrong? I assumed every star is visible from Earth. Since stars are opaque spheres, distant stars can hide behind nearby stars. ...
Scientists classify stars by
... If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightne ...
... If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightne ...
Space Unit - Questions and Answers
... The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune and are also known as the Gas Giants. Their atmosphere consists mainly of hydrogen and helium. They have soupy surfaces and gets denser as you sink to the middle therefore not possible to land on. Pluto is also an outer planet but it is not a ...
... The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune and are also known as the Gas Giants. Their atmosphere consists mainly of hydrogen and helium. They have soupy surfaces and gets denser as you sink to the middle therefore not possible to land on. Pluto is also an outer planet but it is not a ...
Lecture Notes-PPT
... When stars are born they develop from large clouds of molecular gas. After the remnant gas is heated and blow away, the stars collect together by gravity. During the exchange of energy between the stars, some stars reach escape velocity from the protocluster and become runaway stars. The rest become ...
... When stars are born they develop from large clouds of molecular gas. After the remnant gas is heated and blow away, the stars collect together by gravity. During the exchange of energy between the stars, some stars reach escape velocity from the protocluster and become runaway stars. The rest become ...
Big Bang and Life Cycle of Stars
... • According to this theory, all the matter and energy of the universe were at one time concentrated in an incredibly hot dense region, a form of matter called plasma. • At a super heated state, it was too hot for atoms to form, or other properties such as gravity or electromagnetic forces to occur • ...
... • According to this theory, all the matter and energy of the universe were at one time concentrated in an incredibly hot dense region, a form of matter called plasma. • At a super heated state, it was too hot for atoms to form, or other properties such as gravity or electromagnetic forces to occur • ...
Star Formation/Llfe Cycle Notes
... 5) When Stabilizes if becomes a Main Sequence Star a. For Main Sequence stars (such as our Sun) nuclear fusion is when 4 hydrogen atoms fuse into one helium atom. (4H 1He) ...
... 5) When Stabilizes if becomes a Main Sequence Star a. For Main Sequence stars (such as our Sun) nuclear fusion is when 4 hydrogen atoms fuse into one helium atom. (4H 1He) ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.