* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sunmoon - University of Glasgow
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
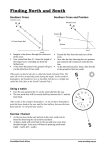
Sun and Moon, Clocks and Calendars Dr Martin Hendry University of Glasgow North North-West North-East West East South-West South-East South If we follow the stars all night, they seem to follow circles on the sky, from East to West This is because the Earth is spinning The Pole Star doesn’t move, because it’s above the North Pole of the Earth To Pole Star If we follow the stars all night, they seem to follow circles on the sky, from East to West This is because the Earth is spinning The Pole Star doesn’t move, because it’s above the North Pole of the Earth If we follow the stars all night, they seem to follow circles on the sky, from East to West This is because the Earth is spinning The Pole Star doesn’t move, because it’s above the North Pole of the Earth To Pole Star Finding the Pole Star To find the Pole Star, first find the Plough, part of the Great Bear. Finding the Pole Star To find the Pole Star, first find the Plough, part of the Great Bear. Pole Star The two end stars are the ‘Pointers’, and point towards the Pole Star, (which is in the Little Bear). Pointers Plough We can use a sundial to tell the time Each day the Sun rises in the East and sets in the West Until about 500 years ago, astronomers thought that the Sun, Moon and planets go around the Earth We now know that the Earth, and all the other planets, go round the Sun During the year, the Sun appears to move through the signs of the ZODIAC Zodiac Constellations The Seasons We have Seasons because the Earth is tilted as it orbits around the Sun March 21st Spring in the Northern Hemisphere, Autumn in the Southern Hemisphere June 21st Summer in the Northern Hemisphere, WInter in the Southern Hemisphere September 21st Autumn in the Northern Hemisphere, Spring in the Southern Hemisphere December 21st Winter in the Northern Hemisphere, Summer in the Southern Hemisphere Phases of the Moon The Moon orbits the Earth once per month. It doesn’t shine itself, but reflects light from the Sun. This is why the Moon shows Phases Phases of the Moon: New Moon, to First Quarter Phases of the Moon: First Quarter, to Full Moon Phases of the Moon: Full Moon, to Third Quarter Phases of the Moon: Third Quarter, to New Moon Orbit of the Moon The gravity of the Earth and the Sun make the Moon’s orbit ‘wobble’ as it goes around the Earth. Solar Eclipses Total Eclipse Zone only about 20km across, but sweeps over many countries as the Earth spins May 7th 2003: Transit of Mercury The Sun is a star, a boiling hot ball of gas. It gives us Heat and Light The Sun is a star, a boiling hot ball of gas. It gives us Heat and Light The Sun is a star, a boiling hot ball of gas. It gives us Heat and Light Without the Sun there could be no life on Earth The Sun is a star, a boiling hot ball of gas. It gives us Heat and Light The Sun is much more than just a way to tell the time!!
























































![SolarsystemPP[2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081776_2-3f379d3255cd7d8ae2efa11c9f8449dc-150x150.png)