Unit8TheUniverse
... A. 13-15 b.y.a. the Universe came into being and began to expand at an incredible rate (Inflation). B. Evidence for the Big Bang: The BBT is not designed to explain the origins of the universe only how it developed. 1). Expanding Universe 2). Background radiation that was predicted and later found. ...
... A. 13-15 b.y.a. the Universe came into being and began to expand at an incredible rate (Inflation). B. Evidence for the Big Bang: The BBT is not designed to explain the origins of the universe only how it developed. 1). Expanding Universe 2). Background radiation that was predicted and later found. ...
Origins of the Universe - Fraser Heights Chess Club
... • It turns out that roughly 68%of the Universe is dark energy. Dark matter makes up about 27%. The rest everything on Earth, everything ever observed with all of our instruments, all normal matter - adds up to less than 5% of the Universe. ...
... • It turns out that roughly 68%of the Universe is dark energy. Dark matter makes up about 27%. The rest everything on Earth, everything ever observed with all of our instruments, all normal matter - adds up to less than 5% of the Universe. ...
Gravitational mass
... • Gravity is so strong that photons can’t escape from its surface. •Can see X-Rays from matter being pulled into it. Ch 33 ...
... • Gravity is so strong that photons can’t escape from its surface. •Can see X-Rays from matter being pulled into it. Ch 33 ...
Our Place in the Cosmos
... Gravity is caused by the curvature of spacetime; the curvature is induced by the presence of matter “Matter tells space how to curve, space tells matter how to move” (John Wheeler) Light rays are bent when they pass near a large mass, a prediction confirmed by Arthur Eddington in 1919 ...
... Gravity is caused by the curvature of spacetime; the curvature is induced by the presence of matter “Matter tells space how to curve, space tells matter how to move” (John Wheeler) Light rays are bent when they pass near a large mass, a prediction confirmed by Arthur Eddington in 1919 ...
EXERCISES: Set 2 of 4 Q1: The absolute magnitude of the Sun in
... its observed flux divided by its observed angular area; thus Σ ∝ f /(δθ)2 . For a class of objects that are both standard candles and standard rulers, deduce the functional dependence of Σ on redshift z. Would observing the surface brightness of this class of objects be a useful way of determining c ...
... its observed flux divided by its observed angular area; thus Σ ∝ f /(δθ)2 . For a class of objects that are both standard candles and standard rulers, deduce the functional dependence of Σ on redshift z. Would observing the surface brightness of this class of objects be a useful way of determining c ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Origin of the Universe
... – Start off with a binary star system – One star comes to end of its life – forms a “white dwarf” (made of helium, or carbon/oxygen) – White Dwarf starts to pull matter off other star… this adds to mass of white dwarf (accretion) – White dwarfs have a maximum possible mass… the ...
... – Start off with a binary star system – One star comes to end of its life – forms a “white dwarf” (made of helium, or carbon/oxygen) – White Dwarf starts to pull matter off other star… this adds to mass of white dwarf (accretion) – White dwarfs have a maximum possible mass… the ...
Earth Science
... 18. As the Earth orbits the Sun, what happens to the orientation of the Earth’s axis? 10. Match the following terms with their definitions. ___ Big Bang theory ___ steady-state theory ___ cosmic background radiation ___ inflationary universe A. background noise caused by weak radiation that comes fr ...
... 18. As the Earth orbits the Sun, what happens to the orientation of the Earth’s axis? 10. Match the following terms with their definitions. ___ Big Bang theory ___ steady-state theory ___ cosmic background radiation ___ inflationary universe A. background noise caused by weak radiation that comes fr ...
Our place in the Universe
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
ppt of lecture - July Lectures
... (2) Expanding: gets cooler (3) Very uniform on large scales, but seeds of galaxy formation ...
... (2) Expanding: gets cooler (3) Very uniform on large scales, but seeds of galaxy formation ...
Astronomy and Cosmology Exam Review
... Big Bang and Cosmology Exam Review 1) One light year is about 9.5x1012 Km 2) What does the red shift tell us about the motion of the universe? It is expanding 3) What is currently the most accepted theory about the origin of the universe called? Big Bang 4) What can I tell about a star based on its ...
... Big Bang and Cosmology Exam Review 1) One light year is about 9.5x1012 Km 2) What does the red shift tell us about the motion of the universe? It is expanding 3) What is currently the most accepted theory about the origin of the universe called? Big Bang 4) What can I tell about a star based on its ...
ITB - In the Beginning
... (the standard model) Developed in the late 1940’s by Gamow– named by Hoyle as an “insult” – it is the current basic model. Out of “nothingness”; the universe has a tiny, hot, beginning – then expands. As the energy-universe expands, it cools enough for matter to form (E=mc2), then atoms to form. Mut ...
... (the standard model) Developed in the late 1940’s by Gamow– named by Hoyle as an “insult” – it is the current basic model. Out of “nothingness”; the universe has a tiny, hot, beginning – then expands. As the energy-universe expands, it cools enough for matter to form (E=mc2), then atoms to form. Mut ...
10.1 PPT
... Red Shift Analysis Edwin Hubble figured out that galaxies were moving away from the earth at a certain speed, which was proportional to the distance from earth. He did this based on his understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
... Red Shift Analysis Edwin Hubble figured out that galaxies were moving away from the earth at a certain speed, which was proportional to the distance from earth. He did this based on his understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
Celestial Objects
... a) red shiftshift- shift toward longer red wavelengths of energy showing that an object is moving AWAY from Earth 1) the farther away the galaxy, the greater the red shift 2) almost all galaxies show a red shiftshiftproof that the universe is expanding (Edwin Hubble was the first to realize this!) ...
... a) red shiftshift- shift toward longer red wavelengths of energy showing that an object is moving AWAY from Earth 1) the farther away the galaxy, the greater the red shift 2) almost all galaxies show a red shiftshiftproof that the universe is expanding (Edwin Hubble was the first to realize this!) ...
Then another Big Bang will occur and the
... cosmic microwave background radiation. It is all around us. The radiation corresponds to a temperature of 3 ...
... cosmic microwave background radiation. It is all around us. The radiation corresponds to a temperature of 3 ...
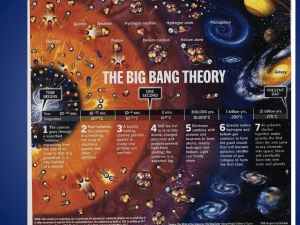
The Big Bang Theory
... 1. Universal expansion and Hubble’s Law a) Hubble observed the majority of galaxies are moving away from us and each other b) The farther, the faster they move c) Red Shift ...
... 1. Universal expansion and Hubble’s Law a) Hubble observed the majority of galaxies are moving away from us and each other b) The farther, the faster they move c) Red Shift ...
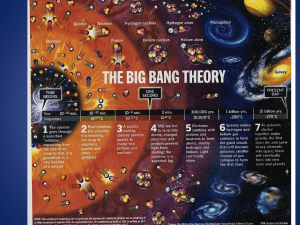
The Big Bang Theory
... 1. Universal expansion and Hubble’s Law a) Hubble observed the majority of galaxies are moving away from us and each other b) The farther, the faster they move c) Red Shift ...
... 1. Universal expansion and Hubble’s Law a) Hubble observed the majority of galaxies are moving away from us and each other b) The farther, the faster they move c) Red Shift ...
Origins Of The Universe
... concentrated into a single incredibly tiny point This began to enlarge rapidly in a hot explosion, and it is still expanding today – this Big Bang happened about 15 billion years ago ...
... concentrated into a single incredibly tiny point This began to enlarge rapidly in a hot explosion, and it is still expanding today – this Big Bang happened about 15 billion years ago ...
Revealing the nature of dark energy
... Missing energy: Dark Energy (energy that is not matter) Missing matter: Dark Matter (matter that doesn’t shine) ...
... Missing energy: Dark Energy (energy that is not matter) Missing matter: Dark Matter (matter that doesn’t shine) ...
Document
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant (c) of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant (c) of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • ...
P1_Physics_Summary_Topic_3
... Describe the lifecycle of a star like our sun and a star bigger than our sun using pictures ...
... Describe the lifecycle of a star like our sun and a star bigger than our sun using pictures ...
Big Bang PPT
... the objects near the very edge of the universe are the oldest objects in the universe. The most distant known objects in ...
... the objects near the very edge of the universe are the oldest objects in the universe. The most distant known objects in ...
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the Universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion. Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed us to understand those physical laws.Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond our own Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible to speculate about the origin of the universe, and allowed the establishment of the Big Bang Theory, by Georges Lemaitre, as the leading cosmological model. A few researchers still advocate a handful of alternative cosmologies; however, most cosmologists agree that the Big Bang theory explains the observations better.Dramatic advances in observational cosmology since the 1990s, including the cosmic microwave background, distant supernovae and galaxy redshift surveys, have led to the development of a standard model of cosmology. This model requires the universe to contain large amounts of dark matter and dark energy whose nature is currently not well understood, but the model gives detailed predictions that are in excellent agreement with many diverse observations.Cosmology draws heavily on the work of many disparate areas of research in theoretical and applied physics. Areas relevant to cosmology include particle physics experiments and theory, theoretical and observational astrophysics, general relativity, quantum mechanics, and plasma physics.