* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt of lecture - July Lectures
Anthropic principle wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Drake equation wikipedia , lookup
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
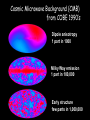
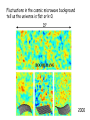
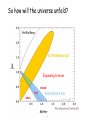
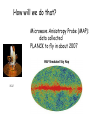
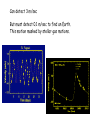
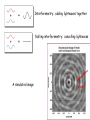
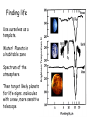
Astrophysics in the 21st Century: The big questions answered? Rachel Webster July Lecture 2002 Two Big Questions: • What is the future of the universe? • Is there extraterrestrial life in the universe? What is the Big Bang? A model to describe the universe: How it started How it is today How it will end……. Early universe (1) Hot (2) Expanding: gets cooler (3) Very uniform on large scales, but seeds of galaxy formation Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) from COBE 1990’s Dipole anisotropy 1 part in 1000 Milky Way emission 1 part in 100,000 Early structure few parts in 1,000,000 The universe now Expanding: Hubble Law, velocity distance Cosmic Element Abundance: explicitly predicted Cosmic Microwave Background: perfect black body These three measurements establish the fundamentals of the Big Bang The universe is expanding The scale of space is getting bigger, but the things inside it held together by gravity etc, stay the same size We measure the size or scale of the universe with the letter ‘a’ one equation! (energy equation) How does the size of the universe change with time? 1 da 4G 2 2 a a k 2 dt 3 2 ‘curvature’ ‘velocity’ ‘gravity’ Cosmological constant or vacuum energy Einstein’s Greatest Blunder? He included it in the equations because he didn’t realise the universe was expanding. Then he wanted to get rid of it. Let’s deal with k. It describes the geometry of space. k>0 k=0 k<0 Fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background tell us the universe is flat or k=0. 2000 How does the expansion velocity change with time? 1 da 4G 2 2 a a k 2 dt 3 2 0 1 a a 2 Expansion with time gravity vacuum energy relative velocity time (deccelerating) (accelerating) Expansion of universe deccelerating constant accelerating Supernova are extremely bright (can be seen a long way away) and have fixed brightness (standard candles) Supernova 1987a in the Large Magellanic Cloud They can be used to measure the change in expansion velocity So how will the universe unfold? Expanding forever Matter Is there anything left to understand? • Verification that the supernova and CMB results are correct • Measurement of all the cosmological parameters to a few % • Next tier of questions: why does the universe have this structure? How will we do that? Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP): data collected PLANCK to fly in about 2007 MAP SNAP: still just a dream Big Bang Questions without answer: Why do we have dark & baryonic matter? What came before the Big Bang? What is vacuum energy? Why did life emerge? Life in the Universe? - the search 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding planets – easy! Finding Earth’s – the next step Finding life Finding intelligence The Greeks: In some worlds there is no Sun and Moon In others they are larger than our world, And in others more numerous. In some parts there are more worlds, In others fewer (…); In some parts they are rising, in others falling. There are some worlds devoid of living creatures Or plants or any moisture. Democritus 460-370 BC Extrasolar planets: the gravity method a planet orbiting a star causes the star to wobble Can detect 3 m/sec But must detect 0.1 m/sec to find an Earth. This motion masked by stellar gas motions. How many planets have we found? 101 this week: http://exoplanets.org http://planetquest.jpl.nasa.gov Finding small planets: Need new techniques & space telescopes Blocking the light – transits Jupiter causes 1% of the light to be blocked Earth would be 0.01% Detected in HD 209458 in 1999 Kepler Mission funded by NASA Discovery Program • To fly in about 2006 • Uses the transit method to find Earth-like planets • Monitors many stars at a time – ½% chance that the planet is aligned for a transit • Will find hundreds of Earths, some in the habitable zone Next technique to be tested: Just look! Direct imaging is hard, as the contrast is a billion to one in the optical; and a million to one in the infrared But we could be clever and cancel the star’s light with nulling interferometry, just leaving the planet Interferometry: adding lightwaves together Nulling interferometry: cancelling lightwaves A simulated image planet Finding life Use ourselves as a template. Water! Planets in a habitable zone Spectrum of the atmosphere Then target likely planets for life-signs…molecules with a new, more sensitive telescope Terrestrial Planet Finder More than 120 organic molecules found in space More than 120 organic molecules found in space Astrophysics in the 21st Century: The big questions answered? Within 15 years, a cosmological model with the critical parameters measured to a few % Within 50 years other planets with life, and visitors on the way By the end of the century, changes probably beyond my comprehension….I won’t be here to comment! Some say the world will end in fire Some say in ice. From what I’ve tasted of desire, I hold with those that favour fire. But if it had to perish twice, I think I know enough of hate To say that for destruction ice Is also great And would suffice. Robert Frost