* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Not a limitation
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Anthropic principle wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
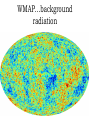
Old ideas of universe • Flat Earth: disproved by Aristotle – Ship sails over horizon – Earth’s shadow on moon circular – North star rises and falls • Some people (uneducated) believed through 1500’s! • Geocentric (earth in center): Ptolemy – Circle orbits (epicycles) – Couldn’t explain retrograde motion Old ideas of universe • Heliocentric: (sun-centered) – Copernicus • Still had circular orbits – Kepler’s 3 Laws • Elliptical orbits, sun not in center • Closer to sun, move faster • Farther from sun, take longer to orbit Edwin Hubble, 1929 • Noticed that light from stars is shifted towards red end of spectrum • Means they’re moving away from us • More it’s shifted, faster they’re moving •Opposite is blue shift (means it’s moving towards us) Edwin Hubble, 1929 • Hubble noticed that most galaxies are moving away from us and the farther they are, the faster they’re moving • If go backwards, means everything was in a small point and exploded and is moving from that point out. • Was called Big Bang to make fun of it and the name stuck! Big Bang Theory • EVERYTHING was in one small point (singularity) that “blew up” and is still moving outwards today • Not really an explosion, so much as a very rapid expansion…like blowing up a balloon • About 13.7 billion years ago • Microwave radiation detected in the 1960’s supports this theory. It’s left over energy from the Big Bang Penzias and Wilson • In addition to Hubble’s evidence • 1960’s discovered microwave radiation all throughout the universe, but couldn’t explain where it came from • Only possible source is it’s left over from Big Bang Other evidence • First elements to form should be simplest….Hydrogen and Helium, and that’s what most of the universe is (>25%)! • Other heavier elements made by stars (fusion up to Iron) and supernovas (other heavier elements) Timeline • Inflationary period: – Rapid expansion, temperature billions of degrees…way too hot even for atoms to exist! • 10-43 sec after – .00000000000000000000000000000000000000 00001 seconds – 4 forces separate (electromagnetism, gravity, weak molecular, strong molecular) – Rules of physics we know now start to work Timeline • 10-35 seconds after – Protons and neutrons form – .00000000000000000000000000000000001 • 10-1 seconds after – Electrons form – .01 sec. • 3 minutes after – 1st atomic nuclei form (H and He) – Temperature down to 1 billion degrees • 300,000 years after – First atoms and light (background radiation) WMAP…background radiation What’s next? • Amount of mass will decide what’s going to happen to the universe: – May continue expanding forever – May continue expanding and then stop at some size – May expand to a point and then collapse (Big Crunch) and explode again • We see the effects (gravity) of some matter we can’t see, so we call it dark matter (e.g. black holes) What’s next? • Galaxies don’t seem to be slowing down (so Big Crunch is doubtful, or we’re still in a period of expansion) • Open universe: idea that not enough matter to keep it all together, and things keep expanding (like molecules from open jar) • Closed universe: idea that enough mass to pull everything back in to Big Crunch • Oscillating Universe: Bang, Crunch, Bang, Crunch forever and ever Limitations • Where’d it come from? • What made it “blow up”? • What’s going to happen next? • Not a limitation: how did life get here. BBT does not even care about this…that’s a topic in Biology next year. Not “just a theory” • Remember, a theory in science is not just some idea somebody cooked up with no evidence. • In science a theory is an attempt to explain observations and has a lot of evidence Not “just a theory” • BBT explains why: – the universe is expanding – has a lot of Hydrogen and Helium – there is background microwave radiation • That’s why it’s a good theory, even if you personally don’t believe it’s true. Steady state theory • Everything is now as it always has been and nothing will ever change…stars, planets, galaxies are the same as they always have been and will never change • Nothing changes, nothing moves in the universe (not same a solar system) Changes to theory/alternates • Anthropic: attempts to answer where life came from – Weak: life exists in small window of time where conditions are just right • Suggests life is a “lucky accident” that will eventually not be possible anymore – Strong: many different things could have happened • Suggests things were planned this way Changes to theory/alternates • Background radiation is not perfectly smooth (as P&W guessed) • pockets of emptiness became space and pockets of matter became galaxies