ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... http://library.thinkquest.org/26220/stars/formation.html What is a nebula (click on protostars)? ...
... http://library.thinkquest.org/26220/stars/formation.html What is a nebula (click on protostars)? ...
Big Bang Theory Scientific origin of the Universe
... Scientific origin of the Universe 1. All matter in the universe began moving together to a single point. 2. At that time the universe was small, hot and dense. 3. 10-15 billion years ago there was an enormous explosion that sent all matter moving outward. 4. Since then all matter in the universe has ...
... Scientific origin of the Universe 1. All matter in the universe began moving together to a single point. 2. At that time the universe was small, hot and dense. 3. 10-15 billion years ago there was an enormous explosion that sent all matter moving outward. 4. Since then all matter in the universe has ...
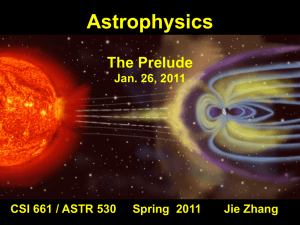
The Prelude - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... •At t=10-6 second, the temperature in the universe dropped to the threshold temperature of 1013 K, at which the photons can not produce proton and anti-proton pairs (and neutron and antineutron pairs) •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to fo ...
... •At t=10-6 second, the temperature in the universe dropped to the threshold temperature of 1013 K, at which the photons can not produce proton and anti-proton pairs (and neutron and antineutron pairs) •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to fo ...
Here
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
... Energy. • As the universe expanded, it cooled. This allowed the first subatomic particles to form (protons, neutron, electrons). • The simplest elements were the first to form. Hydrogen and helium. The fuel for STARS! ...
Historical overview
... After recombination, matter and radiation evolve independently. The radiation left over from this epoch follows a black-body distribution whose effective temperature drops as the universe expands. George Gamow predicted in 1953 that at present this radiation that fills the whole Universe has reached ...
... After recombination, matter and radiation evolve independently. The radiation left over from this epoch follows a black-body distribution whose effective temperature drops as the universe expands. George Gamow predicted in 1953 that at present this radiation that fills the whole Universe has reached ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... • Theory that the universe began as a point and has been expanding ever since – Thought to have begun as an infinitesimally small, hot, and dense “singularity”. – About 14 (13.7) billion years ago ...
... • Theory that the universe began as a point and has been expanding ever since – Thought to have begun as an infinitesimally small, hot, and dense “singularity”. – About 14 (13.7) billion years ago ...
Galaxy Zoo: Pre and post‐workshop information
... Hubble analysed the light from very distant galaxies and found that their spectra were all redshifted. This Doppler effect whereby wavelengths of spectral lines are affected by the motion of the light source indicates all distant galaxies are receding from us. This was a huge discovery as previously ...
... Hubble analysed the light from very distant galaxies and found that their spectra were all redshifted. This Doppler effect whereby wavelengths of spectral lines are affected by the motion of the light source indicates all distant galaxies are receding from us. This was a huge discovery as previously ...
Nineteenth lecture
... The nebulae gradually collapse and commonly start rotating, to form galaxies, like the Andromeda Galaxy, pictured here. (Note the other galaxies also in the picture!) ...
... The nebulae gradually collapse and commonly start rotating, to form galaxies, like the Andromeda Galaxy, pictured here. (Note the other galaxies also in the picture!) ...
Hypothesis vs. Theory ~The Big Bang
... Our Place in the Universe Our study of Astronomy requires us to look UP and not DOWN. Humans today are not used to looking UP, we are not used to observing the sky – it appears to be of little use – and city living with its extensive light pollution often prevents us from seeing, and hence explorin ...
... Our Place in the Universe Our study of Astronomy requires us to look UP and not DOWN. Humans today are not used to looking UP, we are not used to observing the sky – it appears to be of little use – and city living with its extensive light pollution often prevents us from seeing, and hence explorin ...
Homework 1 - Course Pages of Physics Department
... 3. Newtonian cosmology. Use Euclidean geometry and Newtonian gravity, so that we interpret the expansion of the universe as an actual motion of galaxies instead of an expansion of space itself. Consider thus a spherical group of galaxies in otherwise empty space. At a sufficiently large scale you ca ...
... 3. Newtonian cosmology. Use Euclidean geometry and Newtonian gravity, so that we interpret the expansion of the universe as an actual motion of galaxies instead of an expansion of space itself. Consider thus a spherical group of galaxies in otherwise empty space. At a sufficiently large scale you ca ...
Paradigm Shifts in Cosmology
... move away from each other. The general theory of relativity can also explain redshift by thinking that the wavelength of light expands with space while it has been propagating from a galaxy to us. However, the mere fact that galaxies are moving away cannot be decisive evidence for the expansion of s ...
... move away from each other. The general theory of relativity can also explain redshift by thinking that the wavelength of light expands with space while it has been propagating from a galaxy to us. However, the mere fact that galaxies are moving away cannot be decisive evidence for the expansion of s ...
Worksheet
... 8. When we reach 1023 meters (twenty-three powers of ten), the shining lights we see are stars. a. True ...
... 8. When we reach 1023 meters (twenty-three powers of ten), the shining lights we see are stars. a. True ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... A. the star’s luminosity, or brightness B. the star’s color C. the star’s size D. All of these are possible characteristics. 7. Although they did not have telescopes, ancient people studied space. What did they observe? A. details on planets in far-away galaxies B. only the sun and the moon C. the c ...
... A. the star’s luminosity, or brightness B. the star’s color C. the star’s size D. All of these are possible characteristics. 7. Although they did not have telescopes, ancient people studied space. What did they observe? A. details on planets in far-away galaxies B. only the sun and the moon C. the c ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... • unit of distance equal to the average spacing between the Earth and the Sun • equal to about 150 million kilometers (93 ...
... • unit of distance equal to the average spacing between the Earth and the Sun • equal to about 150 million kilometers (93 ...
The Universe: “Beyond the Big Bang” Video Questions
... 28. Einstein proposed that gravity worked because space and time were warped in the presence of matter. 29. Despite what Einstein believed, his theories led to the idea of a moment of creation. 30. What was George Lemaître’s profession? Catholic priest 31. What radical idea was Lemaître’s contribut ...
... 28. Einstein proposed that gravity worked because space and time were warped in the presence of matter. 29. Despite what Einstein believed, his theories led to the idea of a moment of creation. 30. What was George Lemaître’s profession? Catholic priest 31. What radical idea was Lemaître’s contribut ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... • unit of distance equal to the average spacing between the Earth and the Sun • equal to about 150 million kilometers (93 ...
... • unit of distance equal to the average spacing between the Earth and the Sun • equal to about 150 million kilometers (93 ...
Deep Space and Solar System
... • A spectroscope is a scientific instrument that breaks up the light from a star into its component colors in order to identify which elements are present in that star • A spectral line is a bright or dark line found in the spectrum of some radiant sources • A dark line spectrum from a star – Is li ...
... • A spectroscope is a scientific instrument that breaks up the light from a star into its component colors in order to identify which elements are present in that star • A spectral line is a bright or dark line found in the spectrum of some radiant sources • A dark line spectrum from a star – Is li ...
Class 28, 27 July
... – At some temperature, protons and neutrons form – A little later, the protons and neutrons make Helium (most Helium in the universe was formed in the first 3 minutes after the Big Bang) – Nuclei, electrons, and photons in big “soup” • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • ...
... – At some temperature, protons and neutrons form – A little later, the protons and neutrons make Helium (most Helium in the universe was formed in the first 3 minutes after the Big Bang) – Nuclei, electrons, and photons in big “soup” • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • ...
Document
... Unchanging situations need not be static New matter can be created spontaneously as the universe expands (a few hundred atoms per year per galaxy) Expansion of universe and creation of new matter balanced via a negative energy. The universe is constant in its overall density ...
... Unchanging situations need not be static New matter can be created spontaneously as the universe expands (a few hundred atoms per year per galaxy) Expansion of universe and creation of new matter balanced via a negative energy. The universe is constant in its overall density ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
Chapter 14 Origins
... 10. What generalisation can be made about the masses of the stars in the main sequence? 11. Copy the following table, then complete it by writing a short description of the nuclear reaction occurring at each location indicated. 12. Draw an H–R diagram and indicate on it the main star groups. On this ...
... 10. What generalisation can be made about the masses of the stars in the main sequence? 11. Copy the following table, then complete it by writing a short description of the nuclear reaction occurring at each location indicated. 12. Draw an H–R diagram and indicate on it the main star groups. On this ...
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the Universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion. Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed us to understand those physical laws.Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond our own Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible to speculate about the origin of the universe, and allowed the establishment of the Big Bang Theory, by Georges Lemaitre, as the leading cosmological model. A few researchers still advocate a handful of alternative cosmologies; however, most cosmologists agree that the Big Bang theory explains the observations better.Dramatic advances in observational cosmology since the 1990s, including the cosmic microwave background, distant supernovae and galaxy redshift surveys, have led to the development of a standard model of cosmology. This model requires the universe to contain large amounts of dark matter and dark energy whose nature is currently not well understood, but the model gives detailed predictions that are in excellent agreement with many diverse observations.Cosmology draws heavily on the work of many disparate areas of research in theoretical and applied physics. Areas relevant to cosmology include particle physics experiments and theory, theoretical and observational astrophysics, general relativity, quantum mechanics, and plasma physics.