* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit8TheUniverse
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Anthropic principle wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
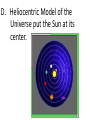
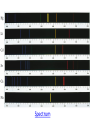
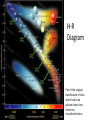
Unit 8 The Universe “Two things are infinite: the universe and human stupidity; and I'm not sure about the universe.” ― Albert Einstein I. The Big Bang Theory (BBT) 1 A. 13-15 b.y.a. the Universe came into being and began to expand at an incredible rate (Inflation). B. Evidence for the Big Bang: The BBT is not designed to explain the origins of the universe only how it developed. 1). Expanding Universe 2). Background radiation that was predicted and later found. 3). Abundance of light elements (H, He, Li) 4). The BBT fits with the known facts of what we know so far. * There are other pieces of evidence, but some are more complex to explain. * This is not a perfect theory, but it fits the observations better than other proposed theories. Parts of the theory can be argued, but are in the minority opinion of scientists. Many parts of the theory have been tested and have withstood the test of time. Alternative Theories See Heliocentric/Geocentric PowerPoint Presentation 1.How old is the universe? 2.What does the BBT describe? 3.What is the evidence for the Big Bang? 4.How is the geocentric model different than the heliocentric model? 5.What is the reason for the evolution of our understanding of the universe? C. Geocentric Model of the Universe put the Earth at its center based on early observations. D. Heliocentric Model of the Universe put the Sun at its center. II. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A. The range of wavelength of electromagnetic radiation extending from short gamma rays to long radio waves and including visible light. Light can be split up using a prism B. A pattern of spectral Lines are produced by different elements. Spectrum 1.What is the electromagnetic spectrum? 2.What is the difference between the geocentric model and the heliocentric model? 3.What allowed scientists to change their ideas on the way the Universe was set up? 4.Can we see all forms of electromagnetic energy? Explain 5.What are spectral lines and what do they have to do with the elements? 6.How old is the Universe? 7.How old is the Earth? 8.What are the pieces of evidence for the BBT? 9.What is Hubble’s Law? C. The Doppler Effect: A change in the observed frequency of a wave occurring when the source and observer are in motion relative to each other. 1 D. Red Shift/Blue Shift: A shift of spectral lines due to the compression or expansion of waves as an object moves towards or away from the observer. STOP III. Star Formation: A. Dependent upon initial mass of the nebula B. Large mass stars: shorter lives, may become neutron stars (pulsars) or blackholes C. Stars come in a variety of sizes and colors. D. The Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram (H-R) is a graph plotting a star’s luminosity (brightness) vs. its temperature, showing the stages of a star’s evolution. Lifecycle of Stars H-R Diagram Part of the original classification of stars which had to be adjusted over time, hence the misordered letters. IV.Formation of Our Solar System: 1 S.S. Sim. A. Nebula- gas/dust cloud was disturbed 4.6 b.y.a. B. Sun formed at the center w/ an accretion disk of dust and gases flattening out along the midplane. Angular Momentum C. Collisions of clumping material formed protoplanets. D. Inner planets were stripped of its gases due to nearness to the Sun. E. Recent observations are in conflict with our present theory. F. The age is based on radiometric dating of Moon rocks, meteors, and the oldest Earth rocks. Age of the Earth (printed material) G. Assuming everything in the solar system formed at the same time, radioactive dating shows the age of the Moon is believed to be ~ 4.4 b.y. and meteorites are around ~4.54 b.y. Mapping the Milky Way Mapping the Milky WayPrinted Informaton What our galaxy on edge would look like